Ethernet/IP offers broad compatibility with industrial automation devices using standard Ethernet protocols, making it ideal for diverse manufacturing environments, while Profinet excels in real-time data exchange and deterministic communication tailored for complex process control systems. To understand which protocol best suits Your automation needs and how they impact system performance, continue exploring the detailed comparison ahead.
Table of Comparison
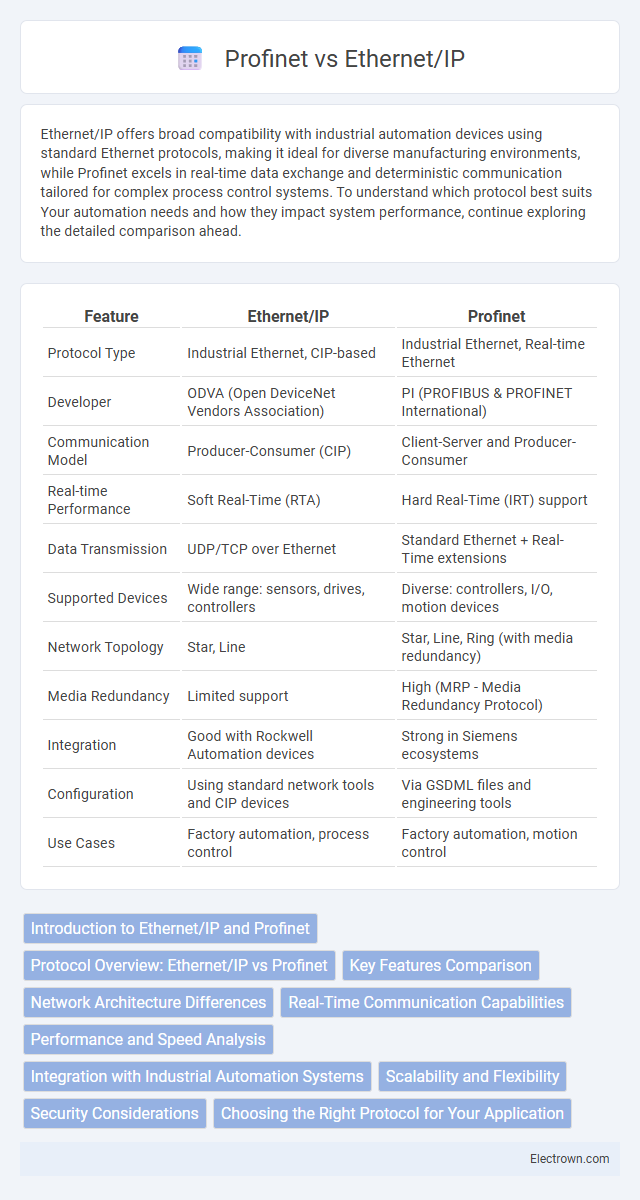
| Feature | Ethernet/IP | Profinet |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol Type | Industrial Ethernet, CIP-based | Industrial Ethernet, Real-time Ethernet |
| Developer | ODVA (Open DeviceNet Vendors Association) | PI (PROFIBUS & PROFINET International) |
| Communication Model | Producer-Consumer (CIP) | Client-Server and Producer-Consumer |
| Real-time Performance | Soft Real-Time (RTA) | Hard Real-Time (IRT) support |
| Data Transmission | UDP/TCP over Ethernet | Standard Ethernet + Real-Time extensions |
| Supported Devices | Wide range: sensors, drives, controllers | Diverse: controllers, I/O, motion devices |
| Network Topology | Star, Line | Star, Line, Ring (with media redundancy) |
| Media Redundancy | Limited support | High (MRP - Media Redundancy Protocol) |
| Integration | Good with Rockwell Automation devices | Strong in Siemens ecosystems |
| Configuration | Using standard network tools and CIP devices | Via GSDML files and engineering tools |
| Use Cases | Factory automation, process control | Factory automation, motion control |
Introduction to Ethernet/IP and Profinet
Ethernet/IP, developed by ODVA, is an industrial protocol that uses standard Ethernet and TCP/IP for data exchange in automation networks, emphasizing interoperability and real-time control. Profinet, created by PROFIBUS & PROFINET International, leverages Industrial Ethernet to facilitate fast, deterministic communication tailored for manufacturing automation and process control. Both protocols support high-speed data transmission but differ in architecture and application focus within industrial environments.
