Monte Carlo simulation provides a probabilistic approach by running thousands of random scenarios to assess risk and uncertainty, while corner analysis evaluates outcomes based on extreme values or boundary conditions to identify worst-case scenarios. Explore the rest of the article to understand how these methods can enhance your decision-making process.
Table of Comparison
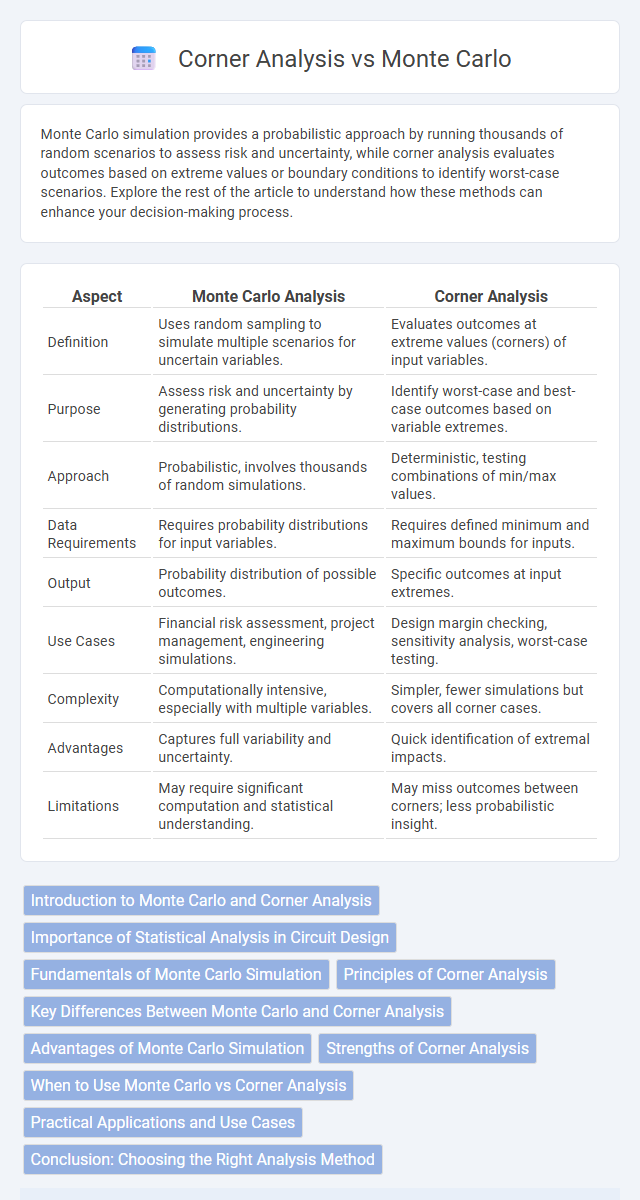
| Aspect | Monte Carlo Analysis | Corner Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uses random sampling to simulate multiple scenarios for uncertain variables. | Evaluates outcomes at extreme values (corners) of input variables. |
| Purpose | Assess risk and uncertainty by generating probability distributions. | Identify worst-case and best-case outcomes based on variable extremes. |
| Approach | Probabilistic, involves thousands of random simulations. | Deterministic, testing combinations of min/max values. |
| Data Requirements | Requires probability distributions for input variables. | Requires defined minimum and maximum bounds for inputs. |
| Output | Probability distribution of possible outcomes. | Specific outcomes at input extremes. |
| Use Cases | Financial risk assessment, project management, engineering simulations. | Design margin checking, sensitivity analysis, worst-case testing. |
| Complexity | Computationally intensive, especially with multiple variables. | Simpler, fewer simulations but covers all corner cases. |
| Advantages | Captures full variability and uncertainty. | Quick identification of extremal impacts. |
| Limitations | May require significant computation and statistical understanding. | May miss outcomes between corners; less probabilistic insight. |
Introduction to Monte Carlo and Corner Analysis
Monte Carlo analysis uses randomized sampling to model the probability distribution of possible outcomes in complex systems, making it ideal for uncertainty quantification in financial projections and risk assessment. Corner analysis examines extreme values and boundary conditions to identify worst-case and best-case scenarios, providing insight into system sensitivities by varying key parameters systematically. Your choice between these methods depends on whether you require probabilistic distribution insights or focused scenario evaluation for decision-making.
