A Gummel plot provides a detailed analysis of a bipolar transistor's current gain by graphing the base and collector currents against the base-emitter voltage, while the transfer characteristic describes the relationship between the output current and input voltage, highlighting device performance under operational conditions. Understanding these differences helps you select the appropriate method to analyze transistor behavior effectively; read on to explore the nuances and applications of both techniques.
Table of Comparison
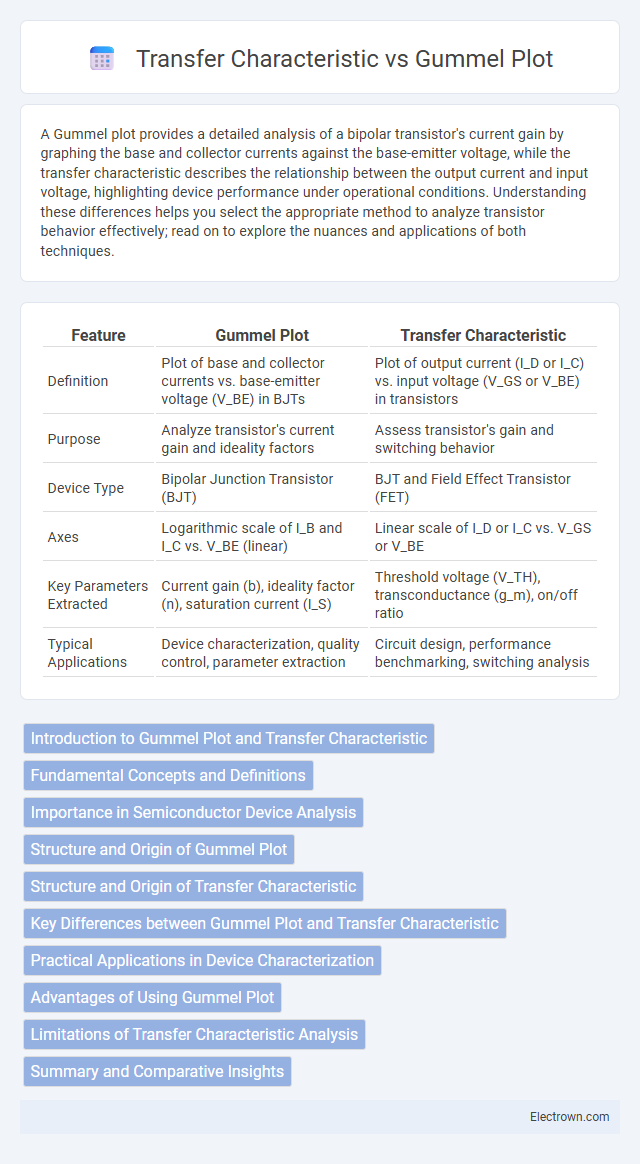
| Feature | Gummel Plot | Transfer Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Plot of base and collector currents vs. base-emitter voltage (V_BE) in BJTs | Plot of output current (I_D or I_C) vs. input voltage (V_GS or V_BE) in transistors |
| Purpose | Analyze transistor's current gain and ideality factors | Assess transistor's gain and switching behavior |
| Device Type | Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) | BJT and Field Effect Transistor (FET) |
| Axes | Logarithmic scale of I_B and I_C vs. V_BE (linear) | Linear scale of I_D or I_C vs. V_GS or V_BE |
| Key Parameters Extracted | Current gain (b), ideality factor (n), saturation current (I_S) | Threshold voltage (V_TH), transconductance (g_m), on/off ratio |
| Typical Applications | Device characterization, quality control, parameter extraction | Circuit design, performance benchmarking, switching analysis |
Introduction to Gummel Plot and Transfer Characteristic
The Gummel plot is a graphical representation used in semiconductor device analysis to visualize the base and collector currents as functions of the base-emitter voltage in a bipolar junction transistor (BJT). Transfer characteristics describe the relationship between input and output signals, typically showcasing how the collector current varies with the base current in a BJT. Understanding both the Gummel plot and transfer characteristic is essential for analyzing transistor behavior and optimizing your circuit performance.
