Current probes measure the flow of electric current in a circuit without interrupting the circuit, while voltage probes detect the electrical potential difference between two points to analyze signal levels. Understanding the key differences between current probes and voltage probes is essential to ensure accurate measurements in your electronic testing--explore the rest of the article to deepen your knowledge.
Table of Comparison
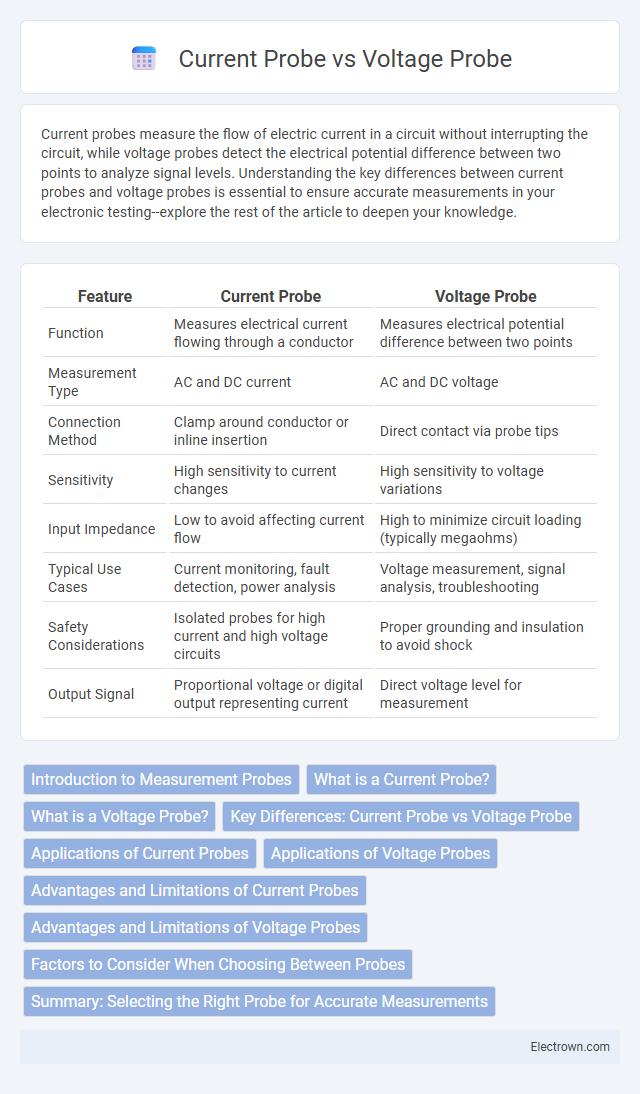
| Feature | Current Probe | Voltage Probe |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Measures electrical current flowing through a conductor | Measures electrical potential difference between two points |
| Measurement Type | AC and DC current | AC and DC voltage |
| Connection Method | Clamp around conductor or inline insertion | Direct contact via probe tips |
| Sensitivity | High sensitivity to current changes | High sensitivity to voltage variations |
| Input Impedance | Low to avoid affecting current flow | High to minimize circuit loading (typically megaohms) |
| Typical Use Cases | Current monitoring, fault detection, power analysis | Voltage measurement, signal analysis, troubleshooting |
| Safety Considerations | Isolated probes for high current and high voltage circuits | Proper grounding and insulation to avoid shock |
| Output Signal | Proportional voltage or digital output representing current | Direct voltage level for measurement |
Introduction to Measurement Probes
Measurement probes are essential tools in electronics for accurately capturing electrical signals, with current probes designed to measure the flow of electric current without direct contact, often using magnetic fields or clamps. Voltage probes, on the other hand, directly connect to the circuit to measure the electrical potential difference between two points, providing accurate voltage readings. Understanding the specific application of your measurement task helps determine whether a current or voltage probe is the most effective choice for precise diagnostics and analysis.
What is a Current Probe?
A current probe is a measurement device designed to accurately detect and measure electrical current flowing through a conductor without direct electrical contact. It typically uses magnetic field sensing technologies such as Hall effect sensors or transformers to convert current into a proportional voltage signal readable by oscilloscopes or data acquisition systems. Current probes enable real-time monitoring of AC and DC currents, making them essential for diagnostics, testing, and troubleshooting in electronic circuits and power systems.
What is a Voltage Probe?
A voltage probe is an essential tool in electrical measurements designed to detect and measure electrical potential difference between two points in a circuit without drawing significant current. Unlike a current probe that measures the flow of electric current, a voltage probe ensures minimal circuit disturbance by presenting high input impedance to the circuit. Your accurate voltage readings depend on using a voltage probe correctly, especially in troubleshooting and analyzing electronic devices.
Key Differences: Current Probe vs Voltage Probe
Current probes measure the flow of electric current through a conductor by detecting the magnetic field generated, while voltage probes measure the electrical potential difference between two points in a circuit. Current probes are typically clamped around a conductor without direct contact, enabling non-intrusive current measurement, whereas voltage probes require direct contact with circuit nodes to measure voltage accurately. Your choice between these probes depends on whether you need to monitor current flow or voltage levels in electronic testing and diagnostics.
Applications of Current Probes
Current probes are essential for measuring electrical current in circuit testing and analysis without direct contact or circuit interruption. You can use current probes in various applications such as power quality monitoring, motor control diagnostics, and troubleshooting electronic equipment to ensure accurate current measurement and system performance. They are particularly valuable in detecting transient currents, inrush currents, and verifying proper operation of power supplies and battery systems.
Applications of Voltage Probes
Voltage probes are essential in measuring electrical potential difference across components in circuits, making them indispensable for troubleshooting, designing, and testing electronic devices. They are widely used in oscilloscopes to capture signal waveforms accurately, ensuring precise voltage readings in both analog and digital electronics applications. Your ability to monitor voltage levels in real-time helps optimize circuit performance and enhances overall device reliability.
Advantages and Limitations of Current Probes
Current probes offer the advantage of measuring current without breaking the circuit, enabling non-intrusive analysis and real-time monitoring in high-frequency or high-current applications. Their limitations include sensitivity to electromagnetic interference, the need for proper calibration to ensure accuracy, and reduced effectiveness in measuring very low currents compared to voltage probes. Unlike voltage probes, current probes may introduce minimal disturbance to the circuit but require careful positioning and shielding to avoid signal distortion.
Advantages and Limitations of Voltage Probes
Voltage probes offer high input impedance, minimizing circuit loading and ensuring accurate voltage measurements, which makes them ideal for sensitive electronic testing. However, their limited bandwidth restricts the ability to measure high-frequency signals accurately, and they cannot measure current directly, necessitating separate current probes for comprehensive analysis. You should consider these advantages and limitations when selecting probes for your specific diagnostic or development tasks.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Probes
When choosing between current probes and voltage probes, consider measurement accuracy, signal type, and bandwidth requirements. Current probes excel in capturing dynamic current waveforms without breaking the circuit, making them ideal for troubleshooting power electronics and motor drives. Voltage probes offer precise voltage measurements with high input impedance, suited for delicate or low-current signals in sensitive electronic circuits.
Summary: Selecting the Right Probe for Accurate Measurements
Current probes accurately measure electrical current without breaking the circuit, making them ideal for analyzing AC or DC currents in various applications. Voltage probes detect potential difference across components, essential for precise voltage readings in high-impedance circuits. Choosing the right probe ensures your measurements reflect true signal characteristics, minimizing errors and enhancing diagnostic reliability.
current probe vs voltage probe Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com