CWDM (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing) and DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) differ primarily in channel spacing and capacity, with CWDM supporting fewer channels over shorter distances at a lower cost, while DWDM offers higher channel density and longer reach suitable for carrier-grade networks. Discover how choosing between CWDM and DWDM can impact your fiber optic network's performance and scalability by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
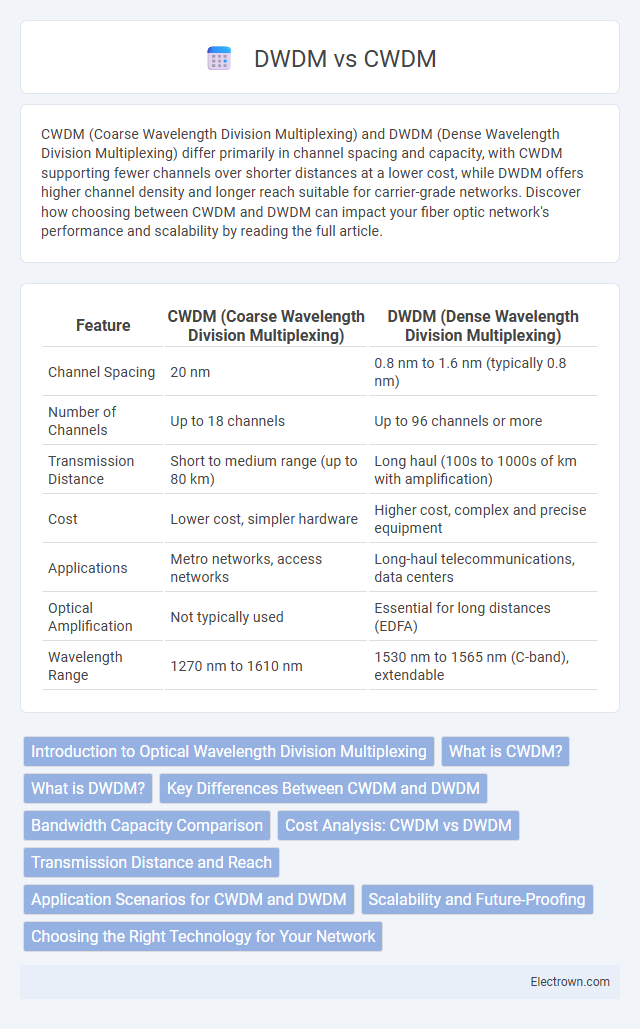
| Feature | CWDM (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing) | DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) |
|---|---|---|
| Channel Spacing | 20 nm | 0.8 nm to 1.6 nm (typically 0.8 nm) |
| Number of Channels | Up to 18 channels | Up to 96 channels or more |
| Transmission Distance | Short to medium range (up to 80 km) | Long haul (100s to 1000s of km with amplification) |
| Cost | Lower cost, simpler hardware | Higher cost, complex and precise equipment |
| Applications | Metro networks, access networks | Long-haul telecommunications, data centers |
| Optical Amplification | Not typically used | Essential for long distances (EDFA) |
| Wavelength Range | 1270 nm to 1610 nm | 1530 nm to 1565 nm (C-band), extendable |
Introduction to Optical Wavelength Division Multiplexing
Optical Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) enables the transmission of multiple data signals simultaneously over a single optical fiber by using different wavelengths of light. Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing (CWDM) typically supports up to 18 channels spaced widely apart at 20 nm intervals, suitable for shorter distances and cost-effective deployments. Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) supports up to 96 channels or more with narrow spacing around 0.8 nm, enabling high-capacity, long-distance communication in metropolitan and core networks.
What is CWDM?
CWDM (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing) is a technology used in fiber optic communications to combine multiple data signals on different wavelengths for transmission over a single fiber. It typically supports up to 18 channels spaced at 20 nm intervals, making it ideal for short to medium distance applications where cost-effectiveness is crucial. Your network can benefit from CWDM's lower power consumption and simpler cooling requirements compared to DWDM, although it offers lower channel capacity and spectral efficiency.
What is DWDM?
DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) is an advanced fiber optic technology that increases bandwidth by transmitting multiple data signals simultaneously on different wavelengths of light within the same fiber. DWDM supports up to 160 channels, each carrying data at high speeds, making it ideal for long-distance communication and large-scale data networks. Your network performance can significantly improve by implementing DWDM, as it maximizes fiber capacity and reduces latency in demanding environments.
Key Differences Between CWDM and DWDM
CWDM (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing) uses fewer wavelengths with wider spacing, typically 18 channels spaced 20 nm apart, ideal for short to medium distances up to 80 km. DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) supports a higher number of tightly packed channels, often 40 to 160, spaced at 0.8 nm or less, enabling ultra-high capacity transmission over long distances exceeding 100 km. CWDM systems are cost-effective with lower power consumption, while DWDM offers superior scalability, spectral efficiency, and is favored for core network and metro area applications.
Bandwidth Capacity Comparison
CWDM (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing) offers lower bandwidth capacity, typically supporting up to 18 wavelengths with 20 nm spacing, suitable for short to medium distances. DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) significantly increases bandwidth by accommodating up to 80 or more closely spaced wavelengths with 0.8 nm spacing, ideal for high-capacity, long-haul networks. Your choice between CWDM and DWDM depends on the required data throughput and network scale.
Cost Analysis: CWDM vs DWDM
CWDM (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing) offers a lower-cost solution compared to DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) due to its simpler technology and less expensive components, making it ideal for short to medium-range fiber networks. DWDM provides higher capacity and spectral efficiency, but this comes with increased costs related to advanced lasers, tighter channel spacing, and complex temperature control systems. Your choice depends on budget constraints and network scalability needs, with CWDM being cost-effective for moderate bandwidth, while DWDM suits long-haul, high-capacity infrastructures despite higher initial investment.
Transmission Distance and Reach
CWDM (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing) typically supports shorter transmission distances up to 80 kilometers due to its wider channel spacing and less precise laser requirements. DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) enables much longer reach, often exceeding 120 kilometers, by using narrower channel spacing and advanced amplification techniques like Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifiers (EDFAs). DWDM's higher spectral efficiency and superior signal integrity make it ideal for long-haul and metro networks demanding extended transmission distances.
Application Scenarios for CWDM and DWDM
CWDM is ideal for metropolitan and access networks where cost-effective, short to medium-distance transmission with fewer channels is required, supporting up to 18 wavelengths typically within 80 km. DWDM suits long-haul and backbone networks demanding high-capacity and dense channel counts, often exceeding 40 wavelengths over distances beyond 80 km, making it optimal for telecom carriers and data centers. Both technologies enhance fiber optic utilization but differ in scalability and cost-efficiency based on specific network size and traffic requirements.
Scalability and Future-Proofing
CWDM (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing) offers limited scalability with typically up to 18 channels spaced at 20 nm intervals, making it suitable for short to medium-distance applications but less adaptable for expanding network demands. DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) supports up to 80 or more channels with 0.8 nm spacing, providing significantly greater scalability and higher data capacity ideal for long-haul and high-bandwidth networks. DWDM's fine channel spacing and advanced modulation techniques make it more future-proof, accommodating evolving bandwidth requirements and network growth more effectively than CWDM.
Choosing the Right Technology for Your Network
Choosing between CWDM and DWDM depends on network capacity, distance, and budget requirements. CWDM offers cost-effective solutions for short to medium distances with fewer channels, ideal for metropolitan area networks. DWDM supports higher channel counts and longer distances, making it suitable for high-capacity backbone networks and data centers needing scalable and robust performance.
CWDM vs DWDM Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com