Shielded vias offer improved electromagnetic interference (EMI) protection and signal integrity by enclosing the via in a grounded shield, making them essential for high-frequency PCB designs. Understanding the differences between shielded and unshielded vias will help you optimize your circuit's performance in the following article.
Table of Comparison
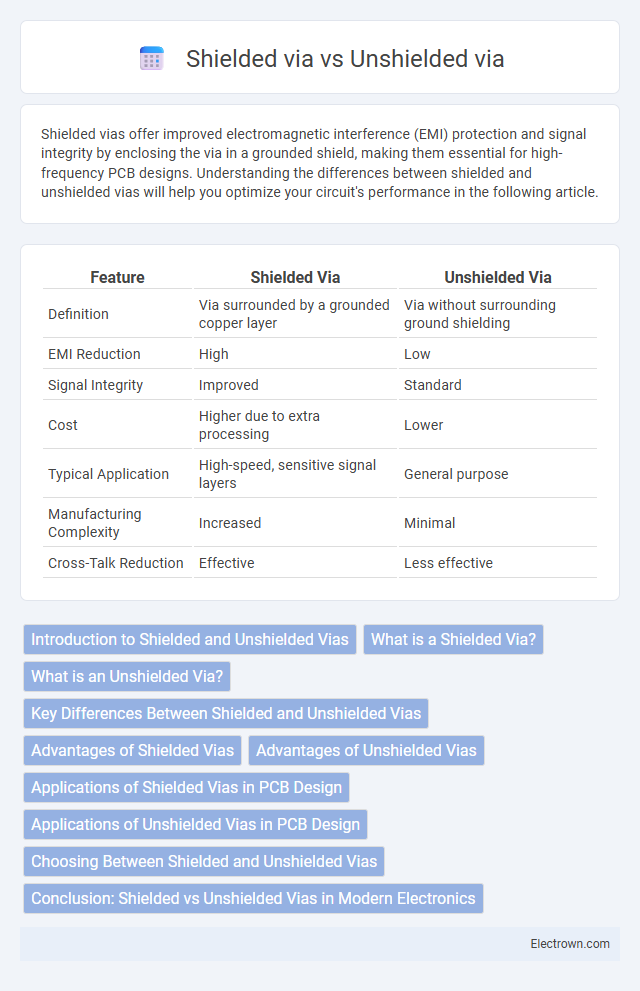
| Feature | Shielded Via | Unshielded Via |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Via surrounded by a grounded copper layer | Via without surrounding ground shielding |
| EMI Reduction | High | Low |
| Signal Integrity | Improved | Standard |
| Cost | Higher due to extra processing | Lower |
| Typical Application | High-speed, sensitive signal layers | General purpose |
| Manufacturing Complexity | Increased | Minimal |
| Cross-Talk Reduction | Effective | Less effective |
Introduction to Shielded and Unshielded Vias
Shielded vias are plated through holes in printed circuit boards (PCBs) surrounded by a grounded conductive layer, reducing electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk in high-frequency applications. Unshielded vias lack this protective layer, making them simpler but more susceptible to noise and signal integrity issues in densely packed or high-speed circuits. The choice between shielded and unshielded vias impacts PCB performance, especially in RF and high-speed digital designs where EMI control is critical.
What is a Shielded Via?
A shielded via is a plated through-hole in a printed circuit board (PCB) surrounded by a grounded copper shield to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and signal crosstalk. Your circuit benefits from improved signal integrity and reduced noise in high-frequency applications when using shielded vias compared to unshielded vias, which lack such protective grounding. This shielding is crucial in sensitive RF or high-speed digital designs where maintaining signal quality is paramount.
What is an Unshielded Via?
An unshielded via is a simple plated-through hole on a printed circuit board (PCB) that electrically connects different layers without any additional shielding. Unlike shielded vias, it lacks protective conductive rings or grounded barriers to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI). Your PCB design may use unshielded vias for straightforward inter-layer connections where signal integrity and EMI are less critical.
Key Differences Between Shielded and Unshielded Vias
Shielded vias incorporate a grounded shielding layer around the via to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk, enhancing signal integrity in high-frequency circuit designs. Unshielded vias lack this protective shielding, making them more susceptible to noise and signal degradation but generally less costly and easier to manufacture. Understanding these key differences helps you optimize PCB designs for performance requirements and cost efficiency.
Advantages of Shielded Vias
Shielded vias provide superior electromagnetic interference (EMI) protection by enclosing the via with a grounded copper shield, reducing crosstalk and signal loss in high-frequency PCB designs. They enhance signal integrity and minimize noise coupling, which is critical in sensitive analog and RF circuits. Your PCB's performance and reliability improve significantly when using shielded vias, especially in complex multilayer boards.
Advantages of Unshielded Vias
Unshielded vias offer the advantage of reduced manufacturing complexity and lower production costs compared to shielded vias, making them ideal for high-volume PCB fabrication. They also provide adequate electrical isolation in many standard applications, minimizing the need for extra shielding in low-frequency or low-noise environments. Their simpler design allows for greater routing flexibility and easier inspection during quality control.
Applications of Shielded Vias in PCB Design
Shielded vias are primarily used in high-frequency PCB designs to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk by enclosing signal vias within a grounded shield layer. These vias are critical in RF and microwave circuits, ensuring signal integrity and enhancing overall performance by reducing noise coupling between adjacent layers. Your PCB designs benefit from shielded vias when implementing sensitive analog, high-speed digital, or mixed-signal applications requiring superior noise suppression.
Applications of Unshielded Vias in PCB Design
Unshielded vias in PCB design are widely used for signal routing in multi-layer boards where cost and manufacturing simplicity are priorities. These vias connect different layers without additional shielding, making them suitable for low-frequency signal transmission and power planes separation. Their applications include general-purpose PCBs in consumer electronics, where electromagnetic interference is minimal, reducing the need for complex shielding techniques.
Choosing Between Shielded and Unshielded Vias
Choosing between shielded and unshielded vias depends largely on your PCB design requirements, such as signal integrity and electromagnetic interference (EMI) control. Shielded vias provide enhanced protection against EMI by surrounding the via with grounded metal layers, making them ideal for high-frequency or sensitive signal paths. Unshielded vias are simpler in construction and cost-effective, suitable for general applications where EMI concerns are minimal.
Conclusion: Shielded vs Unshielded Vias in Modern Electronics
Shielded vias provide enhanced electromagnetic interference (EMI) protection and signal integrity, making them ideal for high-frequency, high-speed PCB designs. Unshielded vias, while cost-effective and simpler to manufacture, may introduce crosstalk and signal degradation in complex circuits. Your choice between shielded and unshielded vias should consider performance requirements, manufacturing costs, and the overall electromagnetic environment of your electronic design.
Shielded via vs Unshielded via Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com