LCD screens offer affordable, bright displays with good color accuracy and energy efficiency, while OLED panels provide superior contrast, deeper blacks, and faster response times ideal for immersive viewing experiences. Discover how choosing between LCD and OLED can impact your device's performance and visual quality in the detailed comparison ahead.
Table of Comparison
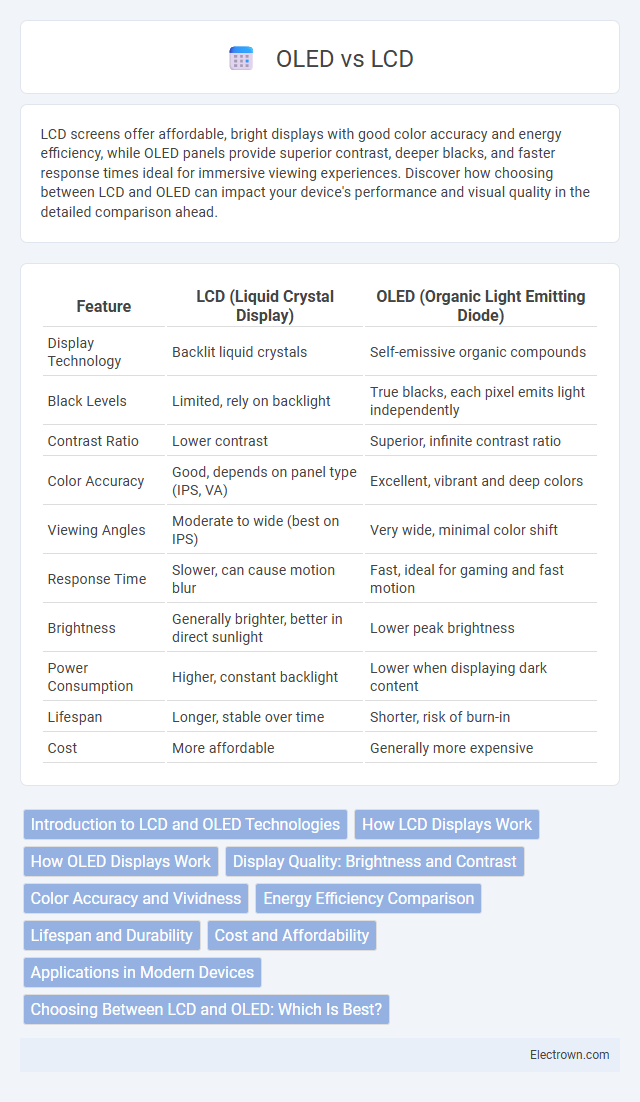
| Feature | LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) | OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) |
|---|---|---|
| Display Technology | Backlit liquid crystals | Self-emissive organic compounds |
| Black Levels | Limited, rely on backlight | True blacks, each pixel emits light independently |
| Contrast Ratio | Lower contrast | Superior, infinite contrast ratio |
| Color Accuracy | Good, depends on panel type (IPS, VA) | Excellent, vibrant and deep colors |
| Viewing Angles | Moderate to wide (best on IPS) | Very wide, minimal color shift |
| Response Time | Slower, can cause motion blur | Fast, ideal for gaming and fast motion |
| Brightness | Generally brighter, better in direct sunlight | Lower peak brightness |
| Power Consumption | Higher, constant backlight | Lower when displaying dark content |
| Lifespan | Longer, stable over time | Shorter, risk of burn-in |
| Cost | More affordable | Generally more expensive |
Introduction to LCD and OLED Technologies
LCD technology uses liquid crystals combined with a backlight to produce images, offering energy efficiency and affordability for various display sizes. OLED technology incorporates organic compounds that emit light individually, enabling deeper blacks, higher contrast ratios, and thinner displays without a backlight. Both technologies play crucial roles in modern screens, with OLED leading in picture quality and LCD maintaining advantages in cost and brightness.
How LCD Displays Work
LCD displays use a backlight to illuminate liquid crystals that modulate light to produce images through varying levels of transparency. These crystals align to block or allow light, creating pixels with distinct colors using RGB filters. The display relies on an array of thin-film transistors (TFT) to control each pixel's brightness and color intensity precisely.
How OLED Displays Work
OLED displays produce images by emitting light through organic compounds that glow when an electric current passes through them, eliminating the need for a separate backlight. Each pixel in an OLED screen is self-illuminating, enabling superior contrast ratios and deeper blacks compared to LCDs. This technology allows for thinner, more flexible displays with faster response times and improved color accuracy.
Display Quality: Brightness and Contrast
OLED displays deliver superior contrast ratios with true blacks by individually lighting pixels off, resulting in deeper shadows and more vibrant colors compared to LCDs. LCD screens rely on backlighting, which limits brightness levels and often produces less intense blacks, reducing overall image depth. Higher peak brightness in some LCD models enhances visibility in bright environments, but OLED's perfect black levels provide unmatched contrast and color accuracy.
Color Accuracy and Vividness
OLED displays outperform LCDs in color accuracy and vividness due to their self-emissive pixels, which produce deeper blacks and a wider color gamut. LCD screens rely on backlighting, limiting contrast and resulting in less vibrant colors, especially in dark scenes. High-end OLED panels achieve near-perfect color reproduction, making them ideal for professional color-critical work and immersive viewing experiences.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
OLED displays generally offer superior energy efficiency compared to LCD screens because each pixel emits its own light, allowing individual pixels to be turned off for true blacks and reduced power consumption. LCDs rely on a constant backlight, resulting in higher energy usage, especially when displaying darker images. Studies show OLED panels can reduce energy consumption by up to 40% in typical usage compared to traditional LCDs.
Lifespan and Durability
OLED displays typically have a shorter lifespan compared to LCDs due to organic materials prone to burn-in and gradual brightness degradation over time. LCD screens use inorganic crystals and LED backlighting, which generally results in longer durability and resistance to screen burn-in. For long-term usage, LCDs offer superior lifespan and reliability, while OLEDs excel in color accuracy and contrast but require more care to maintain longevity.
Cost and Affordability
LCD displays are generally more affordable than OLED screens due to lower manufacturing costs and widespread production techniques. OLED technology, while offering superior contrast and color accuracy, tends to be pricier, making it less accessible for budget-conscious consumers. Your choice between LCD and OLED should consider the balance between initial cost and desired display quality.
Applications in Modern Devices
OLED technology dominates high-end smartphones and premium TVs due to its superior contrast, flexibility, and energy efficiency, providing vibrant colors and deep blacks for an enhanced viewing experience. LCD remains prevalent in budget-friendly devices, computer monitors, and large-screen TVs, offering reliable brightness and cost-effective production. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize cutting-edge display quality or affordability in modern devices.
Choosing Between LCD and OLED: Which Is Best?
Choosing between LCD and OLED depends on usage priorities; OLED displays offer superior color accuracy, deeper blacks, and wider viewing angles due to self-emissive pixels, ideal for high-contrast visuals and immersive media consumption. LCD screens, utilizing backlit technology, typically provide higher brightness levels and better durability, making them suitable for brightly lit environments and longer device lifespans. Consider factors like energy efficiency, cost, and application context to determine the best display technology for your specific needs.
LCD vs OLED Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com