CANopen and DeviceNet are industrial communication protocols based on the CAN bus, with CANopen focusing on device interoperability and flexible device profiles, while DeviceNet emphasizes network management and real-time data exchange for automation systems. Explore the rest of this article to understand how these protocols impact your industrial networking choices and which one suits your application best.
Table of Comparison
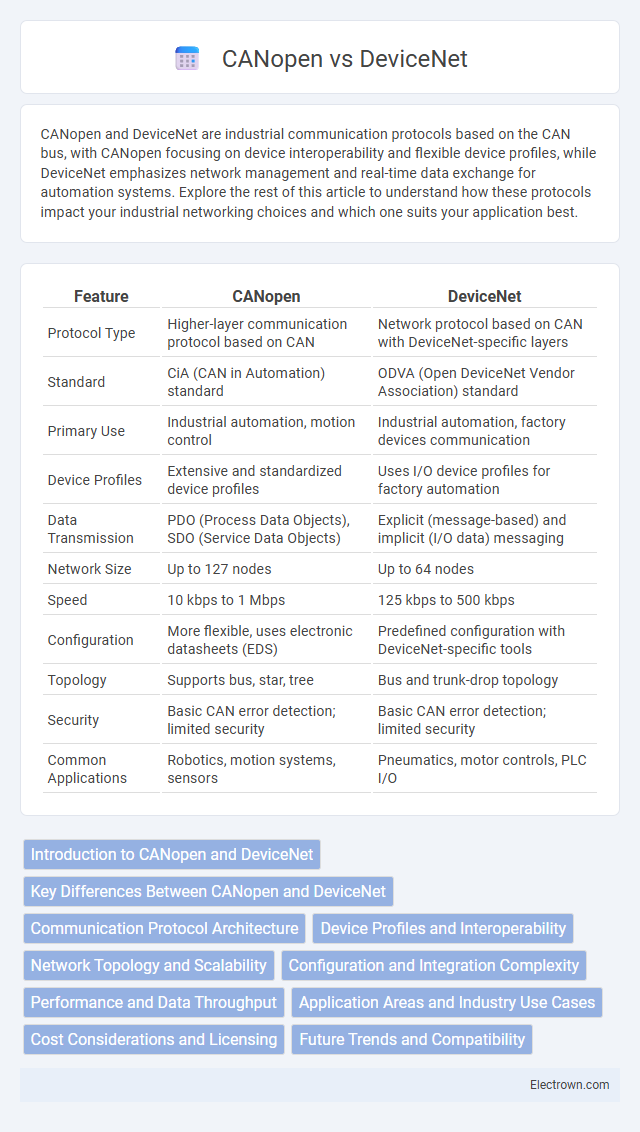
| Feature | CANopen | DeviceNet |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol Type | Higher-layer communication protocol based on CAN | Network protocol based on CAN with DeviceNet-specific layers |
| Standard | CiA (CAN in Automation) standard | ODVA (Open DeviceNet Vendor Association) standard |
| Primary Use | Industrial automation, motion control | Industrial automation, factory devices communication |
| Device Profiles | Extensive and standardized device profiles | Uses I/O device profiles for factory automation |
| Data Transmission | PDO (Process Data Objects), SDO (Service Data Objects) | Explicit (message-based) and implicit (I/O data) messaging |
| Network Size | Up to 127 nodes | Up to 64 nodes |
| Speed | 10 kbps to 1 Mbps | 125 kbps to 500 kbps |
| Configuration | More flexible, uses electronic datasheets (EDS) | Predefined configuration with DeviceNet-specific tools |
| Topology | Supports bus, star, tree | Bus and trunk-drop topology |
| Security | Basic CAN error detection; limited security | Basic CAN error detection; limited security |
| Common Applications | Robotics, motion systems, sensors | Pneumatics, motor controls, PLC I/O |
Introduction to CANopen and DeviceNet
CANopen and DeviceNet are widely used industrial communication protocols based on the Controller Area Network (CAN) technology, designed for automation and control systems. CANopen is favored for its flexible device profiles and real-time communication capabilities in embedded systems, while DeviceNet emphasizes easy integration with industrial devices through a robust media access control layer and extensive support for discrete and analog I/O. Both protocols ensure reliable data exchange and network management but cater to different industrial application requirements and device interoperability standards.
