TWDM-PON and WDM-PON both enhance fiber-optic networks by using wavelength division multiplexing, but TWDM-PON combines time and wavelength division multiplexing to support multiple users on the same fiber more cost-effectively, whereas WDM-PON assigns unique wavelengths per user for dedicated bandwidth and higher security. Explore the rest of the article to understand which technology best suits your network needs.
Table of Comparison
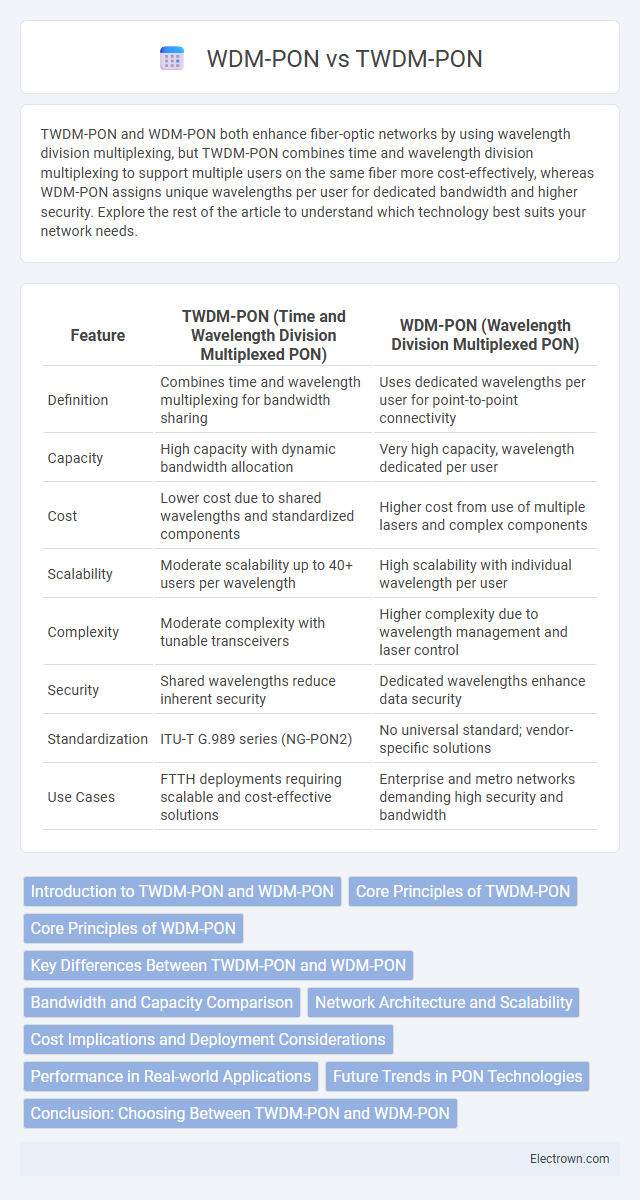
| Feature | TWDM-PON (Time and Wavelength Division Multiplexed PON) | WDM-PON (Wavelength Division Multiplexed PON) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines time and wavelength multiplexing for bandwidth sharing | Uses dedicated wavelengths per user for point-to-point connectivity |
| Capacity | High capacity with dynamic bandwidth allocation | Very high capacity, wavelength dedicated per user |
| Cost | Lower cost due to shared wavelengths and standardized components | Higher cost from use of multiple lasers and complex components |
| Scalability | Moderate scalability up to 40+ users per wavelength | High scalability with individual wavelength per user |
| Complexity | Moderate complexity with tunable transceivers | Higher complexity due to wavelength management and laser control |
| Security | Shared wavelengths reduce inherent security | Dedicated wavelengths enhance data security |
| Standardization | ITU-T G.989 series (NG-PON2) | No universal standard; vendor-specific solutions |
| Use Cases | FTTH deployments requiring scalable and cost-effective solutions | Enterprise and metro networks demanding high security and bandwidth |
Introduction to TWDM-PON and WDM-PON
TWDM-PON (Time and Wavelength Division Multiplexed Passive Optical Network) combines time division and wavelength division multiplexing to enhance bandwidth efficiency in fiber optic networks. WDM-PON (Wavelength Division Multiplexed Passive Optical Network) uses individual wavelengths per user, providing dedicated bandwidth and improved security. Both technologies support high-speed data transmission, but TWDM-PON offers greater scalability and flexibility for accommodating multiple service providers and dynamic bandwidth allocation.
Core Principles of TWDM-PON
TWDM-PON (Time and Wavelength Division Multiplexed Passive Optical Network) leverages multiple wavelengths combined with time-division multiplexing to enhance bandwidth efficiency and support multiple users on the same fiber infrastructure. It operates by assigning distinct wavelengths to different groups of users while dynamically allocating time slots within each wavelength, optimizing network capacity and scalability. This hybrid approach enables TWDM-PON to meet increasing bandwidth demands and provides flexibility in resource allocation compared to WDM-PON, which relies solely on wavelength division multiplexing.
