Mask ROM offers permanent data storage with fast access times but lacks flexibility since its content is fixed during manufacturing, while EPROM provides rewritable memory through ultraviolet light erasure, allowing updates but with slower access speeds. Explore the differences between these memory types to understand which one suits Your project needs better.
Table of Comparison
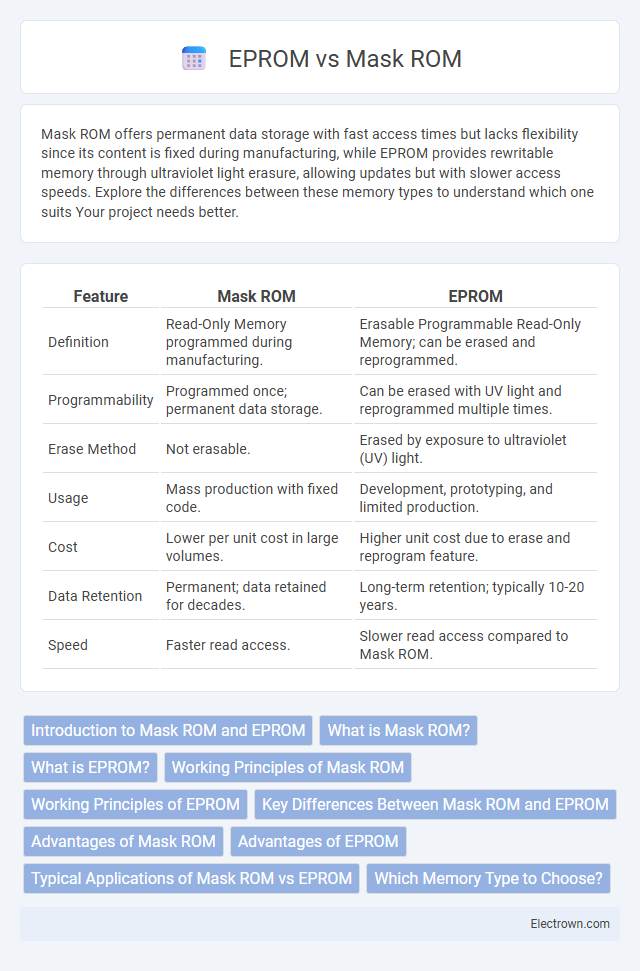
| Feature | Mask ROM | EPROM |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Read-Only Memory programmed during manufacturing. | Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory; can be erased and reprogrammed. |
| Programmability | Programmed once; permanent data storage. | Can be erased with UV light and reprogrammed multiple times. |
| Erase Method | Not erasable. | Erased by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light. |
| Usage | Mass production with fixed code. | Development, prototyping, and limited production. |
| Cost | Lower per unit cost in large volumes. | Higher unit cost due to erase and reprogram feature. |
| Data Retention | Permanent; data retained for decades. | Long-term retention; typically 10-20 years. |
| Speed | Faster read access. | Slower read access compared to Mask ROM. |
Introduction to Mask ROM and EPROM
Mask ROM is a type of read-only memory programmed during the manufacturing process, offering high density and cost-effectiveness for mass production. EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) allows data to be erased using ultraviolet light and reprogrammed multiple times, providing flexibility during development and testing phases. Understanding the differences between Mask ROM and EPROM helps you choose the optimal memory type for your specific application needs.
What is Mask ROM?
Mask ROM (Read-Only Memory) is a type of non-volatile memory where data is permanently written during the semiconductor manufacturing process via photolithographic masks. It offers fast access speeds and cost efficiency for large-scale production but lacks reprogrammability, making it ideal for fixed, unchangeable firmware or data storage. Unlike EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory), Mask ROM cannot be electrically erased or reprogrammed after fabrication.
What is EPROM?
EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) is a type of non-volatile memory that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed, unlike Mask ROM which is permanently programmed during manufacturing. It uses a quartz window to expose the chip to ultraviolet light for erasing data, allowing multiple rewrite cycles. Your applications benefit from EPROM's flexibility and reusability, especially in prototyping and development phases.
Working Principles of Mask ROM
Mask ROM (Read-Only Memory) stores data permanently during the manufacturing process by using a photolithographic mask to define the memory pattern on the silicon wafer. Its working principle relies on fixed logic gates that either allow or block electron flow, encoding data as a series of physical connections or disconnections. Unlike EPROM, which can be electrically erased and reprogrammed, Mask ROM's content is unchangeable after fabrication, making it ideal for cost-effective mass production of fixed data like firmware in embedded systems.
Working Principles of EPROM
EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) operates by storing data in floating-gate transistors that trap charge to represent bits, allowing reprogramming by exposing the chip to ultraviolet light which clears stored charges. Unlike Mask ROM, which is programmed during manufacturing and cannot be altered, EPROM enables you to erase and reprogram data multiple times for flexible use. This rewritable nature makes EPROM ideal for development and testing environments where changes are frequently required.
Key Differences Between Mask ROM and EPROM
Mask ROM is a type of read-only memory programmed during manufacturing, making it cost-effective for large production runs but inflexible for updates. EPROM, or Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory, allows multiple reprogramming cycles by exposing the chip to UV light, providing flexibility for development and testing phases. Your choice depends on whether you need permanent data storage with high-volume cost efficiency or rewritable memory for evolving applications.
Advantages of Mask ROM
Mask ROM offers the advantage of ultra-low per-unit cost and high reliability due to its fixed data pattern being permanently embedded during manufacturing. It consumes less power and provides faster read access times compared to EPROM, making it ideal for high-volume production and embedded systems with stable code requirements. Your choice of Mask ROM ensures security against data modification and tampering, as the content cannot be altered once programmed.
Advantages of EPROM
EPROM offers reprogrammability, allowing data to be erased and rewritten multiple times using ultraviolet light, unlike Mask ROM which is permanently programmed during manufacturing. This flexibility significantly reduces development costs and time for firmware updates and debugging processes. EPROM's adaptability supports iterative design improvements, making it ideal for prototyping and low-volume production runs.
Typical Applications of Mask ROM vs EPROM
Mask ROM is commonly used in consumer electronics such as calculators, printers, and embedded systems where fixed, cost-efficient firmware storage is essential. EPROM finds typical applications in development environments, prototyping, and devices requiring firmware updates like microcontrollers and network equipment. The ability to erase and reprogram EPROM makes it suitable for iterative testing and customization, whereas Mask ROM offers high-volume production with minimal cost per unit.
Which Memory Type to Choose?
Choose Mask ROM for high-volume production where data stability and cost-efficiency are critical, as it offers fast access and low unit price but lacks reprogrammability. Opt for EPROM when flexibility and the ability to update firmware during development or deployment are essential, despite its higher cost and slower write speeds. EPROM's erasable feature via UV light allows multiple programming cycles, making it ideal for prototyping and applications requiring periodic updates.
Mask ROM vs EPROM Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com