A Bias Tee allows DC power to be injected into an RF line without affecting signal transmission, while a DC Block prevents DC current from passing through an RF circuit, protecting sensitive components. Understanding these critical differences can enhance Your signal integrity and system performance; read on to learn how each device suits specific applications.
Table of Comparison
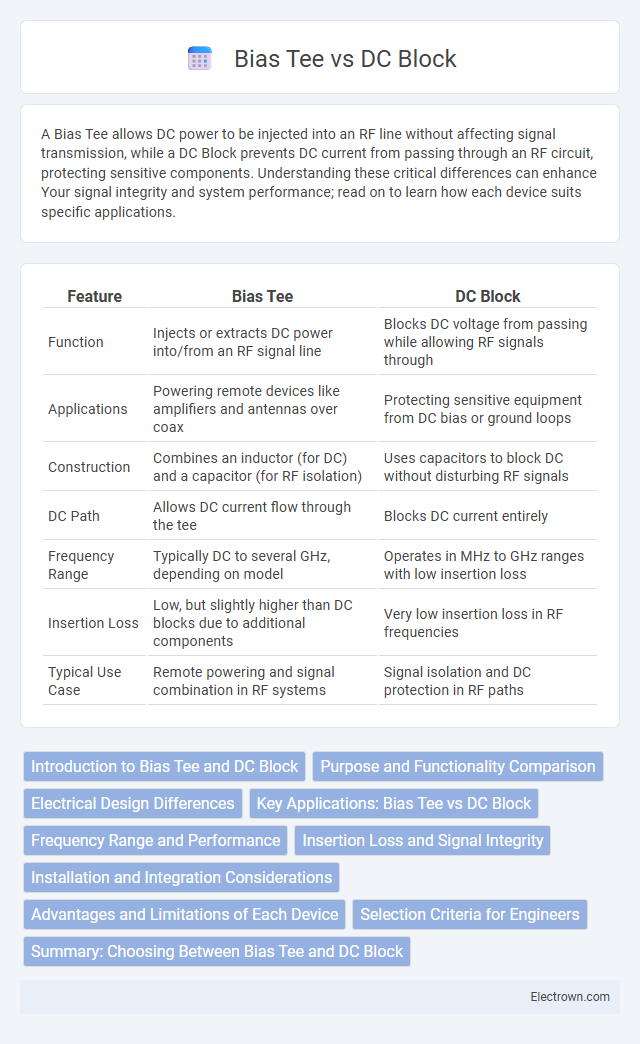
| Feature | Bias Tee | DC Block |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Injects or extracts DC power into/from an RF signal line | Blocks DC voltage from passing while allowing RF signals through |
| Applications | Powering remote devices like amplifiers and antennas over coax | Protecting sensitive equipment from DC bias or ground loops |
| Construction | Combines an inductor (for DC) and a capacitor (for RF isolation) | Uses capacitors to block DC without disturbing RF signals |
| DC Path | Allows DC current flow through the tee | Blocks DC current entirely |
| Frequency Range | Typically DC to several GHz, depending on model | Operates in MHz to GHz ranges with low insertion loss |
| Insertion Loss | Low, but slightly higher than DC blocks due to additional components | Very low insertion loss in RF frequencies |
| Typical Use Case | Remote powering and signal combination in RF systems | Signal isolation and DC protection in RF paths |
Introduction to Bias Tee and DC Block
Bias Tee is a three-port network device used to inject DC power into an RF signal line without disrupting signal integrity, enabling simultaneous transmission of power and RF signals. DC Block is a passive component designed to prevent DC current flow while allowing AC or RF signals to pass, protecting circuits from unwanted DC interference. Both devices play crucial roles in RF systems by managing DC and RF signals but serve distinct functions: Bias Tee combines DC and RF, whereas DC Block separates or isolates DC components.
