BGA (Ball Grid Array) packages offer superior electrical performance and heat dissipation compared to QFP (Quad Flat Package), making them ideal for high-density and high-frequency applications. Discover how choosing the right package affects Your electronic design by reading the full comparison in the article.
Table of Comparison
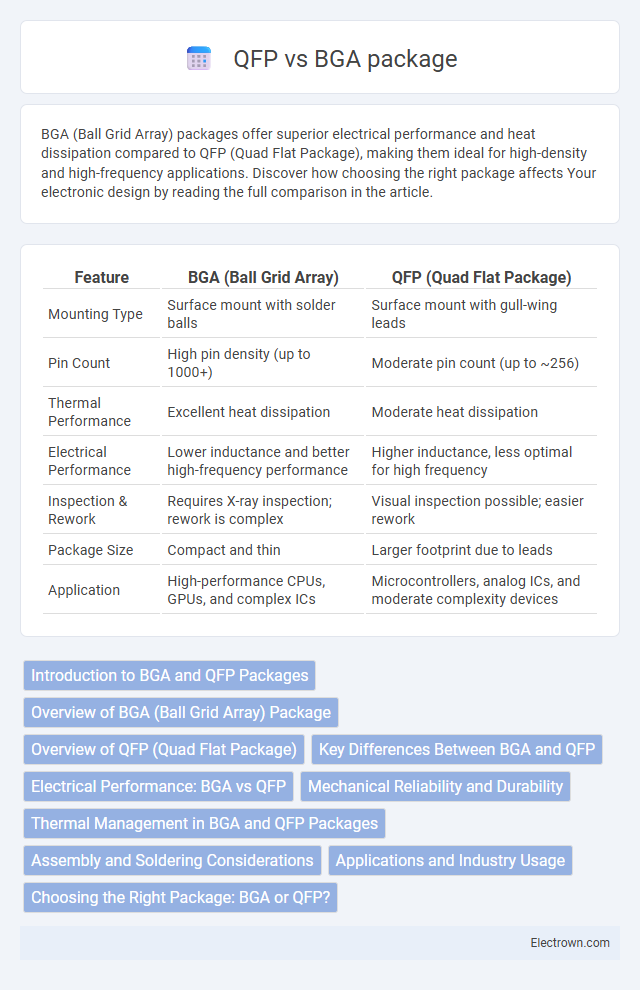
| Feature | BGA (Ball Grid Array) | QFP (Quad Flat Package) |
|---|---|---|
| Mounting Type | Surface mount with solder balls | Surface mount with gull-wing leads |
| Pin Count | High pin density (up to 1000+) | Moderate pin count (up to ~256) |
| Thermal Performance | Excellent heat dissipation | Moderate heat dissipation |
| Electrical Performance | Lower inductance and better high-frequency performance | Higher inductance, less optimal for high frequency |
| Inspection & Rework | Requires X-ray inspection; rework is complex | Visual inspection possible; easier rework |
| Package Size | Compact and thin | Larger footprint due to leads |
| Application | High-performance CPUs, GPUs, and complex ICs | Microcontrollers, analog ICs, and moderate complexity devices |
Introduction to BGA and QFP Packages
Ball Grid Array (BGA) and Quad Flat Package (QFP) are two common types of integrated circuit packages used in electronic devices. BGA features an array of solder balls on the underside, offering better heat dissipation and electrical performance, while QFP has flat leads extending from all four sides, making it suitable for high-pin-count applications. Understanding these packaging options helps you select the optimal solution for your device's size, performance, and manufacturing requirements.
Overview of BGA (Ball Grid Array) Package
The Ball Grid Array (BGA) package features an array of solder balls on the underside, providing superior electrical performance and thermal dissipation compared to traditional packages like QFP (Quad Flat Package). Its compact design allows for higher pin density and improved mechanical reliability by reducing lead inductance and enhancing signal integrity. You benefit from easier automated assembly and stronger connections, making BGAs ideal for advanced, high-frequency applications.
