LDO regulators provide simple, low-noise voltage regulation with minimal external components, ideal for low-dropout applications requiring clean power. Switching regulators offer higher efficiency and better heat dissipation for higher power conversions, making them suitable for battery-operated or high-current devices; explore the article to determine which regulator best fits your design needs.
Table of Comparison
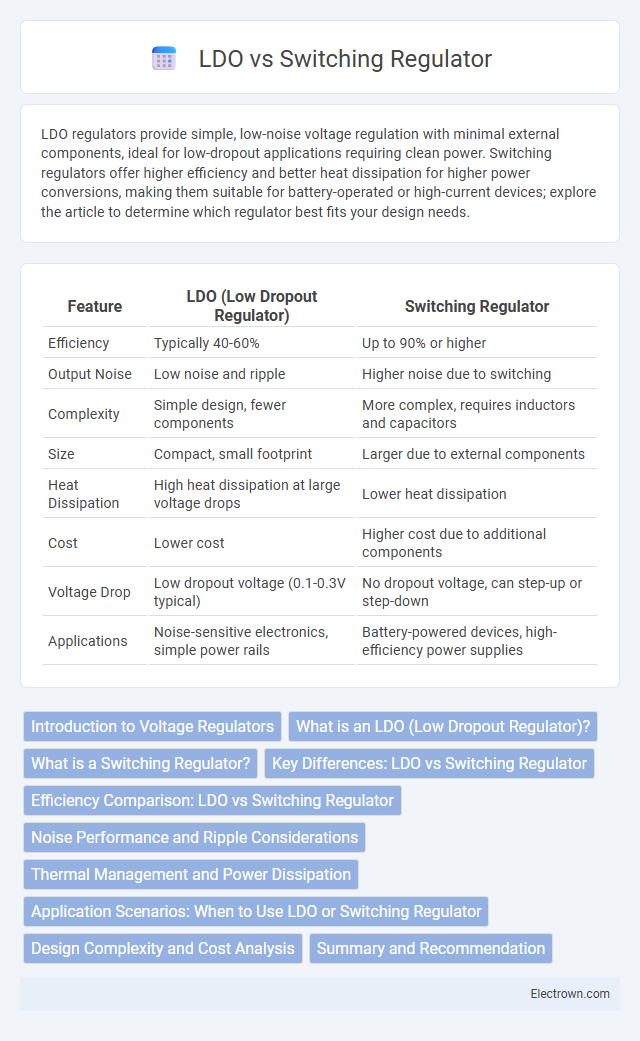
| Feature | LDO (Low Dropout Regulator) | Switching Regulator |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | Typically 40-60% | Up to 90% or higher |
| Output Noise | Low noise and ripple | Higher noise due to switching |
| Complexity | Simple design, fewer components | More complex, requires inductors and capacitors |
| Size | Compact, small footprint | Larger due to external components |
| Heat Dissipation | High heat dissipation at large voltage drops | Lower heat dissipation |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to additional components |
| Voltage Drop | Low dropout voltage (0.1-0.3V typical) | No dropout voltage, can step-up or step-down |
| Applications | Noise-sensitive electronics, simple power rails | Battery-powered devices, high-efficiency power supplies |
Introduction to Voltage Regulators
Voltage regulators maintain a constant output voltage despite variations in input voltage or load conditions, ensuring stable power supply for electronic devices. LDO (Low Dropout) regulators provide a simple, low-noise solution with minimal voltage dropout, ideal for low voltage difference applications. Switching regulators offer higher efficiency by converting voltage through inductors and capacitors, making them suitable for applications requiring significant voltage drops or current.
What is an LDO (Low Dropout Regulator)?
An LDO (Low Dropout Regulator) is a type of linear voltage regulator designed to operate with a very small input-output voltage differential, typically less than 0.3 volts. It efficiently provides a stable, low-noise output voltage by dissipating excess voltage as heat, making it ideal for noise-sensitive analog and RF circuits. Your choice between an LDO and a switching regulator depends on factors like power efficiency, output noise, and voltage differentials required in your application.
What is a Switching Regulator?
A Switching Regulator is a power supply device that efficiently converts electrical energy by rapidly switching its internal components between on and off states, regulating voltage through inductors, capacitors, and diodes. It offers high efficiency, especially for applications requiring significant voltage step-up, step-down, or inversion, making it ideal for battery-powered and energy-sensitive systems. Your design choices will benefit from considering the reduced heat dissipation and extended battery life provided by Switching Regulators compared to Linear Dropout Regulators (LDOs).
Key Differences: LDO vs Switching Regulator
LDO (Low Dropout) regulators provide simple, low-noise voltage regulation with high efficiency at low voltage differentials, ideal for sensitive analog circuits and low power applications. Switching regulators convert power through inductors and capacitors, offering higher efficiency across a broader input voltage range but generating more electromagnetic interference (EMI). Your choice depends on the priority between noise sensitivity, efficiency, and input voltage variation in your power supply design.
Efficiency Comparison: LDO vs Switching Regulator
Switching regulators offer significantly higher efficiency, often between 80% to 95%, by converting input voltage through high-frequency switching, which reduces power loss. Low Dropout Regulators (LDOs) typically exhibit lower efficiency, especially when the input voltage far exceeds the output voltage, because they dissipate excess voltage as heat. When optimizing your power supply, choosing a switching regulator can greatly improve energy efficiency and thermal management compared to an LDO.
Noise Performance and Ripple Considerations
LDO regulators typically offer superior noise performance and lower output ripple compared to switching regulators, making them ideal for noise-sensitive analog and RF circuits. Switching regulators, while more efficient, generate higher ripple and electromagnetic interference (EMI) due to their switching frequency and inductor current variations. When designing your power supply, carefully consider the noise and ripple requirements of your application to choose between the clean output of an LDO or the efficiency benefits of a switching regulator.
Thermal Management and Power Dissipation
LDO regulators generate more heat due to linear voltage drop, necessitating effective thermal management solutions like heat sinks or thermal pads to prevent overheating in your designs. Switching regulators, with higher efficiency and lower power dissipation, reduce thermal stress and often require smaller or fewer thermal management components. Choosing between LDO and switching regulators depends on your system's power dissipation limits and thermal handling capabilities.
Application Scenarios: When to Use LDO or Switching Regulator
LDO regulators are ideal for low-noise, low-dropout voltage applications such as sensitive analog circuits or battery-powered devices requiring minimal voltage ripple. Switching regulators excel in high-efficiency power conversion scenarios, especially when stepping down from higher voltages or supplying high-current loads. Your choice depends on the importance of power efficiency versus noise sensitivity and the available input-output voltage differential.
Design Complexity and Cost Analysis
LDO regulators offer a simpler design with fewer external components, resulting in lower overall costs and easier implementation for low-noise applications. Switching regulators, while more complex due to inductors, diodes, and feedback loops, provide higher efficiency and better performance in power management but increase design time and expenses. Your choice depends on balancing the cost benefits of LDO simplicity against the efficiency gains and design complexity of switching regulators.
Summary and Recommendation
LDO (Low Dropout Regulator) offers simplicity, low noise output, and efficient performance in low voltage difference scenarios, making it ideal for noise-sensitive analog circuits and battery-powered devices. Switching regulators provide higher efficiency over a wide range of input voltages and output loads, suitable for high-power applications and systems requiring heat dissipation management. For cost-sensitive designs with minimal power loss, choose LDOs; for energy-critical or high-current applications, switching regulators deliver superior efficiency and thermal performance.
LDO vs Switching Regulator Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com