Resistive touch screens rely on pressure applied to the screen surface, making them compatible with any input device, while capacitive touch screens use the electrical properties of the human body to detect touch, offering higher sensitivity and multi-touch support. Understanding these fundamental differences can help you choose the best touch technology for your needs; continue reading to explore their advantages, limitations, and ideal applications.
Table of Comparison
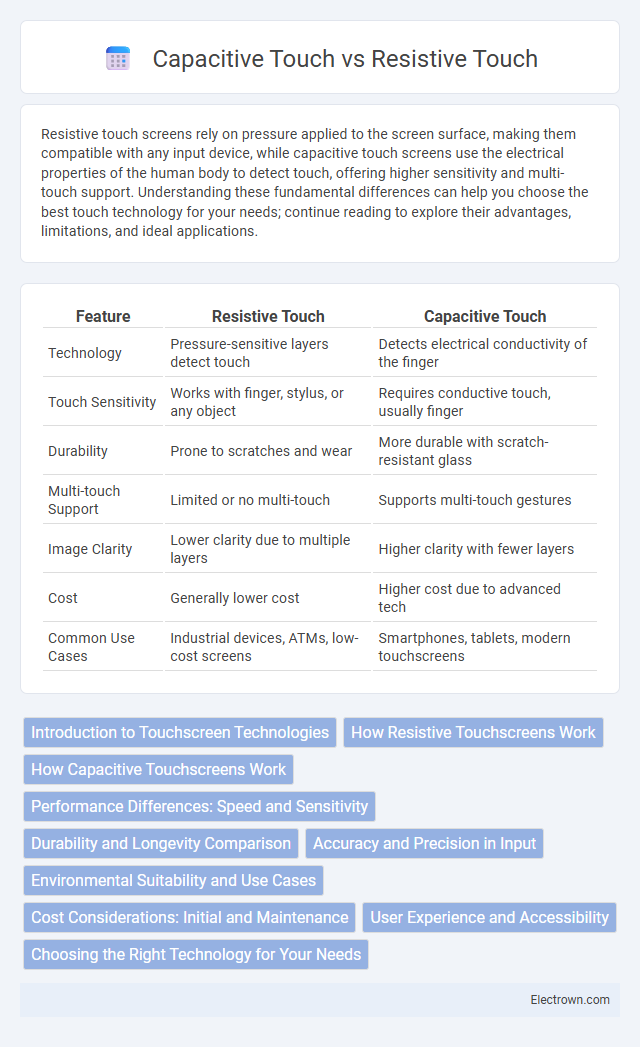
| Feature | Resistive Touch | Capacitive Touch |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Pressure-sensitive layers detect touch | Detects electrical conductivity of the finger |
| Touch Sensitivity | Works with finger, stylus, or any object | Requires conductive touch, usually finger |
| Durability | Prone to scratches and wear | More durable with scratch-resistant glass |
| Multi-touch Support | Limited or no multi-touch | Supports multi-touch gestures |
| Image Clarity | Lower clarity due to multiple layers | Higher clarity with fewer layers |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to advanced tech |
| Common Use Cases | Industrial devices, ATMs, low-cost screens | Smartphones, tablets, modern touchscreens |
Introduction to Touchscreen Technologies
Resistive touchscreens operate through pressure applied to flexible layers that connect circuits, making them compatible with styluses and gloves. Capacitive touchscreens rely on the electrical conductivity of the human finger, offering higher sensitivity and multi-touch capabilities. Your choice between resistive and capacitive technology impacts device responsiveness and usability in various environments.
How Resistive Touchscreens Work
Resistive touchscreens operate through two flexible, electrically conductive layers separated by a small gap that register touch when pressure causes them to make contact. This pressure-sensitive mechanism detects input regardless of the object used, such as a finger, stylus, or gloved hand, making resistive screens versatile for various environments. Common in industrial devices and budget-friendly smartphones, resistive touchscreens offer high accuracy but typically lack the multi-touch capability found in capacitive touch technology.
How Capacitive Touchscreens Work
Capacitive touchscreens operate by detecting changes in the electrical field caused by the conductive properties of your skin when it touches the screen. A grid of electrode layers on the glass surface senses this disturbance and calculates the exact touch location with high accuracy and responsiveness. This technology enables multi-touch gestures and offers greater durability compared to resistive touchscreens.
Performance Differences: Speed and Sensitivity
Resistive touchscreens rely on pressure applied to two conductive layers, resulting in slower response times and reduced sensitivity compared to capacitive touchscreens, which detect changes in electrical fields from the conductive properties of the human finger. Capacitive touch technology offers higher speed and precision, enabling multi-touch gestures and better overall responsiveness. The performance gap is especially noticeable in dynamic applications like gaming or fast typing, where capacitive screens provide smoother, more accurate input detection.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Resistive touchscreens typically offer higher durability against physical damage such as scratches and liquids due to their multi-layered structure, making them suitable for rugged environments. Capacitive touchscreens, while more sensitive and responsive, are generally less resistant to impacts and scratches but benefit from longer longevity when used in controlled settings. The longevity of resistive screens may decline faster with heavy use as pressure affects the layers, whereas capacitive screens maintain consistent performance over time but require careful handling to prevent surface damage.
Accuracy and Precision in Input
Resistive touchscreens offer high accuracy and precision due to their pressure-based input, allowing use with fingers, styluses, or gloves, making them suitable for tasks requiring detailed control. Capacitive touchscreens rely on the electrical properties of the human body, providing faster response but generally less precise input for fine detail. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize exact input or multi-touch capabilities and responsiveness.
Environmental Suitability and Use Cases
Resistive touchscreens perform better in harsh environments with exposure to dust, water, and extreme temperatures, making them ideal for industrial and outdoor applications. Capacitive touchscreens excel in consumer electronics like smartphones and tablets due to their multi-touch capability and high sensitivity but are less effective with gloves or moisture. The environmental suitability of resistive screens suits rugged use cases, while capacitive technology dominates in responsive, everyday devices.
Cost Considerations: Initial and Maintenance
Resistive touchscreens generally have a lower initial cost and are cost-effective for budget-conscious applications due to simpler technology and cheaper materials. Capacitive touchscreens, while pricier upfront, tend to have lower maintenance costs because of their durability and resistance to wear from frequent use. Maintenance expenses for resistive screens often rise over time due to sensitivity degradation and potential need for screen replacement.
User Experience and Accessibility
Resistive touchscreens offer precise input with any object, including styluses or gloved fingers, enhancing accessibility for users with disabilities or in various environmental conditions. Capacitive touchscreens provide a smoother, more responsive experience with multi-touch gestures, improving interactivity and overall user engagement. Your choice between the two impacts ease of use, accuracy, and the ability to accommodate diverse user needs.
Choosing the Right Technology for Your Needs
Resistive touchscreens respond to pressure, making them ideal for environments requiring stylus or glove use, such as industrial applications or healthcare. Capacitive touchscreens offer higher sensitivity and multi-touch capabilities, preferred in consumer electronics for smooth gesture controls and enhanced durability. Selecting the right technology depends on use case requirements including accuracy, environmental factors, and user interface complexity.
Resistive touch vs Capacitive touch Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com