Split-rail power supplies provide both positive and negative voltages relative to a common ground, ideal for powering analog circuits requiring dual polarity. Understanding the differences between split-rail and single-rail supplies can help you choose the right option for your electronics project; continue reading to explore their specific applications and benefits.
Table of Comparison
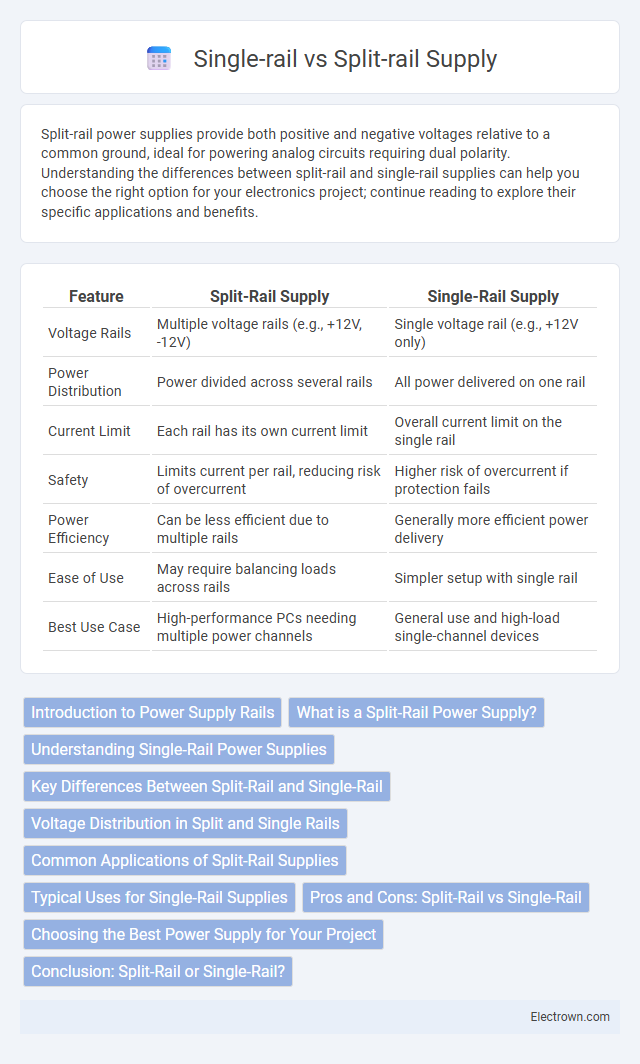
| Feature | Split-Rail Supply | Single-Rail Supply |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Rails | Multiple voltage rails (e.g., +12V, -12V) | Single voltage rail (e.g., +12V only) |
| Power Distribution | Power divided across several rails | All power delivered on one rail |
| Current Limit | Each rail has its own current limit | Overall current limit on the single rail |
| Safety | Limits current per rail, reducing risk of overcurrent | Higher risk of overcurrent if protection fails |
| Power Efficiency | Can be less efficient due to multiple rails | Generally more efficient power delivery |
| Ease of Use | May require balancing loads across rails | Simpler setup with single rail |
| Best Use Case | High-performance PCs needing multiple power channels | General use and high-load single-channel devices |
Introduction to Power Supply Rails
Power supply rails serve as the voltage sources that power different components within an electronic circuit, with single-rail supplies providing one voltage level, while split-rail supplies offer both positive and negative voltages relative to a common ground. Split-rail configurations enable better handling of analog signals and improved noise performance, making them ideal for operational amplifiers and audio equipment. Your choice between split-rail and single-rail supplies depends on the specific voltage and signal requirements of your design for optimal system performance.
What is a Split-Rail Power Supply?
A split-rail power supply provides both positive and negative voltage rails relative to a common ground, enabling circuits to operate with dual polarities, such as +-12V. This design contrasts with single-rail power supplies, which offer only one positive voltage output referenced to ground. Split-rail supplies are essential in applications like analog signal processing or operational amplifiers, where balanced voltage rails improve performance and reduce noise.
Understanding Single-Rail Power Supplies
Single-rail power supplies provide a single source of voltage output, delivering consistent power to all components without multiple voltage rails. This configuration simplifies power distribution and often enhances system stability by ensuring your computer or device receives a steady, unified current. Understanding single-rail power supplies helps you choose reliable power solutions optimized for continuous performance and ease of troubleshooting.
Key Differences Between Split-Rail and Single-Rail
Split-rail power supplies provide separate positive and negative voltage rails, typically +12V and -12V, allowing precise control over bipolar circuits and reducing noise interference. Single-rail supplies offer a single positive voltage output, such as +12V, delivering the entire current capacity through one rail, which simplifies power distribution but can lead to uneven current draw. Your choice depends on application needs; split-rail is preferred for audio and analog circuits requiring symmetric voltages, while single-rail suits systems needing high current on one voltage rail.
Voltage Distribution in Split and Single Rails
Split-rail power supplies provide separate positive and negative voltage rails, typically +12V and -12V, facilitating balanced voltage distribution across components requiring dual polarity. Single-rail power supplies deliver a single positive voltage, usually +12V, distributing current from one rail to all connected devices, which can simplify design but may lead to uneven load and voltage drops. Your choice affects voltage stability and noise performance, as split rails isolate voltage paths while single rails offer uniform voltage but require careful load management.
Common Applications of Split-Rail Supplies
Split-rail power supplies are commonly used in audio equipment, operational amplifiers, and analog circuits requiring both positive and negative voltages to ensure proper signal processing and noise reduction. These supplies provide balanced dual voltages, which help in maintaining signal integrity in sensitive electronics and instrumentation applications. Your design will benefit from split-rail supplies when needing symmetrical power rails for precise analog performance.
Typical Uses for Single-Rail Supplies
Single-rail power supplies are commonly used in gaming PCs, overclocking setups, and high-performance computing due to their ability to deliver consistent voltage and simplified cable management. These supplies provide a single 12V rail with high amperage, ensuring stable power delivery to components such as CPUs and GPUs under heavy load. Their design reduces the risk of overloaded rails, making them ideal for systems requiring reliable and straightforward power distribution.
Pros and Cons: Split-Rail vs Single-Rail
Split-rail power supplies offer multiple voltage rails, which can improve safety and reduce the risk of overloading by distributing current across separate outputs, but require careful balancing to avoid uneven load distribution. Single-rail power supplies provide a single, high-current output that simplifies installation and maximizes power availability for high-demand components, though they may pose increased risk of power spikes and less granular control over power allocation. Choosing between split-rail and single-rail depends on the specific power needs, with split-rail favored for stability and protection, and single-rail preferred for simplicity and maximum power delivery.
Choosing the Best Power Supply for Your Project
When selecting between split-rail and single-rail power supplies, consider your project's voltage and current requirements. Split-rail supplies provide multiple output voltages, typically positive, negative, and ground rails, ideal for analog circuitry and operational amplifiers requiring symmetric power. Single-rail supplies deliver a single output voltage, offering simplicity and higher current capacity, suitable for digital circuits and devices with straightforward power needs.
Conclusion: Split-Rail or Single-Rail?
Split-rail power supplies provide both positive and negative voltages, ideal for applications requiring bipolar power such as analog circuits and operational amplifiers. Single-rail supplies offer a simpler design with only positive voltage, suitable for most digital and low-power devices, reducing complexity and cost. Your choice depends on the specific voltage requirements and circuit design constraints, with split-rail preferred for balanced dual-voltage needs and single-rail favored for straightforward, unipolar power demands.
Split-rail vs Single-rail Supply Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com