Serial IN Serial OUT (SISO) shift registers process data sequentially, inputting and outputting one bit at a time, ideal for simple data storage and transfer tasks. Explore the differences and applications of Serial IN Parallel OUT (SIPO) shift registers to understand which technology best suits Your project needs.
Table of Comparison
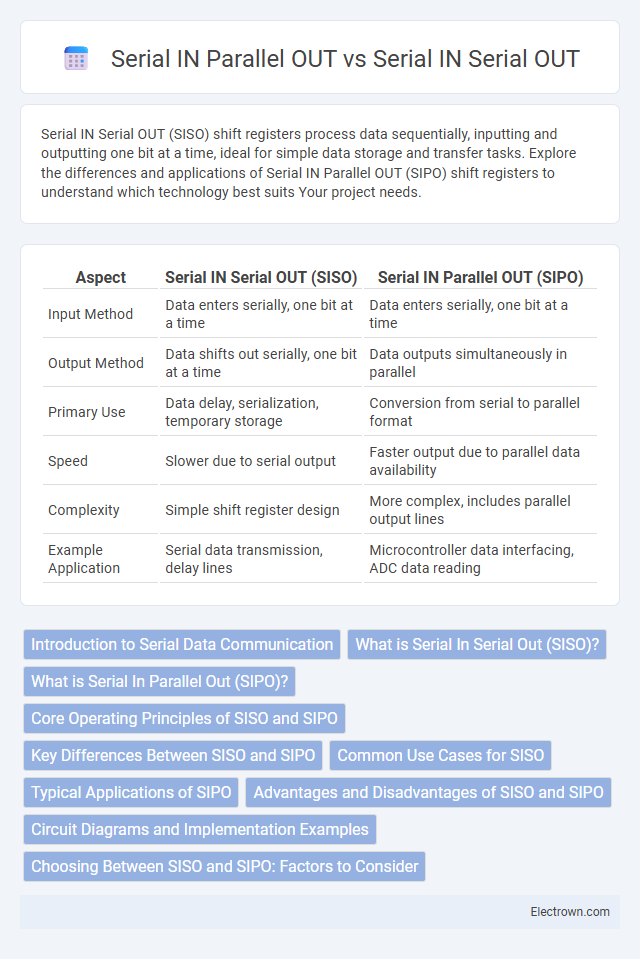
| Aspect | Serial IN Serial OUT (SISO) | Serial IN Parallel OUT (SIPO) |
|---|---|---|
| Input Method | Data enters serially, one bit at a time | Data enters serially, one bit at a time |
| Output Method | Data shifts out serially, one bit at a time | Data outputs simultaneously in parallel |
| Primary Use | Data delay, serialization, temporary storage | Conversion from serial to parallel format |
| Speed | Slower due to serial output | Faster output due to parallel data availability |
| Complexity | Simple shift register design | More complex, includes parallel output lines |
| Example Application | Serial data transmission, delay lines | Microcontroller data interfacing, ADC data reading |
Introduction to Serial Data Communication
Serial IN Serial OUT (SISO) and Serial IN Parallel OUT (SIPO) are fundamental concepts in serial data communication, where data is transmitted bit by bit over a single channel. SISO devices transfer data sequentially both for input and output, ideal for simple shift register applications, while SIPO devices convert incoming serial data into parallel output, enabling simultaneous access to multiple bits. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for designing efficient data transfer systems and optimizing communication protocols in embedded and digital electronics.
What is Serial In Serial Out (SISO)?
Serial In Serial Out (SISO) is a type of shift register where data bits are entered and retrieved sequentially, one bit at a time, maintaining the order of transmission. This design is essential for applications requiring data to be processed or transmitted in a continuous stream without parallel access. Understanding SISO helps you optimize data flow in communication systems and digital circuits where serial data handling is critical.
What is Serial In Parallel Out (SIPO)?