Overview of QFP (Quad Flat Package)
QFP (Quad Flat Package) is a surface-mount integrated circuit package with leads extending from all four sides of a flat rectangular body, offering a reliable and cost-effective solution for high-pin-count devices. Its thin profile and fine lead pitch enable efficient PCB space utilization and improved thermal performance compared to traditional through-hole packages. QFP packages are widely used in microcontrollers, CPUs, and complex digital devices requiring precise soldering and inspection processes.
Key Differences Between BGA and QFP
BGA (Ball Grid Array) and QFP (Quad Flat Package) differ primarily in their soldering and space efficiency; BGA uses an array of solder balls under the package, allowing for higher pin density and better thermal performance, while QFP features flat leads extending from all four sides, facilitating easier inspection but limiting pin count. BGA packages provide superior electrical performance due to shorter lead lengths, which reduces inductance and resistance, whereas QFPs are more susceptible to signal degradation in high-frequency applications. The manufacturing complexity and cost of BGA are higher compared to QFP, but BGA's robust mechanical reliability and improved heat dissipation make it ideal for advanced microprocessors and dense circuit boards.
Electrical Performance: BGA vs QFP
Ball Grid Array (BGA) packages offer superior electrical performance compared to Quad Flat Package (QFP) due to shorter lead lengths and reduced parasitic inductance and capacitance, resulting in improved signal integrity and higher frequency operation. The array of solder balls in BGA enables better thermal and electrical conductivity, minimizing signal crosstalk and power loss. QFP packages, with their longer gull-wing leads, tend to have higher inductance and susceptibility to electromagnetic interference, limiting their effectiveness in high-speed or high-frequency applications.
Mechanical Reliability and Durability
BGA (Ball Grid Array) packages offer superior mechanical reliability and durability compared to QFP (Quad Flat Package) due to their robust solder ball connections that provide better shock and vibration resistance. The uniform distribution of solder balls beneath the BGA reduces stress concentration, minimizing the risk of solder joint cracks during thermal cycling. Your electronic assemblies benefit from enhanced longevity and consistent performance in demanding environments when choosing BGA over QFP packaging.
Thermal Management in BGA and QFP Packages
BGA packages offer superior thermal management compared to QFP packages due to their exposed thermal pads and direct solder connections to the PCB, enabling efficient heat dissipation. QFP packages rely on lead frames and surface-mounted leads, which provide limited thermal conduction and often require additional heat sinks or thermal vias. Your device's performance and reliability can significantly improve by choosing BGA packages where effective heat dissipation is critical.
Assembly and Soldering Considerations
BGA packages require precise solder ball placement and controlled reflow profiles to ensure reliable solder joint formation and minimize voids. QFP packages demand careful lead alignment and solder paste application to prevent bridging and ensure consistent wetting during wave or reflow soldering. Both packages benefit from clean PCB pads and proper thermal management to optimize assembly yield and long-term joint integrity.
Applications and Industry Usage
Ball Grid Array (BGA) packages are widely used in high-performance computing, telecommunications, and automotive electronics due to their superior heat dissipation and compact design that supports higher pin counts for complex integrated circuits. Quad Flat Package (QFP) remains prevalent in consumer electronics, industrial control systems, and lower to mid-range microcontrollers where ease of inspection and soldering is critical. BGA's enhanced electrical performance makes it ideal for advanced GPUs and CPUs, while QFP's cost-effectiveness and simplicity suit applications like home appliances and instrumentation.
Choosing the Right Package: BGA or QFP?
Choosing between BGA and QFP packages depends on factors like board space, thermal performance, and ease of assembly. BGA offers higher pin density and better heat dissipation, making it ideal for complex, high-performance applications. QFP provides easier visual inspection and rework, suitable for designs with moderate pin counts and simpler manufacturing processes.
BGA vs QFP package Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com