Digital potentiometers offer precise, programmable resistance control ideal for modern electronic applications, while analog potentiometers provide manual, continuous adjustment through a physical knob. Explore the rest of the article to understand which potentiometer best fits your project's needs.
Table of Comparison
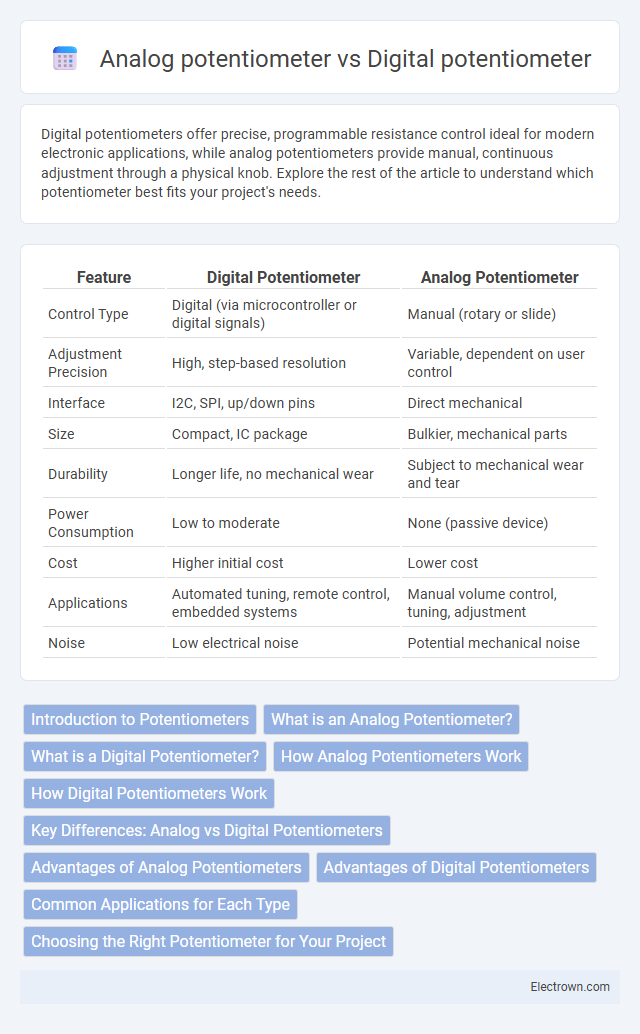
| Feature | Digital Potentiometer | Analog Potentiometer |
|---|---|---|
| Control Type | Digital (via microcontroller or digital signals) | Manual (rotary or slide) |
| Adjustment Precision | High, step-based resolution | Variable, dependent on user control |
| Interface | I2C, SPI, up/down pins | Direct mechanical |
| Size | Compact, IC package | Bulkier, mechanical parts |
| Durability | Longer life, no mechanical wear | Subject to mechanical wear and tear |
| Power Consumption | Low to moderate | None (passive device) |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost |
| Applications | Automated tuning, remote control, embedded systems | Manual volume control, tuning, adjustment |
| Noise | Low electrical noise | Potential mechanical noise |
Introduction to Potentiometers
Potentiometers are variable resistors used to adjust voltage and control electrical devices by varying resistance manually or electronically. Digital potentiometers use semiconductor components controlled by digital signals, offering precise, repeatable adjustments without mechanical wear. Analog potentiometers rely on physical wiper movement along a resistive track, providing simple, intuitive control but limited durability and accuracy.
What is an Analog Potentiometer?
An analog potentiometer is a three-terminal variable resistor used to adjust voltage manually by sliding a wiper across a resistive element, providing continuous and smooth resistance variation. It is commonly applied in volume controls, sensor calibration, and tuning circuits where precise analog adjustment is necessary. You can easily control an analog potentiometer physically, making it ideal for real-time and intuitive adjustments without digital interfaces.
What is a Digital Potentiometer?
A digital potentiometer is an electronic component that mimics the function of a traditional analog potentiometer by digitally controlling resistance through integrated circuits. It allows precise resistance adjustments via digital signals, enabling programmable and repeatable control in applications like volume control, sensor calibration, and signal tuning. Unlike analog potentiometers, digital potentiometers offer enhanced durability, improved accuracy, and ease of integration with microcontrollers and digital systems.
How Analog Potentiometers Work
Analog potentiometers operate by varying resistance through a mechanical wiper that slides along a resistive element, adjusting voltage output in real time. The wiper's position directly changes the resistance ratio between terminals, allowing precise control of electrical signals in applications like volume control and sensing. Your circuits benefit from their simplicity and smooth analog signal modulation without digital interfacing requirements.
How Digital Potentiometers Work
Digital potentiometers operate by using electronic switches such as MOSFETs to simulate a variable resistance through discrete steps controlled by digital signals. Internal resistor ladders are segmented into precise increments, enabling accurate adjustment of resistance values via microcontroller commands over interfaces like SPI or I2C. This method offers enhanced repeatability and programmability compared to analog potentiometers that rely on manual wiper movement for resistance changes.
Key Differences: Analog vs Digital Potentiometers
Analog potentiometers use a physical wiper to vary resistance continuously, offering infinite position adjustment within their range, while digital potentiometers employ integrated circuits with discrete steps to simulate resistance changes electronically. The analog version is prone to wear and noise due to mechanical movement, whereas digital potentiometers provide precise, noise-free settings and easier integration with microcontrollers. Power consumption is typically lower in digital potentiometers, making them suitable for battery-powered and automated systems, contrasting with the purely mechanical design of analog potentiometers.
Advantages of Analog Potentiometers
Analog potentiometers offer precise and continuous voltage adjustment through mechanical rotation, providing tactile feedback important for manual tuning in audio equipment and instrumentation. Their simple construction and direct control eliminate digital artifacts and latency, ensuring smooth and instantaneous response in real-time applications. You benefit from their reliability and simplicity in environments where digital signals might be prone to interference or complexity.
Advantages of Digital Potentiometers
Digital potentiometers offer precise and repeatable resistance adjustments controlled by digital signals, enhancing accuracy in applications such as audio volume control and sensor calibration. They eliminate mechanical wear and noise common in analog potentiometers, resulting in longer device lifespan and improved reliability. Your designs benefit from easy integration with microcontrollers, enabling automated and remote tuning capabilities.
Common Applications for Each Type
Digital potentiometers are commonly used in precision electronic devices such as programmable gain amplifiers, audio equipment, and sensor calibration systems due to their ability to provide accurate, repeatable resistance adjustments through digital control interfaces like SPI or I2C. Analog potentiometers are widely applied in user-controlled volume knobs, light dimmers, and manual tuning circuits where tactile feedback and simple variable resistance are required without the need for digital communication. Each type serves distinct roles, with digital potentiometers excelling in automated systems and analog potentiometers favored in straightforward, direct-manipulation environments.
Choosing the Right Potentiometer for Your Project
Choosing the right potentiometer depends on the precision and control your project requires; digital potentiometers offer programmable resistance values with high repeatability, making them ideal for automated and adjustable circuits. Analog potentiometers provide tactile control and reliable simplicity, suited for manual adjustments and low-cost applications. Evaluate factors like resolution, interface compatibility, and environmental conditions to select the optimal potentiometer for your design needs.
Digital potentiometer vs analog potentiometer Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com