TSMC leads the semiconductor manufacturing industry with cutting-edge technology and a dominant market share, while UMC focuses on specialized and cost-effective foundry services. Discover the key differences between TSMC and UMC to understand which company aligns better with Your business needs. Read on to explore the full comparison.
Table of Comparison
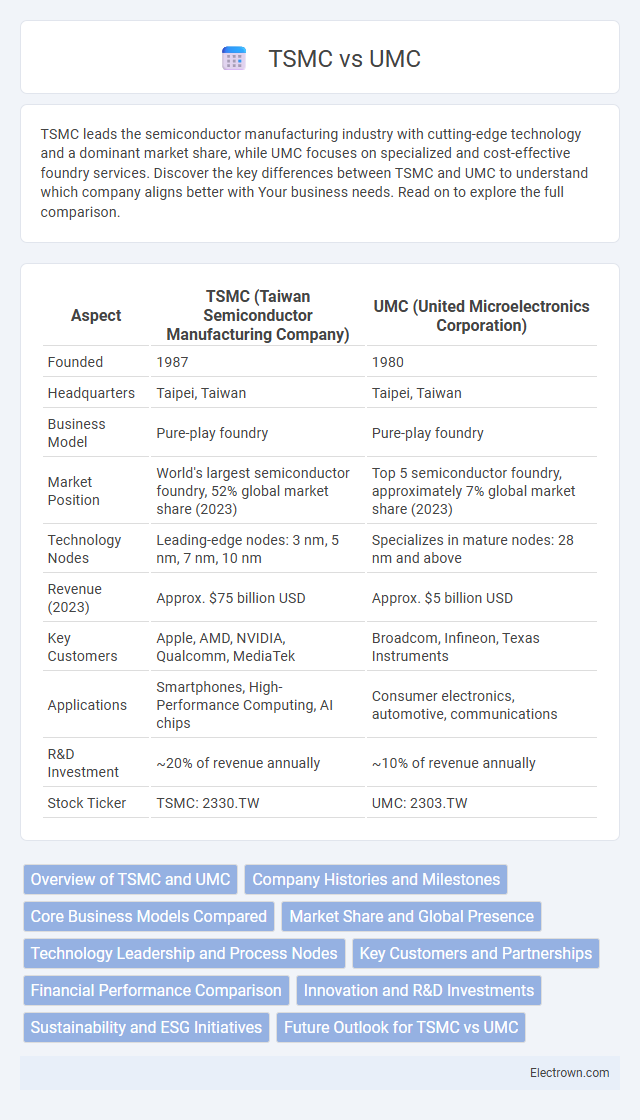
| Aspect | TSMC (Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company) | UMC (United Microelectronics Corporation) |
|---|---|---|
| Founded | 1987 | 1980 |
| Headquarters | Taipei, Taiwan | Taipei, Taiwan |
| Business Model | Pure-play foundry | Pure-play foundry |
| Market Position | World's largest semiconductor foundry, 52% global market share (2023) | Top 5 semiconductor foundry, approximately 7% global market share (2023) |
| Technology Nodes | Leading-edge nodes: 3 nm, 5 nm, 7 nm, 10 nm | Specializes in mature nodes: 28 nm and above |
| Revenue (2023) | Approx. $75 billion USD | Approx. $5 billion USD |
| Key Customers | Apple, AMD, NVIDIA, Qualcomm, MediaTek | Broadcom, Infineon, Texas Instruments |
| Applications | Smartphones, High-Performance Computing, AI chips | Consumer electronics, automotive, communications |
| R&D Investment | ~20% of revenue annually | ~10% of revenue annually |
| Stock Ticker | TSMC: 2330.TW | UMC: 2303.TW |
Overview of TSMC and UMC
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) is the world's largest contract chipmaker, specializing in cutting-edge semiconductor manufacturing technologies including 5nm and 3nm process nodes, serving major clients like Apple and NVIDIA. United Microelectronics Corporation (UMC) focuses on mature and specialty process technologies such as 28nm and above, targeting automotive, IoT, and display driver markets. Both companies play pivotal roles in the global semiconductor supply chain, with TSMC leading in advanced logic manufacturing and UMC concentrating on niche applications with diversified technology offerings.
