Series pass regulators maintain voltage by varying the resistance in series with the load, resulting in high efficiency and better regulation under varying load conditions. Shunt regulators control voltage by diverting current away from the load through a parallel path, which can be simpler but less efficient; explore the rest of this article to understand which regulator suits Your specific needs.
Table of Comparison
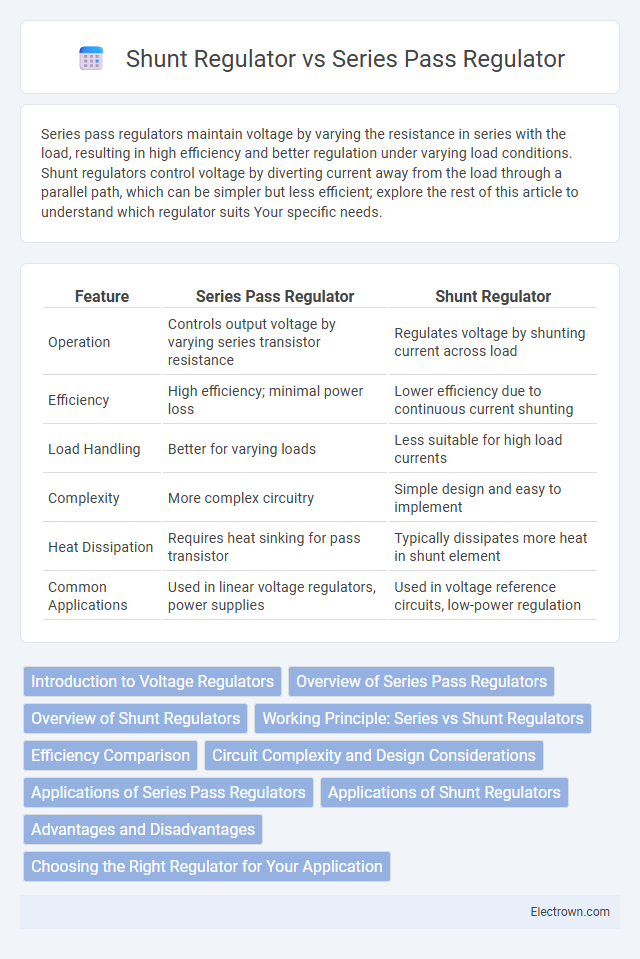
| Feature | Series Pass Regulator | Shunt Regulator |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Controls output voltage by varying series transistor resistance | Regulates voltage by shunting current across load |
| Efficiency | High efficiency; minimal power loss | Lower efficiency due to continuous current shunting |
| Load Handling | Better for varying loads | Less suitable for high load currents |
| Complexity | More complex circuitry | Simple design and easy to implement |
| Heat Dissipation | Requires heat sinking for pass transistor | Typically dissipates more heat in shunt element |
| Common Applications | Used in linear voltage regulators, power supplies | Used in voltage reference circuits, low-power regulation |
Introduction to Voltage Regulators
Voltage regulators maintain a constant output voltage despite variations in input voltage or load conditions, ensuring the stability of electronic circuits. Series pass regulators control voltage by adjusting a series transistor element between input and output, resulting in higher efficiency and better load regulation. Shunt regulators, on the other hand, regulate voltage by shunting current through a parallel element, typically offering simpler design but lower efficiency; understanding these differences helps you choose the right voltage regulator for your application.
Overview of Series Pass Regulators
Series pass regulators control voltage by placing a transistor in series with the load, adjusting the voltage drop across it to maintain a stable output. They provide high efficiency and better regulation under varying load conditions, making them ideal for applications requiring steady voltage. The transistor operates in its active region to continuously regulate voltage, ensuring minimal power loss compared to shunt regulators.
Overview of Shunt Regulators
Shunt regulators maintain voltage by diverting current away from the load through a parallel path, using a voltage reference and a controllable element like a transistor or Zener diode. They offer simple design, low cost, and fast response but are less efficient under high load currents due to continuous power dissipation. Common applications include low-power circuits, voltage references, and noise-sensitive analog devices where stable voltage is critical despite variable load conditions.
Working Principle: Series vs Shunt Regulators
Series pass regulators work by placing a variable resistance element in series with the load, adjusting voltage drop to maintain a stable output. Shunt regulators operate by diverting current away from the load through a parallel element to regulate voltage. Your choice depends on efficiency and load current requirements, as series regulators are more efficient for varying load currents, while shunt regulators offer simpler design suitable for low current applications.
Efficiency Comparison
Series pass regulators offer higher efficiency by operating with lower voltage drop across the transistor, minimizing power dissipation and making them suitable for applications with varying input voltages. Shunt regulators, by contrast, dissipate excess current as heat regardless of load, resulting in lower efficiency especially under heavy load conditions. Your choice depends on the power budget, with series pass regulators favored when energy efficiency is critical.
Circuit Complexity and Design Considerations
Series pass regulators exhibit higher circuit complexity due to the need for a transistor in the main current path, demanding careful thermal management and voltage dropout considerations. Shunt regulators feature simpler designs with fewer components but require higher current consumption and are less efficient for high load currents. Design considerations prioritize stability and load regulation in series types, while shunt regulators emphasize simplicity and cost-effectiveness in low-power applications.
Applications of Series Pass Regulators
Series pass regulators are widely used in applications requiring efficient voltage regulation under varying load conditions, such as power supplies for microprocessors and communication equipment. Their ability to maintain a steady output voltage with minimal power dissipation makes them ideal for battery chargers and low-noise audio devices. These regulators excel in environments where heat management and energy efficiency are critical.
Applications of Shunt Regulators
Shunt regulators are commonly applied in low-power devices and voltage reference circuits where simple, cost-effective voltage stabilization is crucial. They are ideal for maintaining a constant voltage in battery-powered systems, small signal circuits, and as voltage clamps in sensitive analog circuits. Their ability to operate with minimal external components makes them suitable for applications such as transistor biasing, reference voltage generation, and noise filtering in precision instrumentation.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Series pass regulators offer high efficiency and better voltage regulation by placing the control element in series with the load, minimizing power dissipation and improving thermal management. However, they can be more complex and expensive due to the need for a high-power transistor and are less effective at handling rapid load changes. Shunt regulators are simpler and cost-effective, providing fast response to voltage variations by diverting excess current, but they suffer from poor efficiency and generate more heat, making them unsuitable for high-power applications. Your choice depends on the balance between efficiency, complexity, and application requirements.
Choosing the Right Regulator for Your Application
Selecting the right regulator hinges on factors like load current, efficiency, and voltage stability requirements; series pass regulators excel in high current, low dropout applications due to their ability to maintain precise output voltage with minimal power loss. Shunt regulators offer simpler design and better noise performance for low current loads but dissipate more power and are less efficient in higher current scenarios. Evaluating the specific application's voltage variation, power dissipation constraints, and circuit complexity is crucial to optimize overall performance and reliability.
Series pass regulator vs shunt regulator Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com