Core Principles of WDM-PON
Wavelength Division Multiplexing Passive Optical Network (WDM-PON) operates by assigning a unique wavelength to each Optical Network Unit (ONU), enabling dedicated point-to-point communication over a shared fiber infrastructure. This core principle eliminates bandwidth sharing among users, ensuring high security, low latency, and enhanced bandwidth scalability compared to TWDM-PON, which combines time and wavelength division multiplexing. The WDM-PON architecture leverages wavelength-selective components such as Arrayed Waveguide Gratings (AWGs) to route distinct wavelengths to corresponding ONUs, optimizing network efficiency and simplifying network management.
Key Differences Between TWDM-PON and WDM-PON
TWDM-PON (Time and Wavelength Division Multiplexed Passive Optical Network) combines multiple wavelengths with time division multiplexing to efficiently share bandwidth among users, while WDM-PON (Wavelength Division Multiplexed Passive Optical Network) allocates dedicated wavelengths to individual users for higher security and bandwidth. You should consider TWDM-PON for cost-effective scalability and dynamic bandwidth allocation, whereas WDM-PON excels in providing guaranteed bandwidth with minimal latency. Key differences include wavelength reuse in TWDM-PON versus fixed wavelength assignment in WDM-PON, impacting network complexity and user capacity.
Bandwidth and Capacity Comparison
TWDM-PON (Time and Wavelength Division Multiplexed Passive Optical Network) offers increased bandwidth by combining multiple wavelengths and time slots, enabling scalable capacity up to 40 Gbps or higher per PON segment. WDM-PON (Wavelength Division Multiplexed Passive Optical Network) delivers dedicated wavelengths per user, providing fixed high bandwidth and lower latency but with limited flexibility in capacity scaling. TWDM-PON is more efficient for accommodating dynamic bandwidth demands and expanding total network capacity compared to the inherently static bandwidth allocation of WDM-PON.
Network Architecture and Scalability
TWDM-PON utilizes time and wavelength division multiplexing to enable multiple users to share wavelengths dynamically, offering higher scalability through flexible bandwidth allocation. In contrast, WDM-PON assigns dedicated wavelengths to each user, resulting in a simpler network architecture but limited scalability due to fixed wavelength resources. The dynamic resource management in TWDM-PON supports efficient network expansion and better accommodates fluctuating traffic demands compared to the rigid structure of WDM-PON.
Cost Implications and Deployment Considerations
TWDM-PON offers cost advantages by using shared wavelengths and standard optical components, reducing overall expenditure compared to the more expensive, single-wavelength lasers required in WDM-PON. Deployment of TWDM-PON is simpler and more scalable, supporting multiple users over common infrastructure, whereas WDM-PON demands precise wavelength management and higher initial investment for dedicated channels. Your decision between TWDM-PON and WDM-PON should weigh these cost differences against network capacity and complexity requirements.
Performance in Real-world Applications
TWDM-PON offers scalable bandwidth by combining multiple wavelengths on a single fiber, providing cost-effective solutions for dense urban deployments with varied user demands. WDM-PON delivers dedicated wavelengths per user, ensuring ultra-low latency and high security ideal for enterprise and data center interconnections. Real-world performance shows TWDM-PON excels in flexible, high-capacity access networks, while WDM-PON is preferred for guaranteed quality of service in critical applications.
Future Trends in PON Technologies
TWDM-PON (Time and Wavelength Division Multiplexed Passive Optical Network) and WDM-PON (Wavelength Division Multiplexed Passive Optical Network) represent significant advancements in PON technologies, offering higher bandwidth and better scalability. TWDM-PON combines multiple wavelengths with time division multiplexing to optimize bandwidth efficiency, making it a leading choice for future-proofing fiber networks. Your network infrastructure will benefit from evolving support for dynamic wavelength allocation, improved energy efficiency, and enhanced system flexibility, shaping the future trends in passive optical networks.
Conclusion: Choosing Between TWDM-PON and WDM-PON
TWDM-PON offers scalable bandwidth with cost-effective shared infrastructure, making it ideal for metro and access networks requiring flexibility and gradual capacity upgrades. WDM-PON delivers dedicated wavelengths per user, ensuring higher security and guaranteed bandwidth, suitable for high-demand business and data center applications. Selecting between TWDM-PON and WDM-PON depends on factors like network scalability, cost constraints, required security levels, and specific bandwidth guarantees.
TWDM-PON vs WDM-PON Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com