SSB (Single Sideband) and DSB (Double Sideband) are both modulation techniques used in communication systems, with SSB transmitting only one sideband to improve bandwidth efficiency and reduce power consumption, while DSB transmits both sidebands, doubling the bandwidth but simplifying the demodulation process. Discover how understanding the differences between these methods can enhance your communication system's performance by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
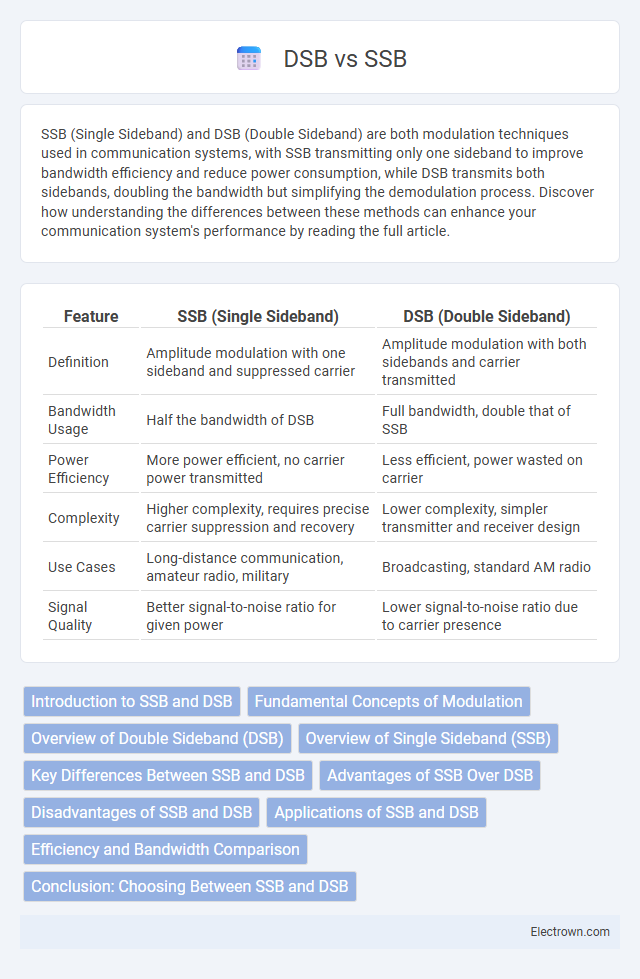
| Feature | SSB (Single Sideband) | DSB (Double Sideband) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Amplitude modulation with one sideband and suppressed carrier | Amplitude modulation with both sidebands and carrier transmitted |
| Bandwidth Usage | Half the bandwidth of DSB | Full bandwidth, double that of SSB |
| Power Efficiency | More power efficient, no carrier power transmitted | Less efficient, power wasted on carrier |
| Complexity | Higher complexity, requires precise carrier suppression and recovery | Lower complexity, simpler transmitter and receiver design |
| Use Cases | Long-distance communication, amateur radio, military | Broadcasting, standard AM radio |
| Signal Quality | Better signal-to-noise ratio for given power | Lower signal-to-noise ratio due to carrier presence |
Introduction to SSB and DSB
Single Sideband (SSB) and Double Sideband (DSB) are modulation techniques used in radio communication to transmit information. SSB transmits only one sideband, either upper or lower, which makes it more bandwidth-efficient and reduces power consumption compared to DSB, which transmits both sidebands. Your choice between SSB and DSB can impact signal clarity, power efficiency, and spectrum utilization in communication systems.
Fundamental Concepts of Modulation
Single Sideband (SSB) modulation transmits only one sideband of the amplitude-modulated signal, eliminating the carrier and the redundant sideband to improve bandwidth efficiency. Double Sideband (DSB) modulation transmits both upper and lower sidebands along with the carrier, doubling the required bandwidth compared to SSB. Understanding your communication system's bandwidth and power constraints helps determine the optimal modulation type for efficient signal transmission.
Overview of Double Sideband (DSB)
Double Sideband (DSB) is a modulation technique in which both the upper and lower sidebands are transmitted symmetrically around the carrier frequency, resulting in a spectrum that occupies twice the bandwidth of the baseband signal. This method retains the entire frequency content of the original signal but is less bandwidth-efficient compared to Single Sideband (SSB) modulation. DSB is commonly used in amplitude modulation (AM) systems where simplicity in implementation and receiver design is prioritized over spectral efficiency.
Overview of Single Sideband (SSB)
Single Sideband (SSB) is a more efficient modulation technique compared to Double Sideband (DSB), transmitting only one sideband and suppressing the carrier signal to reduce bandwidth and power consumption. SSB is widely used in amateur radio, aviation, and marine communications due to its ability to provide clearer signals over long distances with lower interference. Your communication system benefits from improved spectral efficiency and signal clarity when employing SSB modulation.
Key Differences Between SSB and DSB
Single Sideband (SSB) and Double Sideband (DSB) differ primarily in bandwidth efficiency and power usage; SSB transmits only one sideband, reducing bandwidth by half compared to DSB, which transmits both upper and lower sidebands. SSB's reduced bandwidth leads to a more power-efficient signal, making it ideal for long-distance communication and limited-bandwidth channels, while DSB is simpler but less efficient. In terms of complexity, SSB requires more precise filtering and signal processing for recovery, whereas DSB transmission and reception are comparatively straightforward.
Advantages of SSB Over DSB
Single Sideband (SSB) modulation offers significant advantages over Double Sideband (DSB) by requiring less bandwidth, typically only half of what DSB uses, which enhances spectral efficiency. SSB improves transmission range and power efficiency since all the transmitted power is concentrated in a single sideband rather than being split between two. The reduction in signal bandwidth also minimizes interference and noise, resulting in clearer communication channels in professional and amateur radio applications.
Disadvantages of SSB and DSB
Single Sideband (SSB) modulation suffers from disadvantages such as increased complexity in transmitter and receiver design, requiring precise carrier reinsertion and frequency stability. Double Sideband (DSB) signals, while simpler, waste bandwidth by transmitting redundant sidebands, which reduces spectral efficiency and power utilization. Your communication system may face challenges with SSB's difficulty in demodulation and DSB's inefficiency in power and bandwidth usage.
Applications of SSB and DSB
Single Sideband (SSB) modulation is widely used in applications requiring efficient bandwidth and power utilization, such as amateur radio, marine communications, and long-distance HF transmissions. Double Sideband (DSB) modulation finds applications in traditional AM broadcasting and some radar systems where bandwidth constraints are less critical. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right modulation technique for your communication needs.
Efficiency and Bandwidth Comparison
SSB (Single Sideband) modulation improves efficiency by transmitting only one sideband, reducing bandwidth usage to half compared to DSB (Double Sideband), which sends both sidebands. This reduction in bandwidth results in less power consumption and mitigates interference, making SSB ideal for communication systems requiring optimized spectral efficiency. Your system benefits from SSB's narrower bandwidth and lower power requirements, especially in long-distance and bandwidth-limited applications.
Conclusion: Choosing Between SSB and DSB
Choosing between Single Sideband (SSB) and Double Sideband (DSB) depends on bandwidth efficiency and power requirements; SSB offers narrower bandwidth and higher power efficiency, making it ideal for long-distance communication. DSB provides simpler receiver design and better audio quality in shorter-range applications but consumes more spectrum and power. For modern communication systems prioritizing range and spectrum conservation, SSB is typically the preferred option.
SSB vs DSB Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com