A multiplexer efficiently combines multiple input signals into a single output based on selector inputs, simplifying data routing in digital circuits. Explore the rest of the article to understand how a selector plays a crucial role in controlling multiplexers and optimizing your system's performance.
Table of Comparison
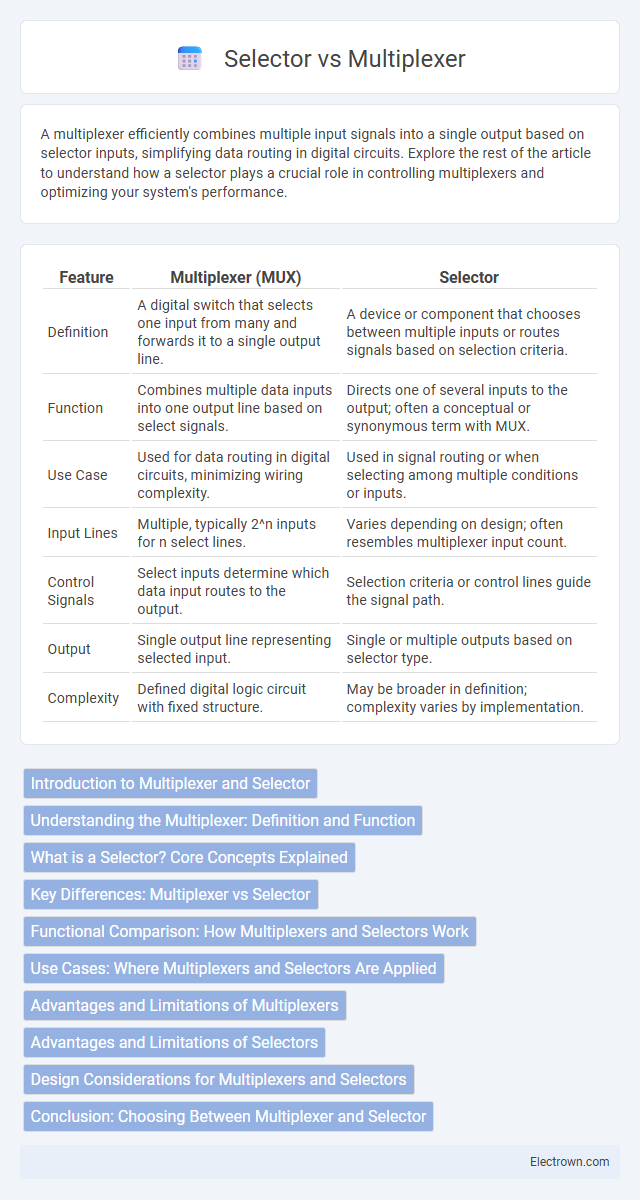
| Feature | Multiplexer (MUX) | Selector |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A digital switch that selects one input from many and forwards it to a single output line. | A device or component that chooses between multiple inputs or routes signals based on selection criteria. |
| Function | Combines multiple data inputs into one output line based on select signals. | Directs one of several inputs to the output; often a conceptual or synonymous term with MUX. |
| Use Case | Used for data routing in digital circuits, minimizing wiring complexity. | Used in signal routing or when selecting among multiple conditions or inputs. |
| Input Lines | Multiple, typically 2^n inputs for n select lines. | Varies depending on design; often resembles multiplexer input count. |
| Control Signals | Select inputs determine which data input routes to the output. | Selection criteria or control lines guide the signal path. |
| Output | Single output line representing selected input. | Single or multiple outputs based on selector type. |
| Complexity | Defined digital logic circuit with fixed structure. | May be broader in definition; complexity varies by implementation. |
Introduction to Multiplexer and Selector
A multiplexer (MUX) is a digital switch that selects one input from multiple inputs and forwards it to a single output line, controlled by select signals. A selector, commonly used in digital circuits, functions similarly by choosing one data line from several inputs based on control signals but is often treated as a simpler or more specific form of a multiplexer. Both components are fundamental in optimizing data routing and minimizing the number of transmission lines in digital systems.
Understanding the Multiplexer: Definition and Function
A multiplexer is a digital device that selects one input from multiple data inputs and forwards it to a single output line based on control signals. It functions as a data selector, reducing the number of data lines needed by allowing multiple signals to share one device or resource. Understanding this, you can optimize circuit designs by efficiently managing data routing and minimizing hardware complexity.
What is a Selector? Core Concepts Explained
A selector is a digital circuit component used to choose one input from multiple data sources based on control signals, effectively routing data to a single output line. It functions by interpreting the selector inputs to activate the corresponding data path, similar to a multiplexer but often with simpler implementation focused on specific selection mechanisms. Core concepts of a selector include input selection, control signal dependency, and single-line data output, making it essential in decision-making processes within digital systems.
Key Differences: Multiplexer vs Selector
A multiplexer (MUX) is a combinational circuit that selects one input from multiple data inputs and directs it to a single output line based on selection signals, optimizing data routing in digital systems. A selector, often used interchangeably with a multiplexer in certain contexts, generally refers to a component or module that chooses signal paths but may not perform data multiplexing or involve binary selection logic. Key differences include the functional role where a multiplexer is specifically designed for binary data selection and transmission, while a selector may serve broader or different control purposes without necessarily combining or encoding multiple inputs into one output.
Functional Comparison: How Multiplexers and Selectors Work
Multiplexers and selectors both serve to choose one input from multiple signals based on control inputs, but multiplexers combine several data inputs into a single output line by using binary control signals. A multiplexer routes one of many inputs to a single output line dynamically, while selectors typically refer to simpler devices that select one channel among several without complex data encoding. Your choice depends on the complexity of input management and the required level of control signal encoding in digital circuits.
Use Cases: Where Multiplexers and Selectors Are Applied
Multiplexers are widely used in data routing applications, such as communication systems, memory management, and digital signal processing, where selecting one input from multiple data sources is essential. Selectors find applications in control systems and microprocessors to manage multiple input signals and direct them to a single output line efficiently. Understanding these use cases helps you optimize hardware design for tasks requiring input prioritization and signal management.
Advantages and Limitations of Multiplexers
Multiplexers provide efficient data routing by allowing multiple input signals to share a single communication line, reducing hardware complexity and cost in digital circuits. Their advantages include simplified design, reduced wiring, and improved signal management, making them ideal for resource-constrained systems. However, multiplexers can introduce latency and signal degradation, and their performance may be limited by the number of inputs they can handle effectively.
Advantages and Limitations of Selectors
Selectors offer streamlined data filtering by efficiently extracting specific elements from collections based on defined criteria, enhancing performance in state management systems like Redux. They reduce computational overhead by memoizing outputs, ensuring your application only recomputes when necessary, which boosts responsiveness and scalability. However, selectors can become complex to maintain in large applications with deeply nested states, potentially leading to increased development time and debugging challenges.
Design Considerations for Multiplexers and Selectors
Design considerations for multiplexers include signal integrity, propagation delay, and minimizing power consumption to ensure efficient data routing across multiple inputs. Selectors require careful attention to input signal compatibility, control logic complexity, and timing synchronization to accurately choose and output the desired input signal. Your system's overall performance depends on balancing these factors to achieve optimal data selection and transmission with minimal latency and noise.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Multiplexer and Selector
Choosing between a multiplexer and a selector depends on the complexity and specific needs of your digital circuit design. A multiplexer efficiently manages multiple data inputs by directing one to a single output based on select lines, ideal for data routing and signal selection. Your choice should align with the required input selection mechanism and output control precision in your electronic system.
Multiplexer vs Selector Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com