Protocol Overview: Ethernet/IP vs Profinet
Ethernet/IP is an industrial network protocol that utilizes the Common Industrial Protocol (CIP) over standard Ethernet, enabling real-time control and automation in manufacturing environments. Profinet, developed by Profibus & Profinet International, is based on standard Ethernet and supports deterministic and real-time communication tailored for industrial automation systems. Both protocols offer high-speed data exchange but differ in architecture and parameter handling, with Ethernet/IP leveraging Ethernet standards and Profinet emphasizing real-time performance and modular device configuration.
Key Features Comparison
Ethernet/IP offers widespread industrial automation compatibility with an open standard supported by ODVA, providing high interoperability and seamless integration across devices using the Common Industrial Protocol (CIP). Profinet, developed by Siemens, excels in real-time data transmission and deterministic communication through its IRT (Isochronous Real-Time) mode, making it ideal for time-critical applications and advanced motion control. Both protocols support diagnostics and safety features, but Ethernet/IP emphasizes ease of use and scalability, while Profinet prioritizes performance and integration with existing PROFIBUS systems.
Network Architecture Differences
Ethernet/IP utilizes a standard Ethernet network with a CIP (Common Industrial Protocol) model enabling flexible star or linear topologies suited for industrial automation. Profinet employs a real-time Ethernet framework based on IEEE 802.3, supporting ring, star, and line network architectures with integrated redundancy for high availability. The key distinction lies in Profinet's optimized deterministic communication and redundancy mechanisms, while Ethernet/IP relies on standard TCP/IP and UDP protocols for greater interoperability across devices.
Real-Time Communication Capabilities
Ethernet/IP employs CIP (Common Industrial Protocol) with explicit messaging to support real-time data exchange, suitable for many industrial automation applications but with limited deterministic capabilities. Profinet utilizes a specialized real-time protocol called IRT (Isochronous Real-Time), enabling precise cycle times down to 31.25 microseconds and deterministic communication essential for motion control and high-speed automation. The superior real-time performance of Profinet makes it preferable in time-critical industrial environments where strict synchronization is required.
Performance and Speed Analysis
Ethernet/IP offers reliable performance with data transfer speeds up to 100 Mbps and supports real-time applications through CIP Sync for time-critical communication. Profinet outperforms Ethernet/IP in speed by supporting gigabit Ethernet and providing deterministic real-time communication via its Isochronous Real-Time (IRT) mechanism, achieving cycle times as low as 31.25 microseconds. Your choice between Ethernet/IP and Profinet should consider the specific performance requirements and network speed needed for your industrial automation setup.
Integration with Industrial Automation Systems
Ethernet/IP offers seamless integration with Rockwell Automation and ODVA-compliant devices, providing extensive support for real-time control and information exchange in industrial automation systems. Profinet excels in integrating Siemens and other IEC-compliant devices, leveraging TCP/IP for high-speed, deterministic communication and enhanced diagnostics. Both protocols support remote I/O, motion control, and safety applications, but Profinet's native integration with PLC and HMI platforms gives it a competitive edge in complex automation networks.
Scalability and Flexibility
Ethernet/IP offers high scalability with seamless integration across various industrial automation devices, supporting extensive network expansion through standard Ethernet infrastructure. Profinet provides enhanced flexibility by enabling real-time data exchange and deterministic communication, making it ideal for complex automation systems requiring precise control. Both protocols support modular system designs, but Profinet excels in adaptability for mixed-device environments due to its robust configuration options and interoperability.
Security Considerations
Ethernet/IP and Profinet both implement security measures to protect industrial networks, but their approaches differ significantly. Profinet incorporates advanced security features like device authentication, access control, and encryption aligned with IEC 62443 standards, enhancing resilience to cyber threats. You should evaluate these protocols based on your network's vulnerability requirements and the criticality of secure communication in your industrial automation environment.
Choosing the Right Protocol for Your Application
Ethernet/IP offers seamless integration with Rockwell Automation systems and excels in high-speed industrial automation environments requiring robust real-time data exchange. Profinet is optimized for Siemens equipment and supports advanced diagnostics and flexibility in mixed vendor networks, making it ideal for complex manufacturing processes. Selecting the right protocol depends on factors such as device compatibility, network topology, required data speed, and existing infrastructure standards in your industrial application.
Ethernet/IP vs Profinet Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com