Die attach provides a robust mechanical and thermal connection by bonding the semiconductor die directly to the substrate, enhancing heat dissipation and reliability in high-power applications. You'll discover in the rest of the article how wire bonding offers flexible interconnections for complex circuit designs and why selecting between the two depends on your specific device requirements.
Table of Comparison
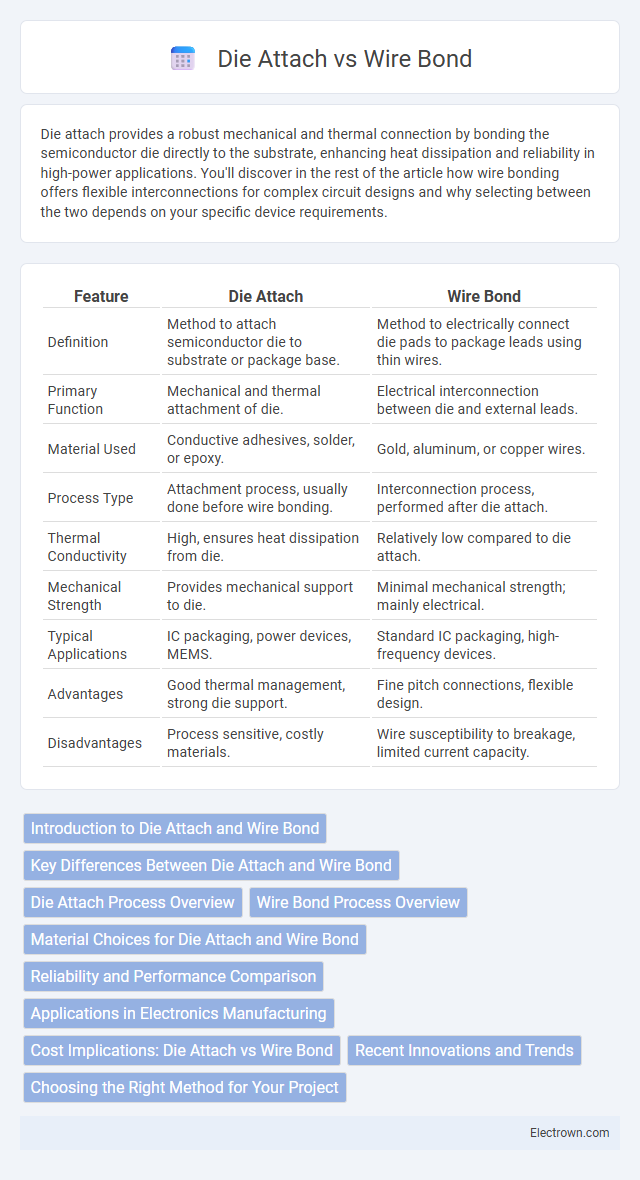
| Feature | Die Attach | Wire Bond |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Method to attach semiconductor die to substrate or package base. | Method to electrically connect die pads to package leads using thin wires. |
| Primary Function | Mechanical and thermal attachment of die. | Electrical interconnection between die and external leads. |
| Material Used | Conductive adhesives, solder, or epoxy. | Gold, aluminum, or copper wires. |
| Process Type | Attachment process, usually done before wire bonding. | Interconnection process, performed after die attach. |
| Thermal Conductivity | High, ensures heat dissipation from die. | Relatively low compared to die attach. |
| Mechanical Strength | Provides mechanical support to die. | Minimal mechanical strength; mainly electrical. |
| Typical Applications | IC packaging, power devices, MEMS. | Standard IC packaging, high-frequency devices. |
| Advantages | Good thermal management, strong die support. | Fine pitch connections, flexible design. |
| Disadvantages | Process sensitive, costly materials. | Wire susceptibility to breakage, limited current capacity. |
Introduction to Die Attach and Wire Bond
Die Attach and Wire Bond are critical semiconductor packaging processes that establish electrical and mechanical connections between the die and the package substrate. Die Attach secures the semiconductor die onto the lead frame or substrate using adhesives or solder, ensuring thermal conductivity and mechanical stability. Wire Bond creates fine electrical interconnections between the die pads and package leads, enabling signal transmission within integrated circuits.
