Load cells and force sensors are both essential devices for measuring force, but load cells typically offer higher accuracy and are commonly used in industrial weighing applications, while force sensors are more versatile for dynamic measurements in various fields. Explore the rest of the article to understand which option best suits your specific needs.
Table of Comparison
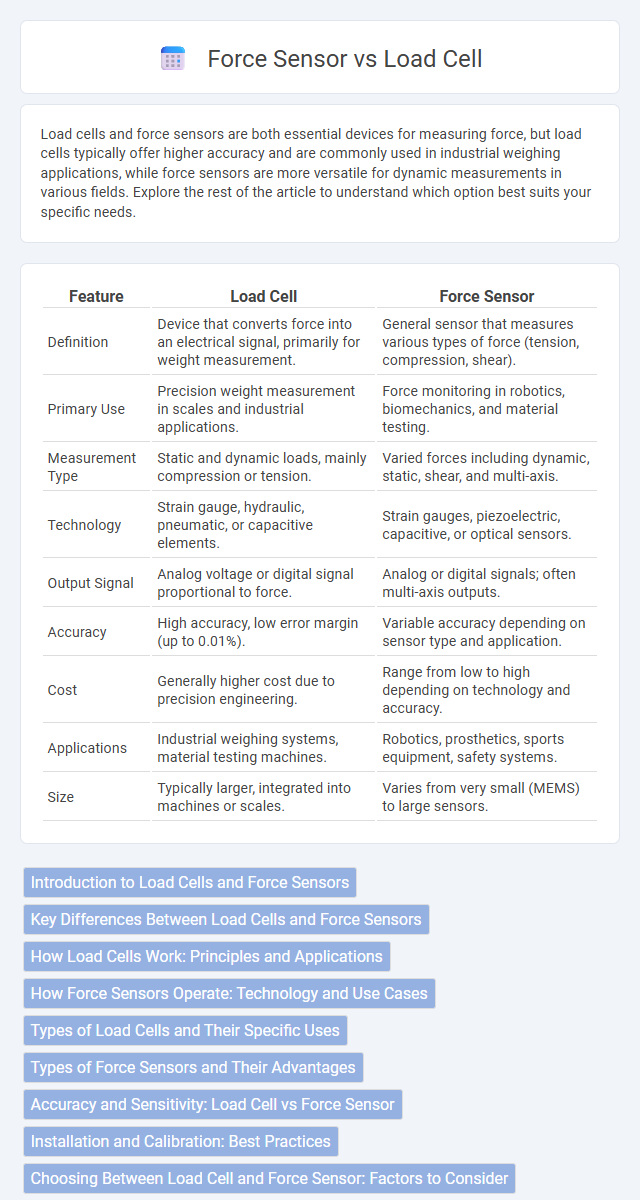
| Feature | Load Cell | Force Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Device that converts force into an electrical signal, primarily for weight measurement. | General sensor that measures various types of force (tension, compression, shear). |
| Primary Use | Precision weight measurement in scales and industrial applications. | Force monitoring in robotics, biomechanics, and material testing. |
| Measurement Type | Static and dynamic loads, mainly compression or tension. | Varied forces including dynamic, static, shear, and multi-axis. |
| Technology | Strain gauge, hydraulic, pneumatic, or capacitive elements. | Strain gauges, piezoelectric, capacitive, or optical sensors. |
| Output Signal | Analog voltage or digital signal proportional to force. | Analog or digital signals; often multi-axis outputs. |
| Accuracy | High accuracy, low error margin (up to 0.01%). | Variable accuracy depending on sensor type and application. |
| Cost | Generally higher cost due to precision engineering. | Range from low to high depending on technology and accuracy. |
| Applications | Industrial weighing systems, material testing machines. | Robotics, prosthetics, sports equipment, safety systems. |
| Size | Typically larger, integrated into machines or scales. | Varies from very small (MEMS) to large sensors. |
Introduction to Load Cells and Force Sensors
Load cells and force sensors are precision instruments designed to measure force or weight accurately in various applications. Load cells typically convert a force into an electrical signal using strain gauges, providing high accuracy for industrial weighing systems and material testing. Your choice between a load cell and a force sensor depends on factors such as measurement range, accuracy requirements, and the specific type of force being measured.