Company Histories and Milestones
TSMC, founded in 1987, pioneered the dedicated semiconductor foundry model, becoming the world's largest contract chip manufacturer and achieving milestones such as mass production of 5nm and 3nm processes. UMC, established in 1980, is Taiwan's first semiconductor company and a key player in mature process technologies, focusing on specialty manufacturing like embedded memory and power management ICs. Both companies have significantly influenced Taiwan's semiconductor industry, with TSMC leading advanced node innovation and UMC maintaining strong market presence in specialty nodes.
Core Business Models Compared
TSMC operates as a pure-play foundry, specializing exclusively in semiconductor manufacturing for a diverse range of clients without designing its own chips, enabling it to serve major global technology companies with advanced process nodes. UMC, while also a foundry, targets more mature technology nodes and focuses on cost-effective production for mid-tier clients in consumer electronics, automotive, and telecom sectors. The fundamental difference lies in TSMC's leadership in cutting-edge fabrication technologies and extensive R&D investment versus UMC's emphasis on volume manufacturing at established nodes and strong customer service for less complex chip designs.
Market Share and Global Presence
TSMC dominates the semiconductor foundry market with over 50% global market share, significantly outpacing UMC's approximate 7%, reflecting its leadership in advanced process technologies and high-volume manufacturing. TSMC's extensive global presence includes fabs and offices in Taiwan, the United States, China, and Europe, supporting a broad customer base across various technology sectors. UMC maintains a smaller but strategic footprint mainly in Taiwan, with expansions focusing on mature nodes for automotive, consumer electronics, and industrial applications.
Technology Leadership and Process Nodes
TSMC dominates the semiconductor industry with its advanced process nodes, leading the market at 3nm technology and pioneering research on 2nm nodes, while UMC primarily focuses on mature nodes like 28nm and 14nm, targeting cost-effective manufacturing solutions. TSMC's technology leadership is reinforced by its extensive R&D investments and collaboration with major tech companies, enabling higher transistor densities and better power efficiency compared to UMC's more specialized and volume-driven approach. This strategic focus allows TSMC to support cutting-edge applications in AI, 5G, and high-performance computing, whereas UMC serves the demand for reliable, mid-range semiconductor products.
Key Customers and Partnerships
TSMC's key customers include tech giants like Apple, AMD, and NVIDIA, leveraging advanced semiconductor manufacturing for cutting-edge devices. UMC primarily serves companies such as MediaTek and Novatek, focusing on mature process technologies suited for diverse applications. Your choice between TSMC and UMC depends on the specific technological needs and partnership alignments within the semiconductor ecosystem.
Financial Performance Comparison
TSMC consistently outperforms UMC in financial metrics, with a 2023 revenue exceeding $75 billion compared to UMC's approximately $6 billion. TSMC's gross margin remains robust at around 53%, while UMC's gross margin hovers near 30%, reflecting stronger operational efficiency. The market capitalization disparity highlights TSMC's dominant industry position, valued at over $450 billion versus UMC's $15 billion.
Innovation and R&D Investments
TSMC leads the semiconductor industry with its substantial R&D investments, allocating over $5 billion annually to develop advanced process technologies such as 3nm and 2nm nodes, driving innovation in chip performance and energy efficiency. UMC, while investing less in R&D, focuses on mature nodes and specialty processes, targeting cost-effective solutions and niche markets. TSMC's aggressive innovation strategy has established it as a technological frontrunner, outperforming UMC in advanced semiconductor fabrication capabilities.
Sustainability and ESG Initiatives
TSMC leads the semiconductor industry with robust sustainability practices, including achieving carbon neutrality in its operations by 2050 and investing in renewable energy projects to reduce its environmental footprint. UMC emphasizes responsible water management and waste reduction, implementing advanced recycling technologies and transparent ESG reporting to enhance its corporate responsibility. Your choice between TSMC and UMC may reflect preferences for cutting-edge environmental commitments or practical sustainability measures within semiconductor manufacturing.
Future Outlook for TSMC vs UMC
TSMC leads the semiconductor foundry market with advanced 3nm and 2nm process nodes, positioning it strongly for future demand in high-performance computing and AI applications. UMC focuses on mature nodes like 28nm and 14nm, targeting stable growth in automotive and IoT sectors but faces challenges in scaling to cutting-edge technologies. TSMC's aggressive R&D investments and strategic partnerships with major tech firms ensure a robust growth trajectory, whereas UMC's emphasis on specialized applications offers steady but limited expansion opportunities.
TSMC vs UMC Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com