Multimode fiber offers cost-effective solutions and easier installation for short-distance industrial networking, while single-mode fiber excels in long-distance communication with higher bandwidth and lower signal attenuation. Understanding these differences can enhance your network's performance; explore the article to learn which fiber type best fits your industrial needs.
Table of Comparison
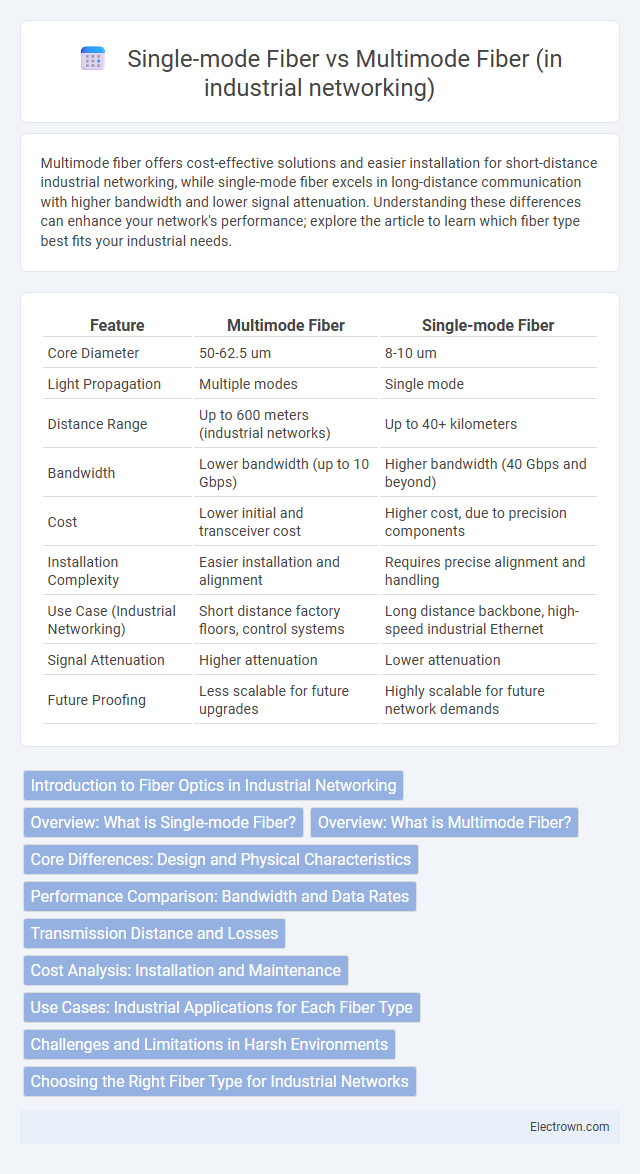
| Feature | Multimode Fiber | Single-mode Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Core Diameter | 50-62.5 um | 8-10 um |
| Light Propagation | Multiple modes | Single mode |
| Distance Range | Up to 600 meters (industrial networks) | Up to 40+ kilometers |
| Bandwidth | Lower bandwidth (up to 10 Gbps) | Higher bandwidth (40 Gbps and beyond) |
| Cost | Lower initial and transceiver cost | Higher cost, due to precision components |
| Installation Complexity | Easier installation and alignment | Requires precise alignment and handling |
| Use Case (Industrial Networking) | Short distance factory floors, control systems | Long distance backbone, high-speed industrial Ethernet |
| Signal Attenuation | Higher attenuation | Lower attenuation |
| Future Proofing | Less scalable for future upgrades | Highly scalable for future network demands |
Introduction to Fiber Optics in Industrial Networking
Fiber optics in industrial networking enable high-speed, long-distance data transmission essential for modern automation and control systems. Single-mode fiber offers low attenuation and high bandwidth suitable for extended industrial environments, while multimode fiber provides cost-effective, shorter-distance communication with easier installation. Selecting the appropriate fiber type depends on network distance requirements, bandwidth needs, and environmental conditions.
Overview: What is Single-mode Fiber?
