Free space optics offers wireless data transmission using light through the air, providing quick deployment and flexibility without the need for cables, while fiber optics delivers high-speed, reliable connectivity with superior bandwidth and minimal signal loss over long distances. Discover how each technology impacts your communication needs by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
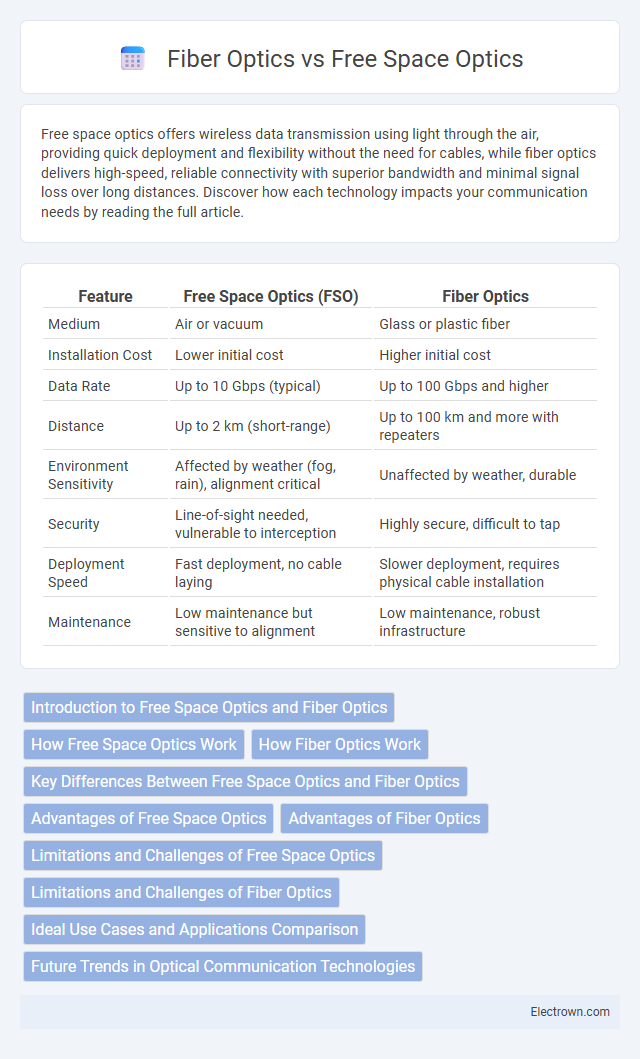
| Feature | Free Space Optics (FSO) | Fiber Optics |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Air or vacuum | Glass or plastic fiber |
| Installation Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Data Rate | Up to 10 Gbps (typical) | Up to 100 Gbps and higher |
| Distance | Up to 2 km (short-range) | Up to 100 km and more with repeaters |
| Environment Sensitivity | Affected by weather (fog, rain), alignment critical | Unaffected by weather, durable |
| Security | Line-of-sight needed, vulnerable to interception | Highly secure, difficult to tap |
| Deployment Speed | Fast deployment, no cable laying | Slower deployment, requires physical cable installation |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance but sensitive to alignment | Low maintenance, robust infrastructure |
Introduction to Free Space Optics and Fiber Optics
Free Space Optics (FSO) transmits data through line-of-sight laser beams in the atmosphere, offering high-speed wireless communication without physical cables, ideal for short-distance and urban deployments. Fiber Optics uses thin strands of glass or plastic fibers to carry data as light pulses, providing ultra-high bandwidth and reliable long-distance connectivity commonly utilized in telecommunications and data centers. Both technologies leverage optical principles but differ significantly in infrastructure requirements, environmental sensitivity, and application scopes.
How Free Space Optics Work
Free Space Optics (FSO) technology transmits data by using light beams through the air, creating a wireless optical link between two points. This method relies on precise alignment of transceivers that convert electrical signals into light pulses and back, enabling high-speed communication without the need for physical cables. Your connectivity can benefit from FSO's rapid deployment and flexibility, especially in areas where fiber optic installation is impractical or cost-prohibitive.
How Fiber Optics Work
Fiber optics work by transmitting data as pulses of light through thin strands of glass or plastic fibers, utilizing total internal reflection to keep the light signals contained within the core. This allows for high-speed, long-distance communication with minimal signal loss compared to free space optics, which rely on line-of-sight transmission through the air. Your network can achieve greater reliability and bandwidth using fiber optics, especially in environments where environmental conditions may disrupt free space signals.
Key Differences Between Free Space Optics and Fiber Optics
Free space optics (FSO) transmits data through light waves in the air, whereas fiber optics use glass or plastic fibers to guide light signals. FSO offers rapid deployment and cost-effectiveness for short-range communication without the need for physical cables, but it is highly susceptible to weather conditions and obstructions. In contrast, fiber optics provide higher bandwidth, lower signal attenuation, and greater reliability over long distances, though installation and maintenance involve more significant infrastructure investments.
Advantages of Free Space Optics
Free Space Optics (FSO) offers advantages such as rapid deployment without the need for underground cabling, making it ideal for urban environments and temporary installations. FSO systems provide high bandwidth and low latency comparable to fiber optics, supporting real-time data transmission with minimal interference. Your communication infrastructure benefits from lower installation costs and flexibility in connecting hard-to-reach locations where fiber optic deployment is impractical.
Advantages of Fiber Optics
Fiber optics offer superior bandwidth capacity and transmission speed compared to free space optics, making them ideal for high-demand data networks. Their immunity to electromagnetic interference ensures stable and reliable communication over long distances without signal degradation. Your network benefits from enhanced security and minimal latency, which are critical for mission-critical applications.
Limitations and Challenges of Free Space Optics
Free Space Optics (FSO) faces significant limitations including susceptibility to weather conditions such as fog, rain, and atmospheric turbulence, which can severely degrade signal quality and reliability. Unlike Fiber Optics, which provides stable and high-capacity data transmission through physical cables, FSO's line-of-sight requirement and limited range restrict its deployment in urban or obstructed environments. To maximize your communication system's effectiveness, consider these environmental challenges when choosing between FSO and Fiber Optics technology.
Limitations and Challenges of Fiber Optics
Fiber optics face limitations such as high installation and maintenance costs, susceptibility to physical damage, and signal attenuation over long distances requiring repeaters. Environmental factors like water infiltration, bending losses, and interference from electromagnetic fields can also degrade performance. Your choice between free space optics and fiber optics should consider these challenges alongside operational requirements and infrastructure constraints.
Ideal Use Cases and Applications Comparison
Free space optics (FSO) excels in short-distance, line-of-sight communication environments such as building-to-building links, disaster recovery scenarios, and temporary networks where rapid deployment is crucial. Fiber optics is ideal for long-distance, high-bandwidth applications like telecommunications backbone infrastructure, data centers, and submarine cables due to its low signal loss and immunity to electromagnetic interference. Both technologies complement each other by addressing different connectivity needs: FSO for flexible, wireless setups, and fiber optics for robust, high-capacity wired connections.
Future Trends in Optical Communication Technologies
Free space optics (FSO) is emerging as a complementary technology to fiber optics, offering flexible and rapid deployment for high-speed data transmission in urban and remote areas. Advances in adaptive optics, machine learning-based beam steering, and hybrid FSO-fiber networks are driving future trends toward enhanced reliability and integration with 5G and beyond communication infrastructures. Fiber optics continue to lead with ultra-high bandwidth and low latency capabilities, but future developments emphasize photonic integration, space-division multiplexing, and quantum communication applications to meet exponentially growing data demands.
Free space optics vs Fiber optics Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com