Key Differences Between CANopen and DeviceNet
CANopen and DeviceNet are both protocols based on the CAN (Controller Area Network) bus but differ significantly in application and architecture. CANopen uses a device profile approach for flexibility and supports complex devices across industrial automation, while DeviceNet is optimized for factory automation with a predefined object model and simpler configuration. Data communication in CANopen follows a standardized object dictionary, enabling interoperability, whereas DeviceNet emphasizes ease of integration with predefined device classes and a simpler network management scheme.
Communication Protocol Architecture
CANopen employs a layered communication protocol architecture based on the OSI model, including the application, communication, and data link layers to support device profiles and network management. DeviceNet uses a simpler two-layer architecture combining the data link and application layers, optimized for industrial automation with predefined messages and explicit and implicit communication. Your choice between CANopen and DeviceNet depends on the required protocol complexity and device interoperability within your network.
Device Profiles and Interoperability
CANopen and DeviceNet differ significantly in device profiles and interoperability; CANopen features standardized device profiles defined by CiA (CAN in Automation) that ensure consistent behavior across devices like sensors, actuators, and drives, facilitating seamless integration. DeviceNet leverages the DeviceNet specification based on CIP (Common Industrial Protocol), providing device profiles that emphasize industrial automation components with strong support for network-wide interoperability and extensive vendor-specific options. The standardized profiles in CANopen promote higher interoperability among diverse manufacturers, while DeviceNet's robust device profile architecture supports complex network management and scalability in industrial environments.
Network Topology and Scalability
CANopen supports flexible network topologies including line, star, and tree, enhancing scalability for small to medium-sized automation systems. DeviceNet primarily utilizes a linear bus topology with limited branching, which can restrict network expansion and device count scalability. CANopen's decentralized architecture allows easier addition of nodes without significant reconfiguration, making it more adaptable for growing industrial networks.
Configuration and Integration Complexity
CANopen offers a more straightforward configuration and integration process with standardized device profiles and a well-defined communication stack, making it easier to implement in complex automation systems. DeviceNet requires managing a more complex network setup and communication parameters due to its reliance on the Common Industrial Protocol (CIP) and extensive device-specific configurations. Your choice between CANopen and DeviceNet will significantly impact the ease of system integration and overall project development time.
Performance and Data Throughput
CANopen offers efficient communication for industrial automation, supporting data rates up to 1 Mbps with rapid node response times ideal for real-time control. DeviceNet also operates at a maximum of 500 kbps but supports larger device networks with more complex messaging, optimizing system scalability over raw throughput. Both protocols leverage the CAN bus, yet CANopen prioritizes deterministic performance, whereas DeviceNet balances throughput with network flexibility and device interoperability.
Application Areas and Industry Use Cases
CANopen excels in medical equipment, automation, and elevator control systems due to its high interoperability and standardization in process control and embedded systems. DeviceNet is widely used in automotive assembly lines, factory automation, and industrial machinery, favored for its robustness in harsh industrial environments and ease of integration with Allen-Bradley controllers. Your choice between these protocols depends on specific application requirements, industry standards, and device compatibility priorities.
Cost Considerations and Licensing
CANopen typically incurs lower licensing fees due to its open-standard nature, reducing overall implementation costs in industrial automation projects. DeviceNet requires a more substantial licensing investment as it is proprietary, with fees needed for both protocol use and hardware certification. Cost considerations often favor CANopen for budget-sensitive applications, while DeviceNet's licensing ensures standardized compliance and vendor support.
Future Trends and Compatibility
CANopen and DeviceNet continue evolving with increased integration of IoT and Industry 4.0 technologies, enhancing network diagnostics and real-time data exchange. CANopen offers greater flexibility and scalability for complex automation systems, while DeviceNet emphasizes straightforward device-level connectivity with widespread industrial adoption. Your choice between these protocols should consider future compatibility with emerging smart factory standards and the specific communication needs of your automation environment.
CANopen vs DeviceNet Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com