The 555 timer is a versatile integrated circuit used primarily for generating precise time delays and oscillations, while a comparator is designed to compare two voltage levels and output a digital signal indicating which input is higher. Understanding the fundamental differences between these components can help you choose the right device for your specific application; continue reading to explore their distinct functions and use cases.
Table of Comparison
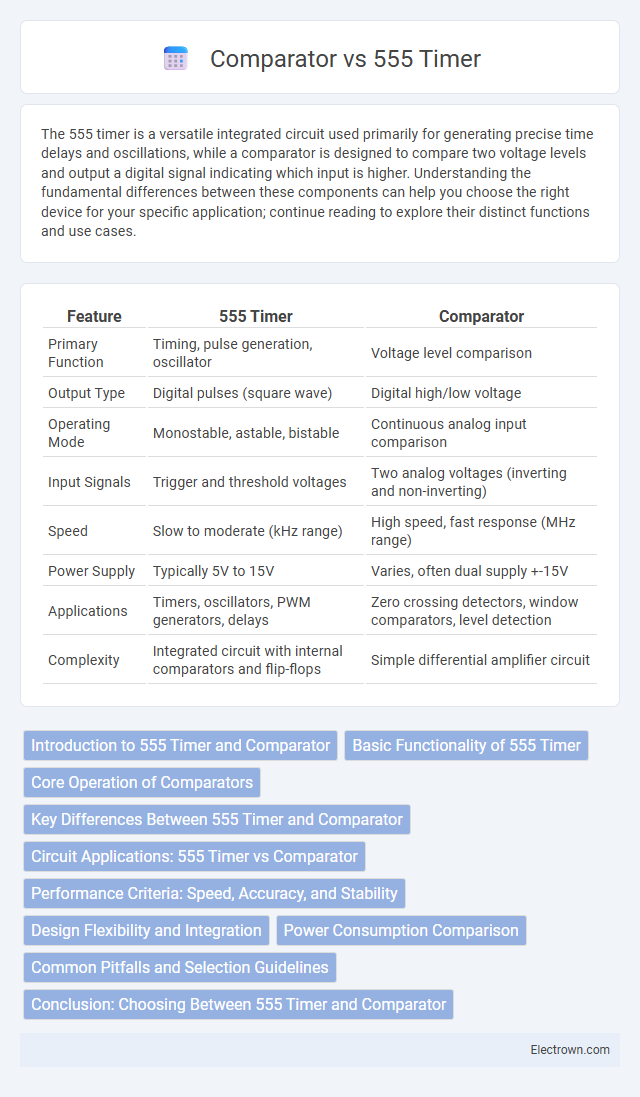
| Feature | 555 Timer | Comparator |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Timing, pulse generation, oscillator | Voltage level comparison |
| Output Type | Digital pulses (square wave) | Digital high/low voltage |
| Operating Mode | Monostable, astable, bistable | Continuous analog input comparison |
| Input Signals | Trigger and threshold voltages | Two analog voltages (inverting and non-inverting) |
| Speed | Slow to moderate (kHz range) | High speed, fast response (MHz range) |
| Power Supply | Typically 5V to 15V | Varies, often dual supply +-15V |
| Applications | Timers, oscillators, PWM generators, delays | Zero crossing detectors, window comparators, level detection |
| Complexity | Integrated circuit with internal comparators and flip-flops | Simple differential amplifier circuit |
Introduction to 555 Timer and Comparator
The 555 timer is a versatile integrated circuit widely used for generating precise time delays, oscillations, and pulse generation in electronic circuits. Comparators, on the other hand, are specialized devices that compare two voltage levels and output a digital signal indicating which input is higher. Understanding the fundamental purpose of each component helps you select the right device for timing or signal comparison applications.
Basic Functionality of 555 Timer
The 555 timer is an integrated circuit used primarily for generating precise time delays or oscillations. It operates in three modes: monostable, astable, and bistable, enabling it to function as a timer, oscillator, or flip-flop. Its internal structure includes comparators, a flip-flop, a discharge transistor, and a voltage divider, all working together to produce accurate timing pulses.
Core Operation of Comparators
Comparators operate by continuously comparing two input voltages and switching their output state when the voltage at the non-inverting input exceeds that at the inverting input, producing a digital signal. Unlike the 555 timer, which relies on internal timing components to generate oscillations or delays, comparators provide instantaneous voltage level comparison with near-zero propagation delay. This core operation makes comparators ideal for applications requiring fast and precise threshold detection or signal conditioning.
Key Differences Between 555 Timer and Comparator
The 555 timer operates as an integrated circuit used primarily for generating precise time delays or oscillations, while a comparator is designed to compare two voltage levels and output a digital signal based on which input is higher. The 555 timer contains flip-flops, comparators, and a discharge transistor internally, enabling it to function in monostable, astable, and bistable modes, whereas a comparator solely provides a binary output without waveform generation. Understanding these key differences will help you select the right component based on whether timing control or voltage comparison is required in your application.
Circuit Applications: 555 Timer vs Comparator
The 555 timer excels in generating precise time delays, pulse generation, and oscillations in circuits such as timers, pulse-width modulators, and flip-flops due to its internal voltage divider and flip-flop design. Comparators are primarily used for voltage level detection, zero-crossing detection, and analog-to-digital conversion interfaces by comparing input voltages and providing a digital output. While 555 timers are favored for timing and waveform generation, comparators offer higher speed and accuracy for signal threshold detection and control applications.
Performance Criteria: Speed, Accuracy, and Stability
The 555 timer excels in stability and ease of use for generating precise time delays, but its speed is limited compared to comparators, which offer faster response times ideal for rapid signal detection and switching. In terms of accuracy, comparators deliver higher precision in threshold detection without the timing drift common in 555 timers due to component tolerances. Your choice between these components depends on prioritizing speed and accuracy with comparators or leveraging the robust stability of a 555 timer for timing applications.
Design Flexibility and Integration
The 555 timer offers versatile design flexibility with its ability to function in astable, monostable, and bistable modes, making it ideal for timing, pulse generation, and oscillator applications. Comparators provide precise voltage threshold detection and faster response times, often integrated into more complex analog circuits for signal processing and waveform shaping. Your choice depends on whether you need robust timing solutions or high-speed voltage comparison integrated with other analog functions.
Power Consumption Comparison
The 555 timer typically consumes more power due to its internal transistor-transistor logic design, drawing tens of milliamps in active mode, whereas comparators often operate on microamps to low milliamps, making them ideal for low-power applications. Your choice between a 555 timer and a comparator significantly impacts battery life and thermal management in precision circuits. For ultra-low power consumption, especially in portable or energy-sensitive devices, comparators are the preferred option.
Common Pitfalls and Selection Guidelines
Selecting between a 555 timer and a comparator hinges on understanding their operational differences and application requirements. Common pitfalls when using a 555 timer include timing inaccuracies due to component tolerances and limited input voltage range, while comparators may suffer from output saturation and slower response in certain configurations. For precision threshold detection and faster switching, comparators are preferred, whereas 555 timers offer versatility for astable and monostable timing circuits requiring less frequency precision.
Conclusion: Choosing Between 555 Timer and Comparator
The 555 timer excels in generating precise time delays and oscillations, making it ideal for simple timing and pulse generation tasks. Comparators provide fast, accurate voltage level detection and are better suited for applications requiring signal comparison or analog-to-digital conversion. Your choice depends on whether you need reliable timing functions or precise voltage comparison in your circuit design.
555 timer vs comparator Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com