Serial In Parallel Out (SIPO) is a type of shift register that captures serial data input sequentially and then outputs it simultaneously on multiple parallel lines. This allows conversion of data from a serial format to a parallel format, making it essential for applications that require data processing in parallel, such as in digital communication and computing systems. Your system benefits from SIPO registers by efficiently handling serial data streams and providing quick parallel access for further processing.
Core Operating Principles of SISO and SIPO
Serial IN Serial OUT (SISO) shift registers operate by entering data bit-by-bit and shifting each bit sequentially through the register, outputting one bit at a time in the same serial fashion. Serial IN Parallel OUT (SIPO) registers also accept data serially but differ by converting the serial input into a parallel output after storing multiple bits simultaneously. Your choice between SISO and SIPO depends on whether you require sequential data processing or immediate parallel data availability for faster operations.
Key Differences Between SISO and SIPO
The key differences between Serial IN Serial OUT (SISO) and Serial IN Parallel OUT (SIPO) shift registers lie in their data output methods and applications. SISO shift registers output data sequentially, one bit at a time, ideal for simple data storage or transfer, while SIPO registers convert serial input into simultaneous parallel outputs, enabling faster data access for parallel processing tasks. Understanding these distinctions helps you choose the appropriate shift register type for data handling efficiency in digital circuits.
Common Use Cases for SISO
Serial IN Serial OUT (SISO) shift registers are primarily used for data storage, transfer, and delay applications in digital circuits where simplicity and minimal hardware are essential. Common use cases include data serialization for communication protocols, temporary data buffering, and digital signal processing tasks like frequency division and pulse delay. Their straightforward design makes them ideal for applications requiring sequential data handling without parallel output demands.
Typical Applications of SIPO
Serial IN Parallel OUT (SIPO) shift registers are commonly used in applications requiring data conversion from serial to parallel form, such as in display systems where multiple LEDs or segments are controlled simultaneously. They enable efficient data expansion by receiving serial data and outputting it in parallel format, which is essential in digital circuits like microcontroller interfacing and data buffering. SIPO registers are also utilized in memory devices and communication systems for synchronizing and distributing parallel data.
Advantages and Disadvantages of SISO and SIPO
Serial IN Serial OUT (SISO) shift registers offer simplicity and require fewer hardware resources, making them ideal for delay elements or simple data storage, but they have slower data access since bits are output sequentially. Serial IN Parallel OUT (SIPO) registers enable faster data retrieval by outputting all bits simultaneously, which is advantageous in applications needing parallel processing or immediate data availability, but they demand more complex circuitry and higher pin counts. SISO excels in minimal design complexity and cost-efficiency, whereas SIPO balances faster access speed with increased hardware complexity and power consumption.
Circuit Diagrams and Implementation Examples
Serial IN Serial OUT (SISO) shift registers consist of a series of flip-flops connected in a chain, allowing data to be shifted one bit at a time through the register; circuit diagrams typically show D flip-flops connected with the serial output of one feeding the serial input of the next. Serial IN Parallel OUT (SIPO) shift registers also use cascaded D flip-flops but feature parallel output lines, enabling all bits to be accessed simultaneously after shifting; implementation examples often involve connecting the flip-flops' Q outputs directly to parallel data lines. Practical circuits for SISO are widely used for simple data delay and storage, while SIPO registers find applications in converting serial data streams into parallel data, such as in microcontroller input interfacing and digital communication systems.
Choosing Between SISO and SIPO: Factors to Consider
Choosing between Serial IN Serial OUT (SISO) and Serial IN Parallel OUT (SIPO) shift registers depends on your data processing needs and speed requirements. SISO is ideal for simple, sequential data transfer where minimal output complexity is required, while SIPO allows simultaneous access to multiple output bits, making it suitable for applications needing parallel data handling. Your choice should prioritize factors like output timing, complexity of control logic, and the need for parallel data output in real-time operations.
Serial IN Serial OUT vs Serial IN Parallel OUT Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com