Passive sensors detect energy naturally emitted or reflected by objects, relying on external sources like sunlight, while active sensors emit their own signal and measure the response, enabling data collection in various lighting conditions. Discover how understanding the differences between passive and active sensors can enhance your technology choices by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
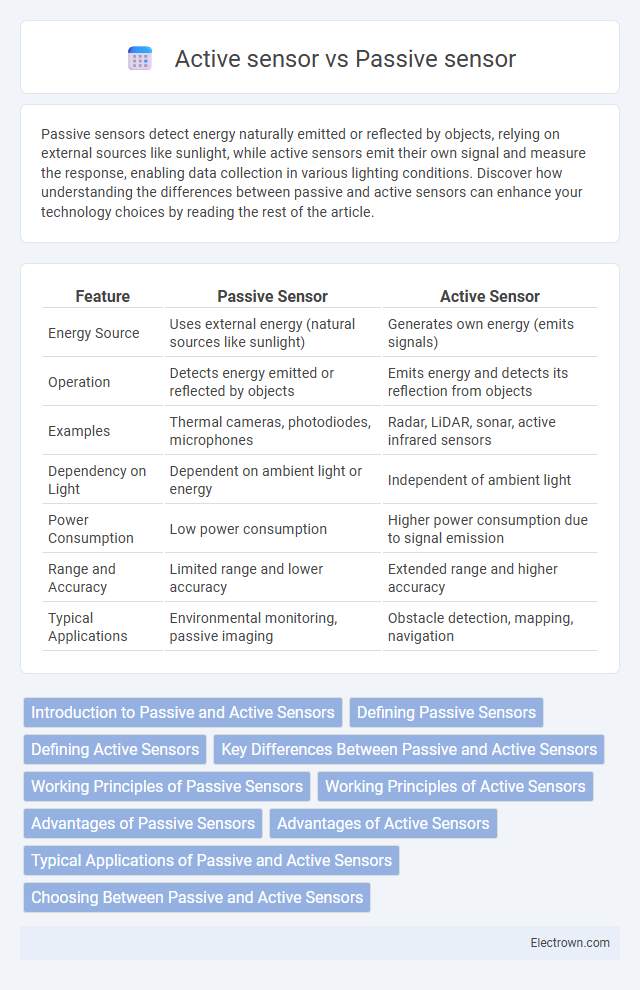
| Feature | Passive Sensor | Active Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Uses external energy (natural sources like sunlight) | Generates own energy (emits signals) |
| Operation | Detects energy emitted or reflected by objects | Emits energy and detects its reflection from objects |
| Examples | Thermal cameras, photodiodes, microphones | Radar, LiDAR, sonar, active infrared sensors |
| Dependency on Light | Dependent on ambient light or energy | Independent of ambient light |
| Power Consumption | Low power consumption | Higher power consumption due to signal emission |
| Range and Accuracy | Limited range and lower accuracy | Extended range and higher accuracy |
| Typical Applications | Environmental monitoring, passive imaging | Obstacle detection, mapping, navigation |
Introduction to Passive and Active Sensors
Passive sensors detect natural energy emitted or reflected by objects, commonly used in applications like thermal imaging and remote sensing of Earth's surface. Active sensors emit their own energy, such as radar or LiDAR, and measure the reflected signals to determine object properties or distances with high accuracy. Understanding the fundamental differences between passive sensors and active sensors is essential for selecting the appropriate technology in fields like environmental monitoring, automotive safety, and industrial automation.
Defining Passive Sensors
Passive sensors detect and measure natural energy emitted or reflected from objects without emitting any signals themselves, relying solely on ambient sources like sunlight or thermal radiation. These sensors are commonly used in applications such as remote sensing, thermal imaging, and environmental monitoring, where detecting existing energy patterns is crucial. Your choice of passive sensors can enhance efficiency by minimizing energy consumption and avoiding signal interference.
Defining Active Sensors
Active sensors emit their own energy, such as radio waves or laser beams, to detect and measure objects or environmental conditions. They capture the reflected signals to create data, enabling precise measurements regardless of ambient light or weather conditions. Examples include radar, LiDAR, and sonar systems commonly used in remote sensing and autonomous vehicles.
Key Differences Between Passive and Active Sensors
Passive sensors detect natural energy or radiation emitted or reflected by objects, such as sunlight or heat, without emitting any signals themselves. Active sensors emit their own energy, like radar or sonar waves, to illuminate the target and measure the returned signal for detection or imaging purposes. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the appropriate sensor type based on power consumption, range, and environmental conditions for your application.
Working Principles of Passive Sensors
Passive sensors detect energy naturally emitted or reflected by objects without emitting any signal themselves, relying on sources like sunlight or thermal radiation. These sensors capture and analyze ambient electromagnetic radiation, such as infrared or visible light, to gather information about the environment or target. Understanding how passive sensors operate can enhance your ability to select the right technology for applications requiring non-intrusive detection and monitoring.
Working Principles of Active Sensors
Active sensors emit their own energy, such as electromagnetic waves or signals, to detect and measure objects or environments by analyzing the reflected signals. These sensors are commonly used in radar, LiDAR, and sonar systems, enabling precise distance measurement, object detection, and imaging in various conditions. Your choice of active sensors ensures reliable data collection even in low-light or obscured environments, enhancing situational awareness and accuracy.
Advantages of Passive Sensors
Passive sensors offer the advantage of low energy consumption since they do not emit any signals but detect natural radiation, making them ideal for long-term environmental monitoring. Their operation is generally simpler and less prone to malfunction because they lack moving parts or transmitting components. Passive sensors also provide more accurate data in applications like remote sensing and thermal imaging, where detecting natural energy sources is crucial.
Advantages of Active Sensors
Active sensors emit their own energy to detect and measure objects, providing reliable data regardless of ambient light or weather conditions. Their ability to capture high-resolution images through clouds, darkness, or smoke offers significant advantages for applications like remote sensing, mapping, and surveillance. You benefit from enhanced accuracy and consistent performance in diverse environments, making active sensors indispensable for precise data acquisition.
Typical Applications of Passive and Active Sensors
Passive sensors are commonly used in applications such as thermal imaging, remote sensing of vegetation health, and passive infrared motion detection, relying on natural energy sources like sunlight or thermal radiation. Active sensors find typical applications in radar systems, LiDAR mapping, and ultrasonic range-finding, where they emit their own signal and measure the reflection to determine distance or material properties. The distinction in application arises from passive sensors' dependence on external energy versus active sensors' self-emission capabilities for precise, controlled measurements.
Choosing Between Passive and Active Sensors
Choosing between passive and active sensors depends on the specific application requirements and environmental conditions. Passive sensors detect natural energy emitted or reflected by objects, ideal for energy-efficient and stealth applications, while active sensors emit their own signal and measure its reflection, providing greater accuracy and functionality in low-light or obstructed environments. Factors such as power availability, target characteristics, and desired detection range play a crucial role in determining the optimal sensor type.
Passive sensor vs Active sensor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com