Key Differences Between Load Cells and Force Sensors
Load cells measure force by converting mechanical load into an electrical signal, making them ideal for precise weight measurement in industrial applications. Force sensors, on the other hand, detect force magnitude without necessarily providing weight-specific data, often used in robotics and touch-sensitive interfaces. Your choice depends on whether accuracy in weight measurement or general force detection is required.
How Load Cells Work: Principles and Applications
Load cells operate by converting mechanical force into an electrical signal using strain gauges that deform under load, altering their resistance. These devices are widely applied in industrial weighing systems, material testing machines, and robotics for precise force measurement and control. Understanding their principles facilitates accurate monitoring of tension, compression, and shear forces across diverse engineering and manufacturing processes.
How Force Sensors Operate: Technology and Use Cases
Force sensors operate by converting applied physical force into measurable electrical signals, using technologies such as strain gauges, piezoelectric materials, or capacitive sensing. These sensors are widely used in industrial automation, robotics, and medical devices to monitor load, pressure, or torque with high precision and real-time feedback. Understanding the operational principles of force sensors enables you to select the right technology for applications requiring accurate force measurement and control.
Types of Load Cells and Their Specific Uses
Strain gauge load cells are widely used for their accuracy in industrial weighing systems, while hydraulic load cells are preferred for harsh environments due to their durability and resistance to overload. Capacitive load cells find applications in precise laboratory measurements, whereas piezoelectric load cells excel in dynamic force measurements such as impact testing. Each type is selected based on factors like sensitivity, environmental conditions, and the nature of the force applied, ensuring optimal performance in specific use cases.
Types of Force Sensors and Their Advantages
Load cells and force sensors come in various types, including strain gauge, piezoelectric, capacitive, and hydraulic sensors, each offering unique advantages. Strain gauge load cells provide high accuracy and durability, making them ideal for industrial weighing and testing applications. You can select the appropriate force sensor based on factors like sensitivity, range, and environmental conditions to optimize measurement performance.
Accuracy and Sensitivity: Load Cell vs Force Sensor
Load cells typically offer higher accuracy and repeatability in measuring force due to their strain gauge technology, making them ideal for precise industrial applications. Force sensors, while sensitive to a broader range of forces, often exhibit lower accuracy and can be influenced by environmental factors such as temperature and humidity. Understanding the specific accuracy and sensitivity requirements of your application will help you choose between a load cell, for consistent high-precision measurements, or a force sensor, for versatile force detection.
Installation and Calibration: Best Practices
Proper installation of load cells requires secure mounting on rigid surfaces to ensure accurate force measurements, while force sensors must be aligned precisely with the direction of applied force to avoid signal distortion. Calibration for load cells involves using traceable weights to establish a reliable output, whereas force sensors often require calibration with known forces or specialized calibration equipment to maintain sensitivity. Your choice between a load cell and a force sensor can impact installation complexity and calibration frequency, so following manufacturer guidelines and maintaining regular calibration schedules ensures optimal performance and measurement accuracy.
Choosing Between Load Cell and Force Sensor: Factors to Consider
Choosing between a load cell and a force sensor depends on the specific measurement requirements, including the type of force (tension, compression, or shear) and the range of forces to be measured. Load cells are ideal for high-precision weight measurements in industrial applications, while force sensors offer versatility for dynamic or multi-axis force detection in various environments. Your choice should consider factors such as accuracy, sensitivity, environmental conditions, and the form factor needed for integration into your system.
Future Trends in Force Measurement Technologies
Emerging trends in force measurement technologies highlight advancements such as smart load cells integrated with IoT connectivity and machine learning algorithms for enhanced precision and predictive maintenance. Force sensors are increasingly incorporating flexible materials and miniaturized designs, enabling their use in wearable devices and robotics. Your selection of force measurement tools will benefit from these innovations, offering improved accuracy and adaptability in diverse industrial and biomedical applications.
Load Cell vs Force Sensor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com