Analog oscilloscopes provide real-time waveform displays with smooth, continuous signal traces ideal for analyzing rapidly changing analog signals, while digital oscilloscopes capture, store, and allow detailed analysis of waveforms, offering advanced features like signal processing and easy data sharing. Discover how choosing between analog and digital oscilloscopes can impact your measurement accuracy and efficiency by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
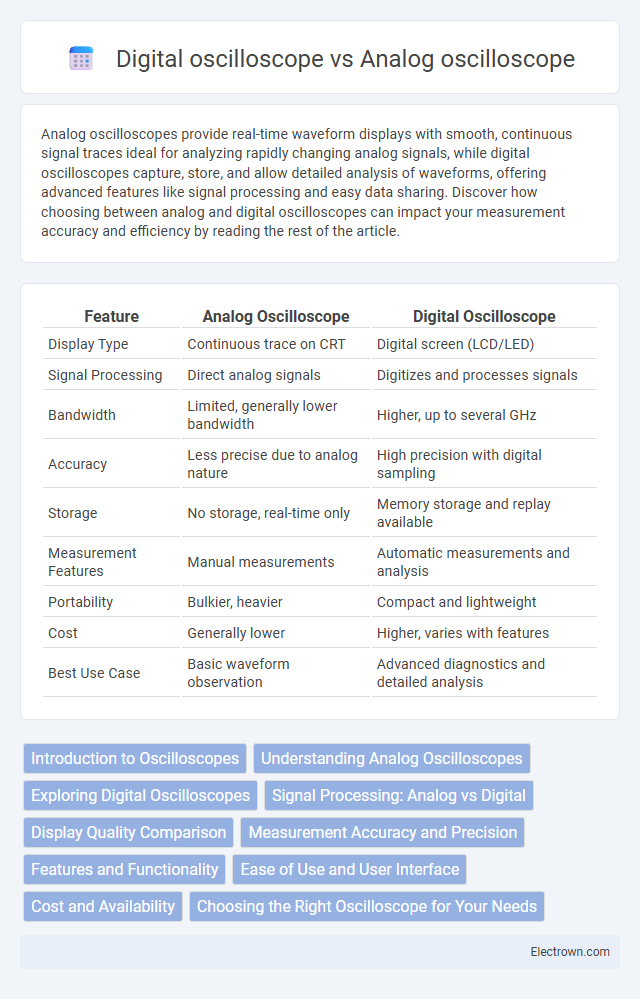
| Feature | Analog Oscilloscope | Digital Oscilloscope |
|---|---|---|
| Display Type | Continuous trace on CRT | Digital screen (LCD/LED) |
| Signal Processing | Direct analog signals | Digitizes and processes signals |
| Bandwidth | Limited, generally lower bandwidth | Higher, up to several GHz |
| Accuracy | Less precise due to analog nature | High precision with digital sampling |
| Storage | No storage, real-time only | Memory storage and replay available |
| Measurement Features | Manual measurements | Automatic measurements and analysis |
| Portability | Bulkier, heavier | Compact and lightweight |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher, varies with features |
| Best Use Case | Basic waveform observation | Advanced diagnostics and detailed analysis |
Introduction to Oscilloscopes
Oscilloscopes are essential electronic instruments that graphically display electrical signals to analyze waveform properties such as amplitude, frequency, and noise. Analog oscilloscopes use continuous voltage signals to produce waveforms on a cathode ray tube, offering real-time, smooth signal visualization ideal for observing fast transient events. Digital oscilloscopes convert analog signals into digital data using an analog-to-digital converter, providing advanced features like signal storage, complex measurements, and detailed analysis through software.
Understanding Analog Oscilloscopes
Analog oscilloscopes display continuous waveforms by directing an electron beam across a phosphorescent screen, providing real-time visualization of voltage signals with high bandwidth and low latency. They excel in capturing transient events and offer intuitive insights through direct voltage-time representation without conversion delays. Unlike digital oscilloscopes, analog models lack storage capabilities and advanced signal processing but remain valuable for analyzing rapidly changing analog signals.
Exploring Digital Oscilloscopes
Digital oscilloscopes offer enhanced precision and versatility compared to analog oscilloscopes, enabling you to capture, store, and analyze complex waveforms with high accuracy. Their advanced features include real-time signal processing, automated measurements, and easy data export for in-depth analysis. Digital oscilloscopes also provide greater bandwidth and resolution, making them essential tools for modern electronics diagnostics and development.
Signal Processing: Analog vs Digital
Analog oscilloscopes display continuous waveforms directly from electrical signals, providing real-time visualization with minimal latency, which is ideal for observing signal behavior as it happens. Digital oscilloscopes convert analog signals into digital data via analog-to-digital converters (ADCs), enabling advanced signal processing techniques like storage, filtering, and complex analysis, enhancing measurement accuracy and flexibility. Understanding your need for immediate signal insight versus detailed post-analysis can help determine whether an analog or digital oscilloscope best suits your application.
Display Quality Comparison
Analog oscilloscopes offer continuous waveform display with smooth, real-time signal representation, providing high resolution for rapidly changing signals. Digital oscilloscopes display waveforms using sampled data, enabling advanced features like zoom, storage, and precise measurements, though sometimes with lower instantaneous clarity. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize real-time analog accuracy or versatile digital analysis capabilities.
Measurement Accuracy and Precision
Digital oscilloscopes offer superior measurement accuracy and precision compared to analog oscilloscopes due to their ability to digitize signals with high sampling rates and advanced signal processing algorithms. Analog oscilloscopes rely on continuous waveforms, which may introduce parallax errors and limited bandwidth, reducing precision in complex or fast signals. Your choice should consider that digital oscilloscopes provide more reliable data analysis and easier measurement repeatability for detailed signal examination.
Features and Functionality
Analog oscilloscopes display continuous waveforms with real-time signal representation, providing high signal fidelity and simple user interfaces ideal for basic waveform analysis. Digital oscilloscopes sample input signals and convert them into digital data, offering advanced features such as storage, mathematical analysis, automatic measurements, and enhanced triggering options. While analog scopes excel in capturing fast transient signals without aliasing, digital scopes provide greater versatility with data processing capabilities, waveform comparison, and better integration with computer systems.
Ease of Use and User Interface
Analog oscilloscopes feature simple, intuitive controls with direct knobs and switches, making them easy for beginners to adjust signals in real-time without menus or complex settings. Digital oscilloscopes offer advanced user interfaces with high-resolution color displays, customizable waveform storage, and automated measurement functions, enhancing usability for detailed analysis but requiring familiarization with software-based controls. The choice between analog and digital oscilloscopes depends on the user's experience level and the need for rapid manual adjustments versus in-depth data manipulation and storage.
Cost and Availability
Analog oscilloscopes are generally more affordable and easier to find on the secondary market due to their simpler technology and long history of production. Digital oscilloscopes, while more expensive upfront, offer advanced features and greater accuracy, making them widely available through specialized electronics suppliers and online retailers. Cost differences often influence the choice between analog models for basic waveform analysis and digital models for precise measurements and data storage.
Choosing the Right Oscilloscope for Your Needs
Choosing the right oscilloscope depends on specific measurement requirements and budget constraints. Analog oscilloscopes provide real-time waveform visualization ideal for simple signal analysis and fast signal changes, while digital oscilloscopes offer advanced features like signal storage, complex triggering, and detailed waveform analysis crucial for modern electronics debugging. Evaluating factors such as bandwidth, sample rate, accuracy, and data processing capabilities ensures optimal tool selection for applications ranging from education to professional engineering.
Analog oscilloscope vs Digital oscilloscope Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com