Optical flow sensors offer high accuracy and non-contact measurement, making them ideal for precise fluid or airflow detection, while MEMS flow sensors provide compact size, low power consumption, and cost-effective solutions suitable for embedded systems and consumer electronics. Discover which sensor best fits Your application by exploring the detailed comparison in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
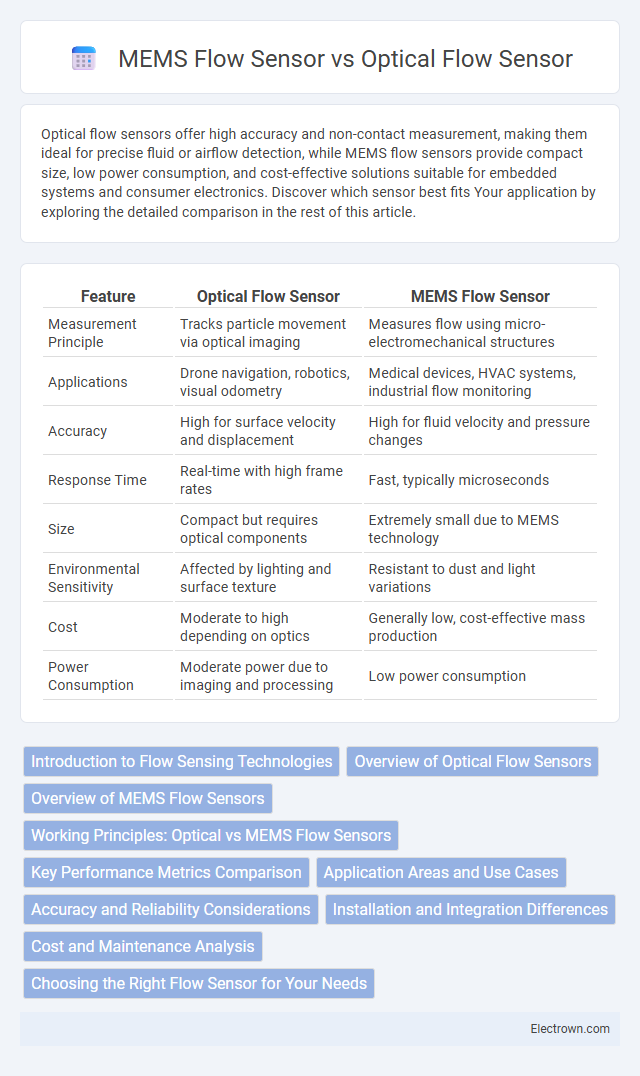
| Feature | Optical Flow Sensor | MEMS Flow Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Principle | Tracks particle movement via optical imaging | Measures flow using micro-electromechanical structures |
| Applications | Drone navigation, robotics, visual odometry | Medical devices, HVAC systems, industrial flow monitoring |
| Accuracy | High for surface velocity and displacement | High for fluid velocity and pressure changes |
| Response Time | Real-time with high frame rates | Fast, typically microseconds |
| Size | Compact but requires optical components | Extremely small due to MEMS technology |
| Environmental Sensitivity | Affected by lighting and surface texture | Resistant to dust and light variations |
| Cost | Moderate to high depending on optics | Generally low, cost-effective mass production |
| Power Consumption | Moderate power due to imaging and processing | Low power consumption |
Introduction to Flow Sensing Technologies
Optical flow sensors utilize image processing techniques to detect motion by tracking particles or surface patterns, providing high accuracy in fluid flow measurement without physical contact. MEMS flow sensors employ microfabricated mechanical structures to measure flow rates through thermal or pressure changes, offering compact size and low power consumption. Your choice between these technologies depends on factors like sensitivity, application environment, and integration requirements.