Purpose and Functionality Comparison
A Bias Tee is designed to inject DC power into an RF signal without disrupting the RF path, facilitating simultaneous power and signal transmission over a single coaxial cable. In contrast, a DC Block prevents DC current from passing through while allowing RF signals to pass, protecting sensitive equipment from unwanted DC voltages. Both components serve complementary roles in RF systems, with Bias Tees enabling power feeding and DC Blocks providing isolation and protection.
Electrical Design Differences
Bias tees incorporate an inductor and a capacitor to combine or separate DC and RF signals, allowing DC power to pass through the inductor while blocking RF frequencies. DC blocks use capacitors to prevent DC current flow while allowing RF signals to pass unimpeded. The electrical design difference lies in the bias tee's ability to inject or extract DC voltage alongside RF signals, unlike the DC block which solely isolates DC components from RF circuits.
Key Applications: Bias Tee vs DC Block
Bias Tee is commonly used in RF circuits to inject DC power into an RF signal line without disrupting the signal, making it essential for powering remote devices like amplifiers and antennas. DC Blocks serve to prevent DC current flow while allowing high-frequency signals to pass, protecting sensitive equipment from unwanted DC voltages in communication systems. Your choice between Bias Tee and DC Block depends on whether you need to supply power to a device remotely or isolate DC currents for signal integrity and equipment safety.
Frequency Range and Performance
Bias Tees typically operate efficiently across a broad frequency range, from a few kHz up to several GHz, enabling simultaneous injection of DC voltage and RF signals without significant signal loss. DC Blocks are designed to eliminate DC components while allowing RF signals to pass, often covering a similar frequency span from MHz to several GHz, but with minimal insertion loss and high isolation to prevent DC leakage. Performance-wise, Bias Tees offer effective DC biasing with low insertion loss and high isolation, whereas DC Blocks provide superior DC isolation and maintain signal integrity by blocking unwanted DC currents in RF paths.
Insertion Loss and Signal Integrity
Bias Tees exhibit minimal insertion loss, typically less than 1 dB, preserving signal integrity by allowing DC power and RF signals to coexist without significant degradation. DC Blocks prevent DC current flow while maintaining low insertion loss, generally around 0.2 to 0.5 dB, ensuring that high-frequency signals pass with minimal distortion. Understanding the insertion loss differences between Bias Tees and DC Blocks is crucial for optimizing your RF system's signal quality and overall performance.
Installation and Integration Considerations
Bias Tee installation requires careful integration to ensure proper DC voltage injection without disrupting RF signals, often involving compact PCB mounting and coaxial connectors compatible with high-frequency transmission lines. DC Block integration focuses on preventing DC current flow while maintaining signal integrity, necessitating precise placement in RF paths and compatibility with characteristic impedance to avoid signal reflection or loss. Both devices must be selected and installed based on frequency range, power handling, and system grounding to achieve optimal performance in RF applications.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Device
Bias Tees allow simultaneous transmission of AC signals and DC power over a single coaxial cable, enhancing system simplicity and reducing wiring complexity. DC Blocks prevent DC current flow while passing RF signals, protecting sensitive equipment from DC-induced damage but requiring separate power lines. Your choice depends on whether you need combined power and signal delivery or isolation from DC components to safeguard device integrity.
Selection Criteria for Engineers
Engineers select a Bias Tee when they need to combine DC power with RF signals in a single coaxial line, ensuring efficient power delivery without signal degradation. A DC Block is chosen to prevent DC current from passing into sensitive RF components, protecting circuits from potential damage or interference. Your choice depends on whether power injection or DC isolation is critical in your RF system design.
Summary: Choosing Between Bias Tee and DC Block
Bias Tee allows simultaneous transmission of DC power and RF signals through a single coaxial cable by combining them, making it ideal for powering remote devices like antennas or amplifiers without interrupting the RF path. DC Block, on the other hand, prevents DC current from passing while allowing RF signals to flow, protecting equipment from unwanted DC voltage or potential ground loops. Your choice depends on whether you need to inject power into the RF line (use Bias Tee) or isolate DC voltage for safety and signal integrity (use DC Block).
Bias Tee vs DC Block Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com