Single-mode fiber is an optical fiber designed for long-distance communication, featuring a small core diameter of about 8-10 microns that allows a single light mode to propagate with minimal signal loss. It offers higher bandwidth and lower attenuation compared to multimode fiber, making it ideal for industrial networking environments requiring high-speed data transfer over extended distances. Your industrial network benefits from enhanced performance and reliability by using single-mode fiber in applications demanding precision and minimal interference.
Overview: What is Multimode Fiber?
Multimode fiber is an optical fiber designed to carry multiple light modes simultaneously, making it ideal for short-distance industrial networking applications such as within data centers or manufacturing plants. It features a larger core diameter, typically 50 or 62.5 microns, which allows multiple light rays to propagate, enabling high bandwidth at lower costs compared to single-mode fiber. This type of fiber supports data rates up to 10 Gbps over distances generally limited to about 550 meters, depending on the specific multimode fiber standard used.
Core Differences: Design and Physical Characteristics
Multimode fiber features a larger core diameter, typically 50 or 62.5 microns, allowing multiple light modes to propagate, which suits shorter distances in industrial networking. Single-mode fiber has a much smaller core, around 8-10 microns, designed for a single light mode transmission, offering higher bandwidth and longer reach essential for high-speed industrial applications. Understanding these core differences helps optimize your network design for performance and distance requirements.
Performance Comparison: Bandwidth and Data Rates
Multimode fiber supports bandwidths up to 10 Gbps over shorter distances typically less than 600 meters, making it suitable for industrial networking environments requiring moderate data rates. Single-mode fiber offers significantly higher bandwidth capacities, reaching up to 100 Gbps or more, enabling long-distance data transmission over several kilometers without signal degradation. The choice between multimode and single-mode fiber in industrial applications depends on required data rates, transmission distance, and overall network performance.
Transmission Distance and Losses
Multimode fiber supports transmission distances typically up to 600 meters with higher attenuation rates around 3.5 dB/km, making it suitable for short-range industrial networking. Single-mode fiber enables much longer transmission distances exceeding 10 kilometers due to its lower attenuation, often below 0.4 dB/km, which minimizes signal loss over extended networks. The reduced modal dispersion in single-mode fiber enhances signal integrity, crucial for high-speed data transmission in industrial environments.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Maintenance
Multimode fiber offers lower initial installation costs in industrial networking due to its larger core size, which simplifies connector alignment and reduces precision equipment requirements. Single-mode fiber, while more expensive to install because of stringent splicing and connectorization standards, provides lower long-term maintenance costs due to its higher durability and resistance to signal degradation over extended distances. Industrial environments benefit from multimode fiber for shorter transmission runs with budget constraints, whereas single-mode fiber justifies its upfront cost through minimized downtime and fewer maintenance interventions in long-haul, high-performance networks.
Use Cases: Industrial Applications for Each Fiber Type
Multimode fiber is commonly used in industrial networking environments requiring cost-effective, short-distance data transmission, such as factory automation, process control systems, and local area networks within manufacturing plants. Single-mode fiber is preferred for long-distance communication in industrial settings, including large-scale oil and gas facilities, power substations, and outdoor infrastructure where high bandwidth and low signal attenuation are critical. These fiber types support different applications based on transmission distance, bandwidth needs, and environmental conditions in industrial networks.
Challenges and Limitations in Harsh Environments
Multimode fiber in industrial networking faces challenges such as higher attenuation and modal dispersion, which limit its effective transmission distance in harsh environments with temperature fluctuations and electromagnetic interference. Single-mode fiber offers superior performance with lower signal loss and immunity to electromagnetic noise, but its delicate core makes installation and maintenance difficult in rugged industrial settings. Both fiber types require robust protective jackets and connectors to withstand mechanical stress, chemical exposure, and vibration commonly found in industrial environments.
Choosing the Right Fiber Type for Industrial Networks
Selecting the appropriate fiber type for industrial networks hinges on factors like distance, bandwidth requirements, and environmental conditions. Single-mode fiber provides higher bandwidth and longer transmission distances, making it ideal for expansive industrial facilities or inter-building connections. Multimode fiber suits shorter distances within a plant, offering cost-efficient installation and simpler maintenance, especially in environments with frequent equipment changes or space constraints.
Multimode Fiber vs Single-mode Fiber (in industrial networking) Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com