Importance of Statistical Analysis in Circuit Design
Statistical analysis such as Monte Carlo and Corner Analysis plays a crucial role in circuit design by ensuring robust performance under process variations and environmental changes. Monte Carlo analysis simulates a wide range of parameter variations to predict circuit yield and identify sensitivity, while Corner Analysis examines extreme fabrication corners to guarantee functionality across worst-case scenarios. Your ability to leverage these techniques helps optimize reliability, performance margins, and manufacturing success rates.
Fundamentals of Monte Carlo Simulation
Monte Carlo simulation utilizes probabilistic modeling and random sampling to analyze the impact of risk and uncertainty in prediction and forecasting models, making it essential for complex decision-making processes. It generates thousands of possible outcomes by varying input parameters based on their probability distributions, leading to a comprehensive understanding of potential variability and risk. This approach contrasts with Corner Analysis, which evaluates outcomes based on fixed extreme values, whereas Monte Carlo provides a dynamic, statistically robust exploration of all possible scenarios.
Principles of Corner Analysis
Corner Analysis focuses on evaluating project outcomes by examining the extreme values--best-case and worst-case scenarios--of key variables, helping identify the boundaries of possible results. This method simplifies risk assessment by concentrating on a limited set of discrete points rather than a continuous range, making it easier to understand the impact of uncertainty on decisions. Your decision-making improves by clearly understanding these potential extremes, guiding risk management and contingency planning effectively.
Key Differences Between Monte Carlo and Corner Analysis
Monte Carlo simulation uses random sampling to model uncertainty and variability across a wide range of possible outcomes, providing probabilistic results for complex systems. Corner Analysis evaluates model outcomes by testing extreme values at the edges of the input parameter ranges, focusing on best-case and worst-case scenarios. Monte Carlo offers a comprehensive risk distribution, while Corner Analysis highlights boundary conditions and sensitivity to parameter extremes.
Advantages of Monte Carlo Simulation
Monte Carlo simulation offers significant advantages in risk analysis by enabling the modeling of complex systems with multiple uncertain variables through random sampling, which provides a probabilistic distribution of outcomes rather than limited scenario results. This method captures the full range of possible variations in inputs, leading to more comprehensive and realistic insights into potential risks and rewards. It also facilitates sensitivity analysis, helping identify which variables most influence the model's outputs and supporting better decision-making under uncertainty.
Strengths of Corner Analysis
Corner Analysis excels at identifying the most extreme and impactful scenarios within a dataset, providing clear insights into best- and worst-case outcomes. Its strength lies in testing the sensitivity of key variables one at a time, making it easier for you to pinpoint critical risk factors. This straightforward approach is particularly useful for quick, focused decision-making when detailed probabilistic data is unavailable.
When to Use Monte Carlo vs Corner Analysis
Monte Carlo simulation is ideal for assessing risk and uncertainty in complex systems with numerous variables and probabilistic inputs, providing a comprehensive distribution of possible outcomes. Corner analysis suits situations where sensitivity to extreme input values is crucial, analyzing system behavior at the extremes or "corners" of variable ranges. Choose Monte Carlo for probabilistic forecasting and risk assessment, while corner analysis is best for evaluating worst-case or best-case scenario impacts on system performance.
Practical Applications and Use Cases
Monte Carlo simulation is widely used in financial risk assessment, project management, and engineering to model uncertainty and variability through random sampling, enabling probabilistic predictions of outcomes. Corner analysis, or sensitivity analysis, excels in identifying critical input variables by evaluating extreme scenario impacts, commonly applied in decision-making and optimization problems. Both techniques complement each other in fields like oil and gas exploration, supply chain management, and environmental modeling to enhance risk evaluation and strategic planning.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Analysis Method
Choosing between Monte Carlo and Corner Analysis depends on the complexity and goals of your risk assessment. Monte Carlo simulation excels in modeling uncertainty through random sampling, offering probabilistic outcomes ideal for dynamic systems with numerous variables. Corner Analysis provides clear insights by evaluating extreme parameter values, making it effective for identifying worst-case scenarios in simpler, deterministic models.
Monte Carlo vs Corner Analysis Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com