A current loop controls the flow of electric current to maintain a constant output regardless of load changes, making it ideal for long-distance signal transmission and industrial automation. Understanding the differences between current loops and voltage loops will help you choose the best approach for your specific application--read on to discover more.
Table of Comparison
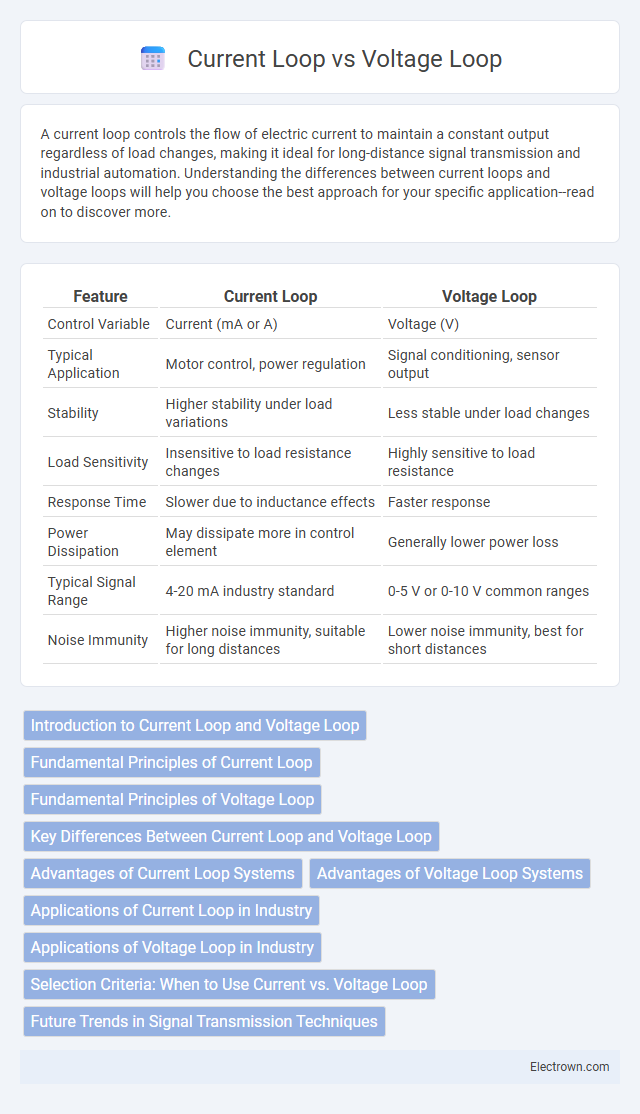
| Feature | Current Loop | Voltage Loop |
|---|---|---|
| Control Variable | Current (mA or A) | Voltage (V) |
| Typical Application | Motor control, power regulation | Signal conditioning, sensor output |
| Stability | Higher stability under load variations | Less stable under load changes |
| Load Sensitivity | Insensitive to load resistance changes | Highly sensitive to load resistance |
| Response Time | Slower due to inductance effects | Faster response |
| Power Dissipation | May dissipate more in control element | Generally lower power loss |
| Typical Signal Range | 4-20 mA industry standard | 0-5 V or 0-10 V common ranges |
| Noise Immunity | Higher noise immunity, suitable for long distances | Lower noise immunity, best for short distances |
Introduction to Current Loop and Voltage Loop
Current loops measure and control electrical current to transmit signals over long distances with high noise immunity, commonly used in industrial automation due to their consistent performance despite resistance changes. Voltage loops detect and regulate voltage levels, providing faster response times and simplicity in circuits with shorter distances or lower noise environments. Understanding the distinctions between current loop and voltage loop is crucial for optimizing Your system's accuracy and reliability in various electrical applications.
Fundamental Principles of Current Loop
The fundamental principle of a current loop involves transmitting signals through a constant current, typically 4-20mA, ensuring consistent signal integrity over long distances and minimizing the impact of voltage drops or electrical noise. This method allows for precise and reliable measurement in industrial instrumentation by converting sensor output into a standardized current signal proportional to the measured variable. The current loop boosts efficiency in control systems, maintaining accurate data transmission even in environments with significant electromagnetic interference.
Fundamental Principles of Voltage Loop
Voltage loop control is based on maintaining a constant voltage by continuously adjusting output to match a reference signal, ensuring system stability and precision. This method relies on feedback mechanisms that measure voltage levels and correct deviations, optimizing performance in power supplies and amplifier circuits. Your system benefits from reliable voltage regulation, minimizing fluctuations and enhancing operational efficiency.
Key Differences Between Current Loop and Voltage Loop
Current loop systems transmit signals using a constant 4-20 mA current, ensuring immunity to electrical noise and long-distance signal integrity, while voltage loops operate with varying voltage levels, which can be susceptible to voltage drops and interference. Current loops are generally preferred in industrial process control for precise and reliable measurements, whereas voltage loops are simpler and often used in lower-cost or less critical applications. The fundamental difference lies in the signal transmission method--current being regulated versus voltage being variable--which impacts accuracy, noise resistance, and system complexity.
Advantages of Current Loop Systems
Current loop systems offer superior noise immunity due to their ability to maintain accurate signal transmission over long distances without signal degradation. They provide inherent simplicity in wiring and fault detection, often using standard 4-20 mA signals that are less susceptible to voltage drops and electromagnetic interference. Industrial environments benefit from current loops as they ensure reliable and consistent sensor data for process control applications.
Advantages of Voltage Loop Systems
Voltage loop systems offer superior accuracy and stability in controlling output voltage compared to current loop systems. These systems minimize voltage drops and maintain consistent voltage levels, which is crucial for sensitive electronics and precise power management. Your devices benefit from enhanced performance and reduced risk of damage due to voltage fluctuations.
Applications of Current Loop in Industry
Current loop systems, particularly the 4-20 mA loop, dominate industrial applications due to their robustness in transmitting signals over long distances without significant signal loss. Your process control equipment benefits from current loops in environments with electrical noise, ensuring accurate sensor readings for flow, temperature, and pressure monitoring. These loops are crucial in automation for reliable and consistent communication between field instruments and control systems.
Applications of Voltage Loop in Industry
Voltage loops are essential in industrial applications requiring precise voltage regulation for components like power supplies, amplifiers, and sensors, ensuring stable operation and improved performance. They are commonly used in motor control systems to maintain constant voltage levels, enhancing motor efficiency and preventing damage due to voltage fluctuations. Voltage loops also play a critical role in audio equipment and instrumentation, delivering accurate signal conditioning and maintaining signal integrity under varying load conditions.
Selection Criteria: When to Use Current vs. Voltage Loop
Current loops are ideal for long-distance signal transmission and environments with electrical noise, offering stable and accurate measurements for industrial process controls. Voltage loops suit applications requiring simpler wiring and shorter distances, where signal integrity is less affected by resistance or external interference. Your choice depends on installation conditions, signal precision needs, and environmental factors influencing measurement reliability.
Future Trends in Signal Transmission Techniques
Current loop systems are evolving with enhanced digital modulation to improve noise immunity and long-distance transmission, while voltage loop techniques are integrating advanced wireless protocols and IoT connectivity for real-time data analytics. Your choice between current loop and voltage loop depends on future-proofing requirements such as scalability, energy efficiency, and compatibility with smart sensor networks. Innovations in semiconductor materials and AI-driven signal correction are shaping the next generation of signal transmission, emphasizing reliability and seamless integration across industrial automation platforms.
Current loop vs Voltage loop Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com