Key Differences Between Die Attach and Wire Bond
Die attach provides a mechanical and thermal connection by adhering the semiconductor die to the substrate, ensuring efficient heat dissipation and structural support. Wire bond, on the other hand, focuses on establishing electrical connections between the die pads and the package leads using fine wires such as gold or aluminum. Your selection between die attach and wire bond depends on factors like thermal management, electrical performance, and production complexity.
Die Attach Process Overview
The die attach process secures the semiconductor die to the substrate or lead frame using conductive adhesives, solder, or epoxy materials, ensuring mechanical stability and thermal conductivity. This step is crucial for maintaining reliable electrical performance and heat dissipation in electronic packages. Your choice between die attach and wire bond impacts overall device assembly, affecting signal integrity and packaging density.
Wire Bond Process Overview
Wire bond process involves creating electrical interconnections between a semiconductor die and its package using fine wires, typically gold, aluminum, or copper. Ultrasonic energy, heat, and pressure are applied to form metallurgical bonds at the bond pads on the die surface and the lead frame or substrate. This method provides flexibility for complex circuit layouts and is widely used in microelectronic packaging for its reliability and cost-effectiveness compared to die attach techniques.
Material Choices for Die Attach and Wire Bond
Die attach materials typically include silver-filled epoxies, solder alloys, and conductive adhesives, chosen for their excellent thermal conductivity and strong mechanical bonding properties. Wire bond materials predominantly utilize gold, aluminum, and copper wires, selected for their superior electrical conductivity, ductility, and reliable bond formation with semiconductor pads. Material selection critically influences overall device performance, thermal management, and long-term reliability in semiconductor packaging.
Reliability and Performance Comparison
Die attach offers superior thermal conductivity and mechanical stability, enhancing the reliability of high-power and high-frequency semiconductor devices. Wire bonding provides flexibility and cost-effectiveness but may introduce higher resistance and inductance, impacting performance in ultra-high-speed applications. Your choice between die attach and wire bond should consider the specific reliability and performance requirements of your electronic assembly.
Applications in Electronics Manufacturing
Die attach methods provide robust mechanical support and efficient thermal conduction for power devices and high-performance integrated circuits in electronics manufacturing. Wire bonding is widely used for connecting semiconductor dies to package leads in microelectronics due to its flexibility and cost-effectiveness for high-volume production. Both techniques are essential in assembling sensors, automotive electronics, and consumer devices, with die attach preferred for heat dissipation and wire bonding for intricate signal routing.
Cost Implications: Die Attach vs Wire Bond
Die attach typically incurs higher upfront costs due to specialized materials and equipment, but it offers enhanced reliability and thermal performance that can reduce long-term expenses. Wire bonding is generally more cost-effective for low to medium volume production because of its simpler process and lower material costs. Choosing between die attach and wire bond depends on balancing initial investment against application-specific requirements and lifecycle cost savings.
Recent Innovations and Trends
Recent innovations in die attach technology emphasize advanced thermally conductive adhesives and precision laser soldering, boosting heat dissipation and mechanical reliability in semiconductor packages. Wire bond methods see trends in ultra-fine gold and copper wire development, improving electrical performance and enabling finer pitch connections for compact device designs. Both techniques integrate automation and AI-driven quality control to enhance production efficiency and consistency in high-volume manufacturing.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Project
Die attach offers superior thermal conductivity and mechanical stability, making it ideal for high-power or high-reliability applications. Wire bond provides flexibility and cost-effectiveness, suited for complex circuit designs with multiple interconnections. Consider your project's electrical performance, production volume, and budget to determine whether die attach or wire bond best meets your specific needs.
Die Attach vs Wire Bond Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com