Surface-emitting LEDs emit light perpendicular to the chip surface, offering broader viewing angles and easier integration into compact designs, while edge-emitting LEDs direct light horizontally from the chip edge, providing higher output power and better beam collimation suited for fiber optic communications. Understanding these key differences can help you choose the right LED type for your applications--read on to explore their specific advantages and use cases.
Table of Comparison
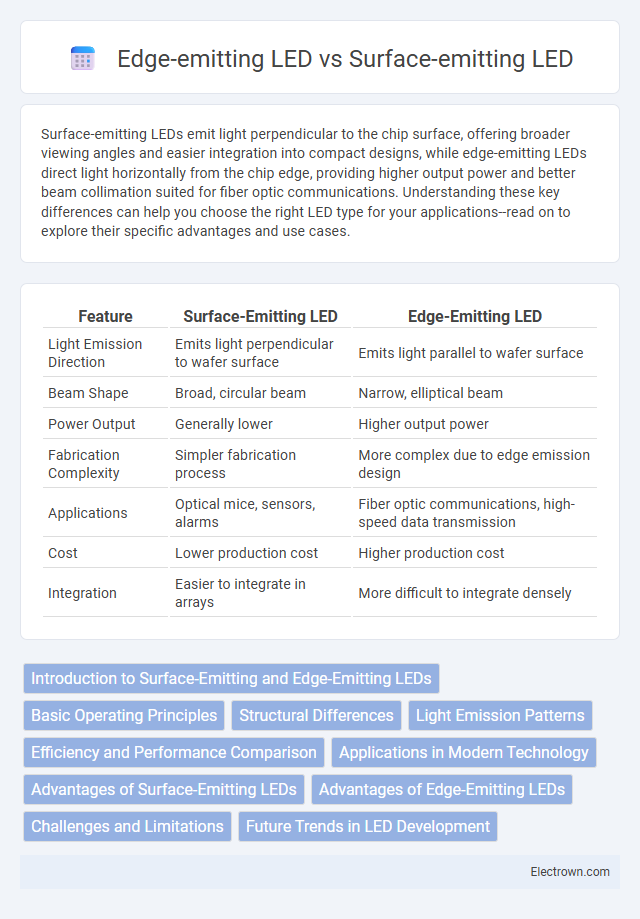
| Feature | Surface-Emitting LED | Edge-Emitting LED |
|---|---|---|
| Light Emission Direction | Emits light perpendicular to wafer surface | Emits light parallel to wafer surface |
| Beam Shape | Broad, circular beam | Narrow, elliptical beam |
| Power Output | Generally lower | Higher output power |
| Fabrication Complexity | Simpler fabrication process | More complex due to edge emission design |
| Applications | Optical mice, sensors, alarms | Fiber optic communications, high-speed data transmission |
| Cost | Lower production cost | Higher production cost |
| Integration | Easier to integrate in arrays | More difficult to integrate densely |
Introduction to Surface-Emitting and Edge-Emitting LEDs
Surface-emitting LEDs emit light perpendicularly from the chip surface, offering high beam quality and easy integration into arrays for applications like optical communications and sensing. Edge-emitting LEDs release light from the chip edge through a cleaved facet, providing higher output power and longer coherence length suitable for fiber optic communication and laser diode pumping. The structural difference influences their optical performance, beam shape, and integration capabilities in photonic systems.
Basic Operating Principles
Surface-emitting LEDs emit light perpendicular to the semiconductor chip surface through a broad emission area, resulting in a wide beam angle and easy coupling with optical components. Edge-emitting LEDs generate light parallel to the chip surface, allowing for higher output power and better beam collimation due to the longer cavity length. Understanding these basic operating principles helps you select the appropriate LED type based on the desired light directionality and power requirements.
Structural Differences
Surface-emitting LEDs emit light perpendicular to the chip surface with a vertical cavity design and multiple quantum wells, allowing compact, uniform light output. Edge-emitting LEDs generate light parallel to the chip surface via a waveguide structure, enhancing beam directionality and coherence for optical communication. The structural variation affects thermal management and integration in devices, influencing performance in different applications.
Light Emission Patterns
Surface-emitting LEDs emit light perpendicularly from the chip surface, producing a wide and uniform emission pattern suitable for applications requiring broad illumination. Edge-emitting LEDs direct light horizontally from the chip edge, resulting in a narrow, highly collimated beam ideal for fiber optic communication and focused lighting. Understanding these light emission patterns helps you select the most efficient LED type for your specific lighting or signaling needs.
Efficiency and Performance Comparison
Surface-emitting LEDs typically offer higher efficiency and better heat dissipation due to their larger emitting area, resulting in superior performance for high-power applications. Edge-emitting LEDs concentrate light along the edge, providing higher brightness and better beam directionality but often require more complex thermal management to maintain efficiency. You can achieve optimal device performance by selecting the LED type that best aligns with your power and beam shaping requirements.
Applications in Modern Technology
Surface-emitting LEDs (VCSELs) are widely used in high-speed data communication, 3D sensing, and LiDAR systems due to their compact size, low power consumption, and uniform beam profile. Edge-emitting LEDs excel in applications requiring higher output power and longer distance illumination, such as automotive headlights, optical fiber communication, and industrial machine vision. The choice between these LEDs depends on factors like emission pattern, power requirements, and integration with existing technology platforms.
Advantages of Surface-Emitting LEDs
Surface-emitting LEDs offer significant advantages such as simpler manufacturing processes and lower production costs due to their vertical light emission structure. Their design allows for higher integration density in two-dimensional arrays, leading to improved scalability and uniform light distribution, making them ideal for applications like optical communication and sensing. Your systems benefit from enhanced beam quality and easier alignment compared to edge-emitting LEDs.
Advantages of Edge-Emitting LEDs
Edge-emitting LEDs offer higher power output and greater efficiency compared to surface-emitting LEDs due to their waveguide structure that enables better light extraction and beam direction. Their narrow emission angle allows for precise coupling with optical fibers, making them ideal for high-speed data communication and sensing applications. You can benefit from improved performance and reliability in systems requiring focused, high-intensity light sources.
Challenges and Limitations
Surface-emitting LEDs face challenges such as lower output power and efficiency due to their vertical emission structure, which limits light extraction and heat dissipation. Edge-emitting LEDs, while offering higher brightness and beam quality, struggle with complex fabrication processes and alignment sensitivity, impacting yield and cost. Your choice between these LEDs must consider trade-offs in performance, manufacturing complexity, and thermal management requirements.
Future Trends in LED Development
Surface-emitting LEDs (VCSELs) are advancing with higher efficiency, faster modulation speeds, and improved beam quality, making them ideal for applications like LiDAR and high-speed data communication. Edge-emitting LEDs continue to evolve with increased output power and enhanced thermal management, supporting their use in industrial lighting and large-scale displays. Your choice between these technologies will depend on future application demands, with VCSELs leading in compact, high-performance roles and edge-emitters excelling in high-power, broad-area illumination.
Surface-emitting LED vs Edge-emitting LED Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com