Overview of Optical Flow Sensors
Optical flow sensors use image-based techniques to measure the motion of particles or surfaces, providing high-resolution and precise flow measurements in applications such as robotics and drones. These sensors employ cameras or photodiodes to capture sequential images, analyzing changes in light patterns to determine velocity and direction of fluid or object movement. Optical flow sensors excel in detecting micro-movements and non-contact flow rates, offering advantages over MEMS flow sensors that rely on thermal or mechanical sensing elements.
Overview of MEMS Flow Sensors
MEMS flow sensors utilize microelectromechanical systems technology to measure fluid flow with high precision and miniaturized form factors. These sensors detect flow rates by sensing changes in pressure, thermal variations, or mechanical deflections within micro-scale structures, enabling applications in automotive, medical, and industrial sectors. Compared to optical flow sensors, MEMS flow sensors offer enhanced durability, compact size, and cost-effective mass production.
Working Principles: Optical vs MEMS Flow Sensors
Optical flow sensors detect movement by capturing changes in reflected light patterns on a surface, using image processing to measure flow velocity or displacement accurately. MEMS flow sensors rely on microelectromechanical systems technology, detecting flow through thermal, mechanical, or pressure variations caused by fluid movement over microscale structures. Your choice between optical and MEMS sensors depends on application specifics such as sensitivity, environmental conditions, and required precision.
Key Performance Metrics Comparison
Optical flow sensors offer high-resolution velocity measurements and excellent accuracy in detecting fluid movement, making them ideal for precise applications requiring detailed flow analysis. MEMS flow sensors excel in compactness, low power consumption, and cost-effectiveness, providing reliable flow rate detection with fast response times suitable for integration in portable devices. Your choice depends on the need for either detailed flow visualization (optical) or efficient, scalable sensing solutions (MEMS) based on key performance metrics such as sensitivity, response time, and operational environment.
Application Areas and Use Cases
Optical flow sensors excel in applications requiring precise motion detection and velocity measurement, such as drone navigation, robotics, and gesture control. MEMS flow sensors are widely used in medical devices, HVAC systems, and automotive industries due to their compact size and ability to measure fluid flow accurately. Your choice depends on whether you need high-resolution optical tracking or reliable fluid flow measurement in compact, embedded systems.
Accuracy and Reliability Considerations
Optical flow sensors offer high accuracy due to their ability to directly track particle movement, making them suitable for precise fluid velocity measurements in controlled environments. MEMS flow sensors rely on thermal or mechanical principles, which may introduce variability under temperature fluctuations but provide robust reliability in harsh or compact applications. Compared to MEMS, optical flow sensors generally deliver superior measurement fidelity, whereas MEMS flow sensors excel in durability and integration into miniaturized systems.
Installation and Integration Differences
Optical flow sensors require a clear line of sight and are often mounted in positions where visual tracking of particles or fluid movement is possible, making installation more sensitive to environmental factors like lighting and cleanliness. MEMS flow sensors, on the other hand, integrate directly into fluid channels or pipes with compact, robust designs that simplify physical integration and reduce space requirements. Your choice depends on the application environment and how seamlessly the sensor needs to blend with existing hardware systems.
Cost and Maintenance Analysis
Optical flow sensors typically have higher initial costs due to advanced imaging technology and complex calibration requirements, whereas MEMS flow sensors offer lower upfront expenses with simpler design and mass production benefits. Maintenance for optical flow sensors can be intensive, involving frequent cleaning and calibration to ensure accuracy, while MEMS sensors generally require less upkeep and provide better long-term reliability. Your choice between the two should consider both budget constraints and the anticipated maintenance workload to optimize operational efficiency.
Choosing the Right Flow Sensor for Your Needs
Optical flow sensors utilize light patterns to measure fluid dynamics with high accuracy, making them ideal for applications requiring precise velocity detection and minimal interference. MEMS flow sensors leverage microelectromechanical systems technology to provide compact, cost-effective solutions with excellent responsiveness and durability in various environments. Understanding your specific requirements for sensitivity, size, budget, and environmental conditions ensures you select the optimal flow sensor for reliable and efficient performance.
Optical flow sensor vs MEMS flow sensor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com