Synchronous motors provide constant speed with high efficiency suitable for applications requiring precise speed control, while servo motors offer accurate position, velocity, and torque control, ideal for dynamic and complex motion tasks. Explore the rest of the article to understand which motor best suits your specific needs and applications.
Table of Comparison
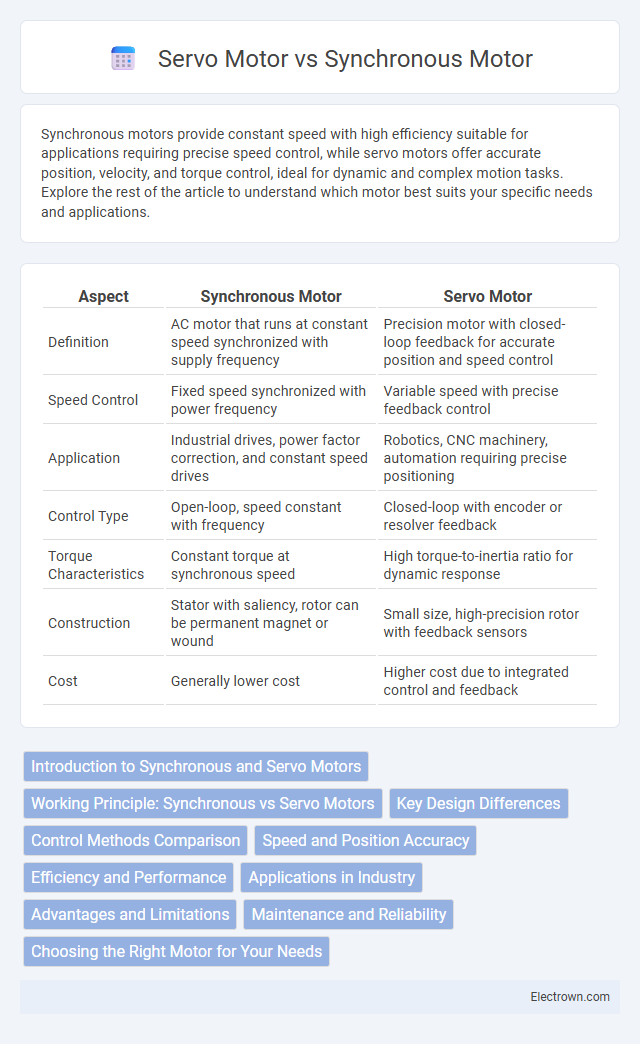
| Aspect | Synchronous Motor | Servo Motor |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | AC motor that runs at constant speed synchronized with supply frequency | Precision motor with closed-loop feedback for accurate position and speed control |
| Speed Control | Fixed speed synchronized with power frequency | Variable speed with precise feedback control |
| Application | Industrial drives, power factor correction, and constant speed drives | Robotics, CNC machinery, automation requiring precise positioning |
| Control Type | Open-loop, speed constant with frequency | Closed-loop with encoder or resolver feedback |
| Torque Characteristics | Constant torque at synchronous speed | High torque-to-inertia ratio for dynamic response |
| Construction | Stator with saliency, rotor can be permanent magnet or wound | Small size, high-precision rotor with feedback sensors |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to integrated control and feedback |
Introduction to Synchronous and Servo Motors
Synchronous motors operate at a constant speed synchronized with the supply frequency, making them ideal for applications requiring precise speed control and efficiency in industrial machinery. Servo motors provide high-precision positioning and speed control through closed-loop feedback systems, commonly used in robotics, CNC machines, and automation. Both motor types rely on electromagnetic principles but differ in control mechanisms, applications, and performance characteristics.
Working Principle: Synchronous vs Servo Motors
Synchronous motors operate by rotating at a constant speed synchronized with the frequency of the supply current, utilizing a rotor that locks in step with the stator's rotating magnetic field. Servo motors function through feedback mechanisms, precisely controlling angular position, velocity, and acceleration based on input signals for accurate motion control. The key distinction lies in synchronous motors maintaining fixed speed without feedback, while servo motors continuously adjust performance via closed-loop control systems.
Key Design Differences
Synchronous motors feature a rotor that rotates at a constant speed synchronized with the supply frequency, utilizing a permanent magnet or electromagnet, while servo motors incorporate a feedback system and high-precision control for accurate position, speed, and torque. The design of a synchronous motor emphasizes stable speed and efficiency in constant-speed applications, whereas servo motors prioritize dynamic response, precision, and flexibility with encoders or resolvers integrated for feedback. Your choice depends on whether you need precise motion control (servo motor) or efficient, consistent speed operation (synchronous motor).
Control Methods Comparison
Synchronous motors utilize rotor position feedback for precise speed control, often employing field-oriented control (FOC) to maintain constant speed under varying loads, making them suitable for applications demanding steady operation. Servo motors incorporate advanced closed-loop control systems with high-resolution encoders or resolvers, enabling precise position, speed, and torque control through sophisticated PID or adaptive algorithms, ideal for dynamic and exacting motion tasks. The main distinction in control methods lies in servo motors' enhanced feedback and responsiveness, providing higher precision and flexibility compared to the relatively simpler synchronous motor controls.
Speed and Position Accuracy
Synchronous motors provide consistent speed due to their operation synchronized with the power supply frequency, ideal for applications requiring constant velocity. Servo motors excel in precise position accuracy and rapid acceleration, controlled via feedback systems that continuously adjust motor output. The choice between these motors depends on the criticality of speed stability versus positional precision in the application.
Efficiency and Performance
Synchronous motors exhibit high efficiency due to their constant speed operation and minimal slip, making them ideal for applications requiring precise speed control. Servo motors offer superior performance by providing rapid acceleration, precise positioning, and dynamic response, essential for tasks demanding accuracy and flexibility. Understanding your application's efficiency needs and performance criteria helps determine whether a synchronous motor's steady output or a servo motor's agile control is more suitable.
Applications in Industry
Synchronous motors are widely used in industries for applications requiring constant speed and high power, such as compressors, pumps, and conveyor systems. Servo motors dominate precision control tasks in robotics, CNC machinery, and automated manufacturing, where accurate position, speed, and torque control are crucial. Industries leverage synchronous motors for heavy-duty and continuous operation, while servo motors excel in dynamic and precise motion control environments.
Advantages and Limitations
Synchronous motors offer high efficiency and precise speed control, making them ideal for applications requiring constant speed under varying loads, while their limitation lies in the need for an external excitation source. Servo motors provide excellent torque control and rapid response, essential for precise positioning tasks in robotics and CNC machines, but they can be complex and costly due to their feedback systems. Understanding these advantages and limitations helps you select the appropriate motor type for your specific industrial or automation needs.
Maintenance and Reliability
Synchronous motors generally require less frequent maintenance due to their simple construction and robust design, making them highly reliable for continuous operation. Servo motors, while offering precise control and high performance, need regular maintenance to ensure the integrity of feedback devices and electronic components. Understanding the maintenance demands helps you choose a motor that balances reliability with your system's operational needs.
Choosing the Right Motor for Your Needs
Choosing the right motor depends on application-specific requirements such as precision, speed control, and load characteristics. Synchronous motors offer excellent efficiency and constant speed for industrial machinery, while servo motors provide superior torque control and dynamic response for robotics and automation. Evaluating factors like torque demands, positional accuracy, and control complexity ensures optimal motor selection for performance and cost-effectiveness.
synchronous motor vs servo motor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com