Low Noise Amplifiers (LNA) enhance weak signals by minimizing added noise, making them essential in improving receiver sensitivity, while High Power Amplifiers (HPA) boost signal strength for transmission, ensuring long-distance communication with adequate power levels. Explore the rest of the article to understand how selecting the right amplifier can optimize Your communication system performance.
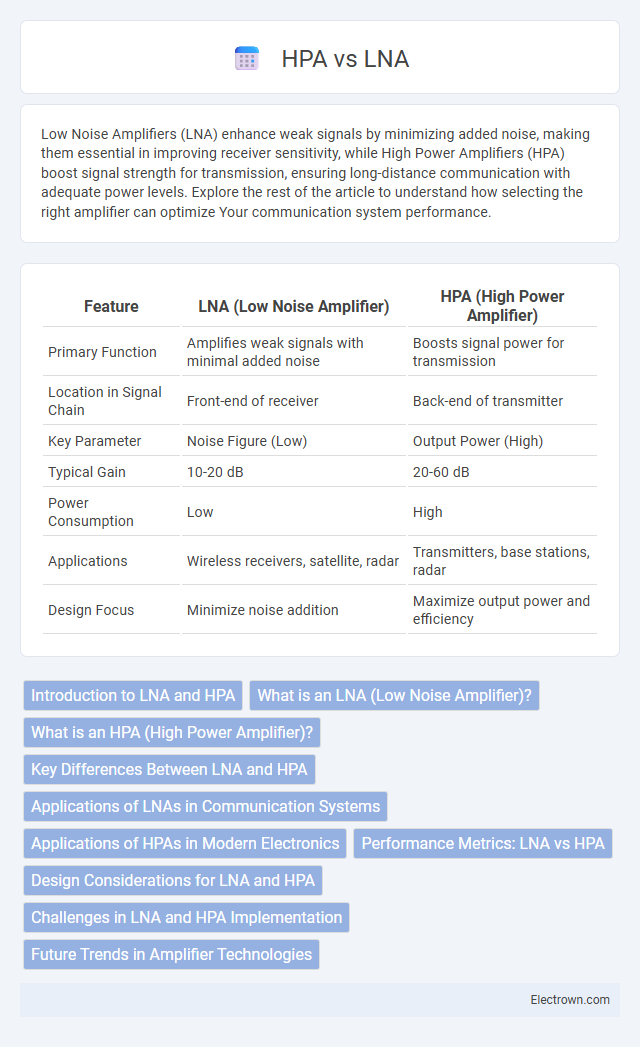
Table of Comparison
| Feature | LNA (Low Noise Amplifier) | HPA (High Power Amplifier) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Amplifies weak signals with minimal added noise | Boosts signal power for transmission |
| Location in Signal Chain | Front-end of receiver | Back-end of transmitter |
| Key Parameter | Noise Figure (Low) | Output Power (High) |
| Typical Gain | 10-20 dB | 20-60 dB |
| Power Consumption | Low | High |
| Applications | Wireless receivers, satellite, radar | Transmitters, base stations, radar |
| Design Focus | Minimize noise addition | Maximize output power and efficiency |
Introduction to LNA and HPA
Low Noise Amplifiers (LNAs) are essential in communication systems for amplifying weak signals with minimal added noise, enhancing signal clarity and receiver sensitivity. High Power Amplifiers (HPAs) boost signal strength to overcome transmission losses and ensure reliable long-distance communication. Understanding the balance between LNAs and HPAs allows you to optimize system performance for both signal quality and coverage range.
What is an LNA (Low Noise Amplifier)?
An LNA (Low Noise Amplifier) is a critical component in communication systems that amplifies weak RF signals with minimal added noise, preserving signal quality for further processing. Your receiver's sensitivity improves significantly due to the LNA's ability to enhance signal strength while maintaining a low noise figure. Unlike HPAs (High Power Amplifiers), LNAs focus on signal clarity at low power levels rather than boosting output power.
What is an HPA (High Power Amplifier)?
An HPA (High Power Amplifier) is a crucial component in communication systems designed to boost signal strength for transmission over long distances. It amplifies low-level input signals to a higher power level, ensuring clear and reliable communication, especially in satellite and radar applications. Your system's performance depends on the HPA's ability to maintain signal integrity while delivering maximum power output efficiently.
Key Differences Between LNA and HPA
Low Noise Amplifiers (LNA) primarily focus on amplifying weak signals with minimal added noise, essential for improving signal-to-noise ratio in sensitive receiver systems. High Power Amplifiers (HPA), in contrast, emphasize delivering high output power for signal transmission, often used in the final stages of communication systems. Key differences include LNA's low noise figure and moderate gain versus HPA's high gain and power handling with a higher noise figure.
Applications of LNAs in Communication Systems
Low Noise Amplifiers (LNAs) are essential in communication systems where maintaining signal integrity is critical, such as in satellite receivers, cellular base stations, and wireless sensor networks. LNAs amplify weak signals without significantly increasing noise, enhancing the overall signal-to-noise ratio and enabling clearer transmission over long distances or through interference. Your communication devices benefit from LNAs by achieving better sensitivity and improved performance in low-signal environments.
Applications of HPAs in Modern Electronics
High Power Amplifiers (HPAs) play a critical role in modern electronics by boosting signal strength in communication systems, radar, and satellite transmissions, ensuring reliable long-distance data transfer. Unlike Low Noise Amplifiers (LNA), which primarily enhance weak signals while minimizing noise, HPAs focus on delivering high output power to overcome signal attenuation in transmission paths. Your electronic devices rely on HPAs for maintaining signal integrity and achieving efficient power amplification in diverse applications such as wireless base stations and electronic warfare systems.
Performance Metrics: LNA vs HPA
Low Noise Amplifiers (LNA) excel in offering minimal noise figures typically ranging from 0.3 to 1 dB, crucial for enhancing weak signal reception without distortion, while High Power Amplifiers (HPA) prioritize output power levels reaching several watts to ensure signal strength over long distances. LNAs provide moderate gain, usually between 10 to 20 dB, with a primary focus on preserving signal integrity, whereas HPAs deliver significantly higher gain, often above 40 dB, optimized for driving transmission loads. Your system performance depends on selecting the right balance between the low noise figure of LNAs and the high output power capability of HPAs for specific communication needs.
Design Considerations for LNA and HPA
Design considerations for LNAs include minimizing noise figure and ensuring high linearity to amplify weak signals with minimal distortion, while maintaining low power consumption and optimal impedance matching. HPAs require careful attention to power efficiency, thermal management, and linearity to deliver strong output power without signal degradation, often involving the use of robust semiconductor materials and advanced cooling techniques. Both devices demand precise impedance matching and stability across the operating frequency range to optimize overall system performance in RF and microwave applications.
Challenges in LNA and HPA Implementation
Low Noise Amplifiers (LNA) face challenges such as achieving a balance between noise figure reduction and linearity, while managing power consumption and maintaining stability across wide frequency bands. High Power Amplifiers (HPA) struggle with efficiency optimization, thermal management, and distortion minimization under high output power conditions. Both components require advanced semiconductor technologies and precise circuit design to address signal integrity and integration in modern communication systems.
Future Trends in Amplifier Technologies
Future trends in amplifier technologies emphasize the integration of Low Noise Amplifiers (LNA) and High Power Amplifiers (HPA) with advanced materials like Gallium Nitride (GaN) for enhanced efficiency and thermal performance. You can expect improvements in linearity and power gain that cater to 5G and satellite communication demands. The push towards miniaturization and intelligent adaptive amplification will redefine signal processing capabilities in next-generation devices.
LNA vs HPA Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com