Fundamental Concepts and Definitions
Gummel Plot and Transfer Characteristic are essential tools for analyzing bipolar junction transistor (BJT) behavior, with the Gummel Plot representing the logarithmic current versus base-emitter voltage, highlighting transistor gain and leakage currents. The Transfer Characteristic graph directly relates output current to input voltage or current, emphasizing linearity and device switching performance. Understanding these fundamental concepts enables you to optimize transistor models for circuit design and performance evaluation.
Importance in Semiconductor Device Analysis
Gummel plots provide critical insight into the current-voltage behavior of bipolar junction transistors by separately characterizing the base and collector currents, enabling precise extraction of key parameters such as ideality factors and saturation currents. Transfer characteristics, depicting the relationship between input voltage and output current, are essential for evaluating device gain and linearity in field-effect transistors and other semiconductor components. Together, these analyses form the foundation for optimizing semiconductor device performance, ensuring accurate modeling and stable circuit design.
Structure and Origin of Gummel Plot
The Gummel plot graphically represents the base and collector currents of a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) as a function of the base-emitter voltage, revealing the transistor's charge transport phenomena and recombination processes. Its structure originates from the exponential increase of the base current and the collector current in forward-active operation, providing key insights into current components like diffusion and recombination currents within the base region. Unlike the transfer characteristic, which depicts the output current versus input current or voltage directly, the Gummel plot is essential for extracting fundamental device parameters such as ideality factors, saturation currents, and recombination coefficients.
Structure and Origin of Transfer Characteristic
The Gummel plot represents the relationship between the base current and collector current as a function of base-emitter voltage in bipolar junction transistors, emphasizing the exponential increase due to carrier injection and recombination processes. Transfer characteristics detail the current gain (b) behavior by plotting collector current against base current, reflecting the transistor's amplification capability originating from charge transport mechanisms in the base region. These characteristics arise from the transistor's layered semiconductor structure, where the interaction of emitter injection efficiency and base transport factor defines the overall transfer behavior.
Key Differences between Gummel Plot and Transfer Characteristic
The Gummel Plot characterizes the relationship between base-emitter voltage and both base and collector currents in bipolar junction transistors, emphasizing current gain and device behavior under forward-active conditions. Transfer Characteristic, on the other hand, describes the output current as a function of input voltage or current, highlighting transistor switching and amplification properties. Key differences include the type of displayed parameters--current-voltage curves in Gummel Plots versus input-output transfer functions--and the focus on device physics versus operational performance metrics.
Practical Applications in Device Characterization
Gummel plots are essential for extracting transistor parameters such as ideality factors and saturation currents, which provide detailed insight into device physics and recombination mechanisms in bipolar junction transistors (BJTs). Transfer characteristics, representing drain current versus gate voltage in field-effect transistors (FETs), are crucial for evaluating threshold voltage, transconductance, and device switching behavior. Both techniques are widely used in semiconductor device characterization to improve circuit design and optimize transistor performance in integrated circuits.
Advantages of Using Gummel Plot
The Gummel plot provides a detailed insight into the transistor's base and collector current behavior over a range of base-emitter voltages, enabling precise parameter extraction such as current gain and ideality factor. Unlike transfer characteristics, the Gummel plot separates the currents, making it easier to identify non-idealities and recombination effects within the device. Using a Gummel plot helps you accurately model transistor performance and improve design optimization in analog and digital circuit applications.
Limitations of Transfer Characteristic Analysis
Transfer characteristic analysis often falls short in providing detailed insights into transistor behavior under varying bias conditions, limiting its effectiveness for comprehensive device modeling. The Gummel plot complements this by depicting current components as functions of base-emitter voltage, enabling detection of non-idealities such as high injection effects and recombination currents that transfer characteristics may overlook. Understanding these limitations helps you achieve more accurate parameter extraction and improved transistor performance evaluation.
Summary and Comparative Insights
The Gummel plot and transfer characteristic provide crucial insights into bipolar junction transistor (BJT) performance, with the Gummel plot illustrating the relationship between base-emitter voltage and collector current on a semi-log scale, emphasizing current gain and recombination effects. In contrast, the transfer characteristic displays the collector current as a function of base current, highlighting the transistor's current amplification behavior and linear region operation. Comparing both, the Gummel plot excels in detailed diode junction analysis, while the transfer characteristic offers straightforward interpretation of transistor gain and switching behavior in circuit applications.
Gummel Plot vs Transfer Characteristic Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com