Port expanders increase the number of input/output pins available on microcontrollers, enabling more peripherals to connect, while multiplexers (mux) select one input from multiple signals to route through a single output line, optimizing signal paths. Understanding the differences between a port expander and a mux can help you choose the best solution for your electronics project; read on to explore their functions and applications in detail.
Table of Comparison
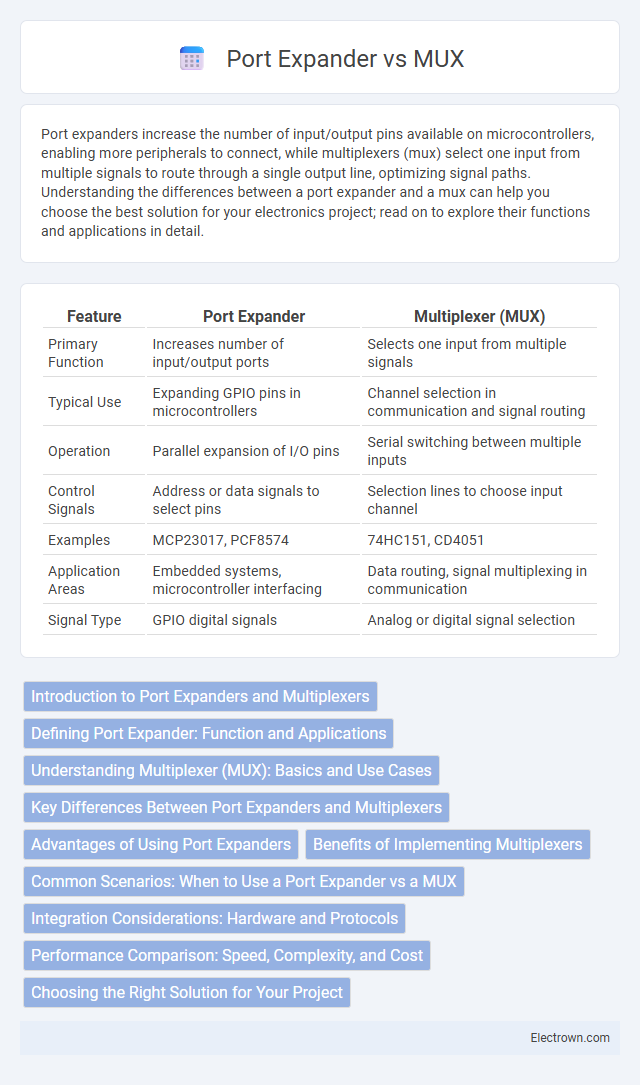
| Feature | Port Expander | Multiplexer (MUX) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Increases number of input/output ports | Selects one input from multiple signals |
| Typical Use | Expanding GPIO pins in microcontrollers | Channel selection in communication and signal routing |
| Operation | Parallel expansion of I/O pins | Serial switching between multiple inputs |
| Control Signals | Address or data signals to select pins | Selection lines to choose input channel |
| Examples | MCP23017, PCF8574 | 74HC151, CD4051 |
| Application Areas | Embedded systems, microcontroller interfacing | Data routing, signal multiplexing in communication |
| Signal Type | GPIO digital signals | Analog or digital signal selection |
Introduction to Port Expanders and Multiplexers
Port expanders increase the number of input/output (I/O) pins available on a microcontroller, enabling connection to multiple sensors or devices through protocols like I2C or SPI. Multiplexers (mux) select one signal from multiple inputs and forward it to a single output line, optimizing the use of limited I/O pins by time-sharing connections. Both components improve circuit scalability but serve distinct functions: port expanders add physical I/O pins, while multiplexers manage signal routing among existing pins.
