DC-DC converters efficiently change one DC voltage level to another, enabling your devices to operate at the required voltage while maintaining energy efficiency. Understanding the differences between DC-DC and AC-DC converters is essential to optimize your power management--read on to explore their functions and applications.
Table of Comparison
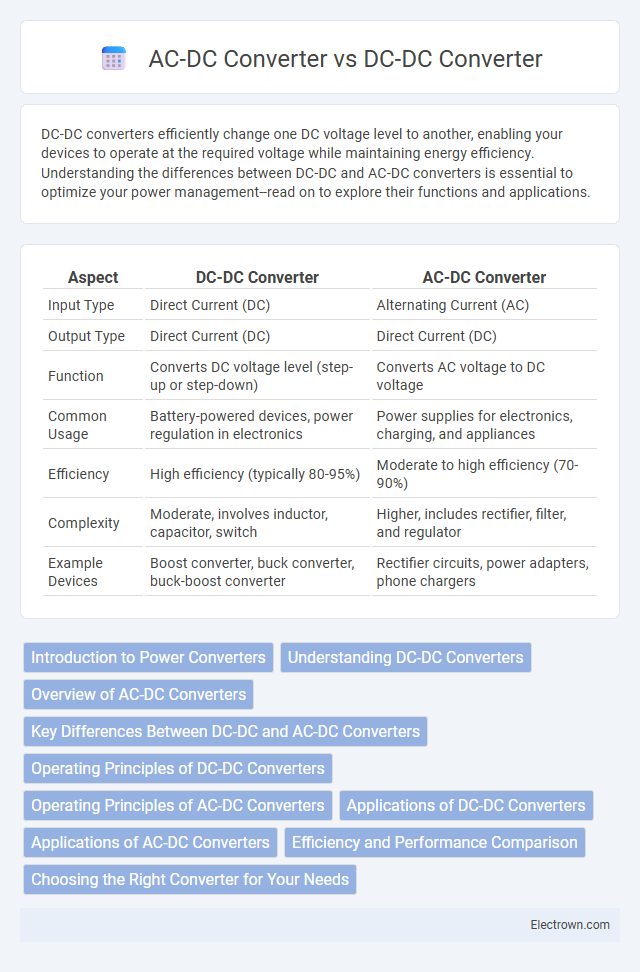
| Aspect | DC-DC Converter | AC-DC Converter |
|---|---|---|
| Input Type | Direct Current (DC) | Alternating Current (AC) |
| Output Type | Direct Current (DC) | Direct Current (DC) |
| Function | Converts DC voltage level (step-up or step-down) | Converts AC voltage to DC voltage |
| Common Usage | Battery-powered devices, power regulation in electronics | Power supplies for electronics, charging, and appliances |
| Efficiency | High efficiency (typically 80-95%) | Moderate to high efficiency (70-90%) |
| Complexity | Moderate, involves inductor, capacitor, switch | Higher, includes rectifier, filter, and regulator |
| Example Devices | Boost converter, buck converter, buck-boost converter | Rectifier circuits, power adapters, phone chargers |
Introduction to Power Converters
Power converters are essential devices that transform electrical energy from one form to another, enabling compatibility between different power sources and electronic devices. DC-DC converters specifically regulate and convert voltage levels within direct current circuits, while AC-DC converters change alternating current to direct current to power electronic equipment. Understanding the key differences and applications of these converters helps optimize your system's efficiency and performance in various electrical and electronic scenarios.
Understanding DC-DC Converters
DC-DC converters efficiently transform one level of direct current (DC) voltage to another, essential for powering electronic devices with varying voltage requirements. These converters use switching regulators to provide stable output voltage while minimizing energy loss, making them ideal for battery-powered applications. Understanding DC-DC converters helps you optimize power management by matching voltage needs precisely without converting to alternating current (AC).
Overview of AC-DC Converters
AC-DC converters, also known as rectifiers, transform alternating current (AC) from the power grid into direct current (DC) suitable for electronic devices. These converters use components like diodes, thyristors, or silicon-controlled rectifiers to regulate voltage and current. Understanding AC-DC converters helps you optimize power supply efficiency and device performance in various applications.
Key Differences Between DC-DC and AC-DC Converters
DC-DC converters regulate the voltage level within a direct current (DC) system, efficiently stepping up or down voltage for applications like battery-powered devices and solar power systems. AC-DC converters transform alternating current (AC) from the power grid into DC, serving as power supplies for electronic devices such as computers and LED lighting. Understanding these key differences can help you select the right converter based on your voltage transformation needs and the type of current you are working with.
Operating Principles of DC-DC Converters
DC-DC converters operate by switching electronic components such as transistors and inductors to efficiently convert one DC voltage level to another, using methods like buck, boost, or buck-boost configurations. These converters regulate output voltage through pulse-width modulation (PWM) to maintain a stable and precise voltage despite variations in input or load. Your applications benefit from the high efficiency and compact design of DC-DC converters, which are essential for power management in battery-operated and portable devices.
Operating Principles of AC-DC Converters
AC-DC converters operate by rectifying alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) using components such as diodes, thyristors, or silicon-controlled rectifiers to control the conversion process. The rectification process involves transforming the sinusoidal input voltage into a pulsating DC voltage, which is then smoothed by filters and regulators to provide stable DC output. Your choice of an AC-DC converter depends on the required output voltage, current stability, and efficiency for your specific electronic application.
Applications of DC-DC Converters
DC-DC converters are widely used in battery-powered devices, renewable energy systems, and electric vehicles where voltage regulation and efficient power conversion are crucial. These converters enable your electronics to function reliably by stepping up or down voltage levels to match specific component requirements. Their applications span portable gadgets, telecommunications equipment, and industrial automation, highlighting their importance in managing power supply in diverse environments.
Applications of AC-DC Converters
AC-DC converters are primarily used in power supplies for electronic devices, enabling the conversion of alternating current from the mains into stable direct current necessary for sensitive electronics such as computers, televisions, and battery chargers. They are essential in renewable energy systems, converting AC generated by wind turbines or hydroelectric generators into DC for battery storage and DC loads. Industrial automation and telecommunication equipment also rely on AC-DC converters to ensure consistent and reliable DC power from AC sources.
Efficiency and Performance Comparison
DC-DC converters typically offer higher efficiency in voltage regulation applications by minimizing power loss through precise switching techniques, often achieving efficiencies above 90%. AC-DC converters, while essential for converting mains electricity to DC power, generally exhibit slightly lower efficiency due to the complexity of rectification and filtering processes. Your choice between the two should consider the specific power requirements and frequency of operation to optimize performance and energy savings.
Choosing the Right Converter for Your Needs
Selecting the right converter depends on your power source and application requirements; DC-DC converters efficiently regulate voltage levels within DC systems, making them ideal for battery-powered devices and renewable energy setups. AC-DC converters are essential for transforming alternating current from the grid into stable direct current, suitable for household electronics and industrial equipment. Evaluating the input voltage type, output stability, efficiency, and compatibility with your system ensures optimal performance and energy savings.
DC-DC Converter vs AC-DC Converter Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com