Point-to-point wiring offers direct, dedicated connections between components, enhancing signal integrity and ease of troubleshooting, while bus wiring simplifies installation by sharing a single communication path but may face performance bottlenecks as device numbers increase. Discover which wiring method best suits Your specific project requirements by reading the full article.
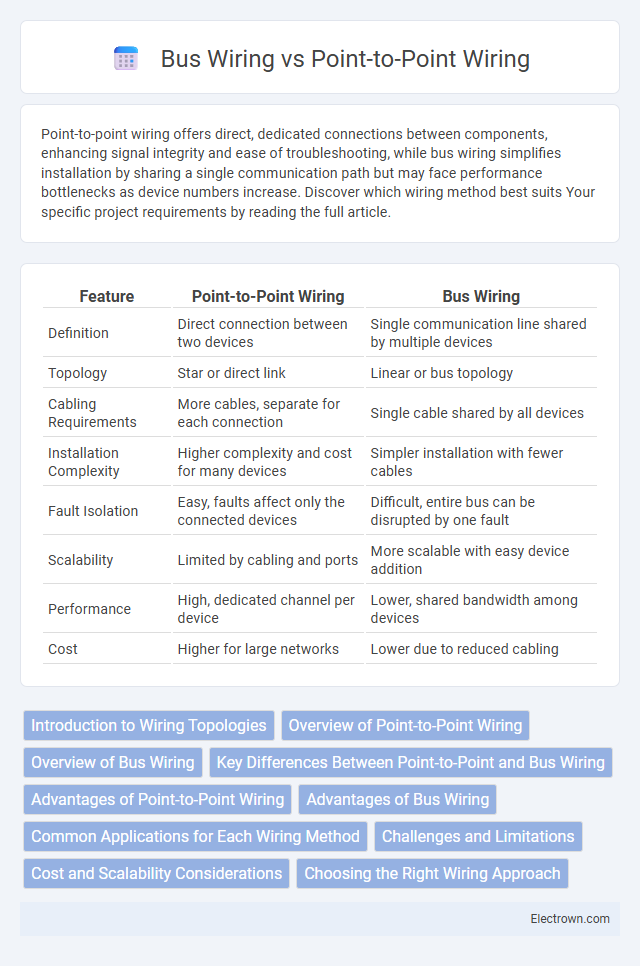
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Point-to-Point Wiring | Bus Wiring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct connection between two devices | Single communication line shared by multiple devices |
| Topology | Star or direct link | Linear or bus topology |
| Cabling Requirements | More cables, separate for each connection | Single cable shared by all devices |
| Installation Complexity | Higher complexity and cost for many devices | Simpler installation with fewer cables |
| Fault Isolation | Easy, faults affect only the connected devices | Difficult, entire bus can be disrupted by one fault |
| Scalability | Limited by cabling and ports | More scalable with easy device addition |
| Performance | High, dedicated channel per device | Lower, shared bandwidth among devices |
| Cost | Higher for large networks | Lower due to reduced cabling |
Introduction to Wiring Topologies
Point-to-point wiring connects devices directly with individual cables, ensuring dedicated communication paths that reduce signal interference and enhance reliability. Bus wiring uses a single communication line shared among multiple devices, which simplifies cabling but may lead to data collisions and difficulty in troubleshooting. Selecting the appropriate topology depends on factors like network size, signal integrity requirements, and maintenance considerations.
Overview of Point-to-Point Wiring
Point-to-point wiring involves connecting each component directly to another using individual wires, creating dedicated paths for signal transmission that minimize interference and signal loss. This method is commonly used in custom or high-performance electronic circuits due to its reliability and ease of troubleshooting. Unlike bus wiring, point-to-point wiring eliminates shared lines, enhancing signal integrity and reducing potential crosstalk in complex systems.
Overview of Bus Wiring
Bus wiring is a method where all devices are connected to a single communication line or bus, allowing signals to travel along this shared pathway. This approach simplifies the wiring layout and reduces the amount of cable needed compared to point-to-point wiring. You benefit from easier installation and scalability, but must ensure proper termination and signal integrity to avoid data collisions and communication errors.
Key Differences Between Point-to-Point and Bus Wiring
Point-to-point wiring connects each device directly to another, creating a dedicated path for signals, whereas bus wiring uses a single communication line shared by multiple devices. The key differences include complexity, with point-to-point wiring being more intricate due to numerous connections, while bus wiring simplifies installation but may face signal interference and bandwidth limitations. Your choice affects troubleshooting ease, system expandability, and overall network reliability.
Advantages of Point-to-Point Wiring
Point-to-point wiring offers enhanced reliability by providing direct, dedicated connections between components, reducing the risk of signal interference and faults. This method simplifies troubleshooting and maintenance since each wire corresponds to a specific path, making it easier to identify and fix issues. Your electronic or electrical system benefits from improved performance and reduced signal degradation when using point-to-point wiring compared to bus wiring configurations.
Advantages of Bus Wiring
Bus wiring offers streamlined installation with fewer cables by connecting multiple devices along a single communication line, reducing material costs and simplifying maintenance. This wiring method enhances scalability, making it easier to add or remove devices without extensive rewiring. Your system benefits from improved organization and reduced clutter, optimizing space in control panels and network setups.
Common Applications for Each Wiring Method
Point-to-point wiring is commonly used in complex electronic devices and high-frequency circuits where precise, direct connections minimize interference and signal loss, such as in aerospace and audio equipment. Bus wiring is prevalent in large-scale commercial and industrial installations like building automation and data communication systems, where multiple devices share a common communication line for efficient data transfer. Your choice between these methods depends on application complexity, signal integrity requirements, and scalability.
Challenges and Limitations
Point-to-point wiring presents challenges such as increased complexity and higher labor costs due to the need for individual connections between devices, which can lead to more potential failure points. Bus wiring faces limitations in signal degradation and reduced reliability as more devices are added, potentially causing data collisions and network interruptions. Your choice between these methods should consider the balance between scalability and maintenance difficulty to optimize system performance.
Cost and Scalability Considerations
Point-to-point wiring typically incurs higher initial costs due to increased material usage and labor intensity, but it offers superior scalability by allowing easy addition or modification of individual connections without disrupting the whole system. In contrast, bus wiring reduces upfront expenses with fewer cables and simpler installation, yet faces scalability challenges as adding new devices often requires segment upgrades or impacts overall bus performance. Evaluating cost-effectiveness and scalability depends on system size, future expansion plans, and maintenance complexity within industrial or network environments.
Choosing the Right Wiring Approach
Choosing the right wiring approach depends on your specific application requirements, environmental factors, and scalability needs. Point-to-point wiring offers direct, reliable connections ideal for simple circuits with minimal interference, while bus wiring supports multiple devices over a common pathway, enhancing flexibility and reducing cable complexity. Consider factors such as installation cost, maintenance convenience, and signal integrity to determine whether point-to-point or bus wiring best suits your project.
Point-to-Point Wiring vs Bus Wiring Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com