Defining Port Expander: Function and Applications
A port expander increases the number of input/output ports available on a microcontroller or computer, enabling more devices or sensors to connect through a single interface. It functions by using protocols like I2C or SPI to communicate with the main controller while managing multiple peripheral connections, enhancing scalability in embedded systems, robotics, and IoT devices. Your projects benefit from port expanders by efficiently expanding connectivity without requiring additional microcontroller pins, simplifying complex hardware designs.
Understanding Multiplexer (MUX): Basics and Use Cases
A multiplexer (MUX) is a digital switch that selects one input from multiple signals and forwards it to a single output line, optimizing data flow in communication systems. Commonly used in applications like data routing, signal processing, and resource sharing, MUX devices efficiently manage multiple data streams to reduce wiring complexity and improve system performance. Your ability to understand the basics of MUX technology enables better design decisions in electronics and embedded systems where signal selection and control are crucial.
Key Differences Between Port Expanders and Multiplexers
Port expanders increase the number of input/output ports available on a microcontroller by using protocols like I2C or SPI, enabling simultaneous access to multiple peripherals. Multiplexers (MUX) selectively route multiple input signals to a single output line, optimizing the use of limited I/O pins but allowing only one active connection at a time. Key differences include expanders providing parallel access to all connected devices while multiplexers offer time-shared access, influencing design choices based on the need for concurrent data handling or resource conservation.
Advantages of Using Port Expanders
Port expanders significantly increase the number of input/output (I/O) pins available on microcontrollers, enabling the connection of multiple peripherals without redesigning the circuit board. They optimize space and cost by reducing the need for additional microcontrollers or larger chipsets, making them ideal for compact designs. Port expanders provide straightforward control over numerous devices via serial protocols like I2C or SPI, enhancing system scalability and flexibility.
Benefits of Implementing Multiplexers
Implementing multiplexers in your system streamlines data management by allowing multiple input signals to share a single communication line, reducing wiring complexity and overall hardware costs. Multiplexers enhance system efficiency by enabling faster data transmission and improving signal integrity through controlled switching. Compared to port expanders, multiplexers offer greater flexibility in dynamic signal routing, making them ideal for applications requiring real-time data selection and optimized resource utilization.
Common Scenarios: When to Use a Port Expander vs a MUX
Port expanders are ideal for scenarios where you need to increase the number of input/output pins on a microcontroller or FPGA without adding complexity to signal routing, such as connecting multiple sensors or LEDs in embedded systems. MUX devices are better suited for applications requiring the selection of one signal from many sources to send to a single destination, like audio or data channel selection in communication systems. Your choice depends on whether you need to multiply signal lines with individual access or switch between several signals dynamically.
Integration Considerations: Hardware and Protocols
Port expanders and multiplexers differ significantly in hardware integration and communication protocols. Port expanders typically use I2C or SPI interfaces to increase the number of I/O ports, offering straightforward connectivity with microcontrollers and requiring minimal additional hardware complexity. Multiplexers operate by selecting one input from multiple signals through control lines, often demanding precise timing and protocol management to ensure seamless signal routing within your system.
Performance Comparison: Speed, Complexity, and Cost
Port expanders offer faster data transfer rates due to dedicated lines for each I/O, while multiplexers (mux) rely on time-sharing signals, which can introduce latency and complexity in signal routing. In terms of design complexity, port expanders are simpler to implement but tend to be more costly due to additional hardware requirements, whereas multiplexers reduce cost by minimizing pin count but demand more intricate control logic. Your choice between a port expander and a mux should balance speed needs and budget constraints, with expanders favored for high-performance applications and muxes for cost-sensitive, space-limited designs.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Project
Choosing the right solution for your project involves evaluating whether a port expander or a multiplexer (mux) best suits your input/output requirements. Port expanders increase the number of available I/O pins, ideal for projects needing simultaneous control of multiple peripherals, while multiplexers efficiently select between multiple signals, optimizing limited pin resources. Assess your need for real-time processing speed and signal complexity to determine if expanding I/O capacity or switching between inputs aligns better with your project goals.
port expander vs mux Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com