Microdisplay OLED offers superior contrast, faster response times, and deeper blacks compared to Microdisplay LCD, which often provides better brightness and lower power consumption. Explore the rest of the article to determine which technology best suits your specific display needs.
Table of Comparison
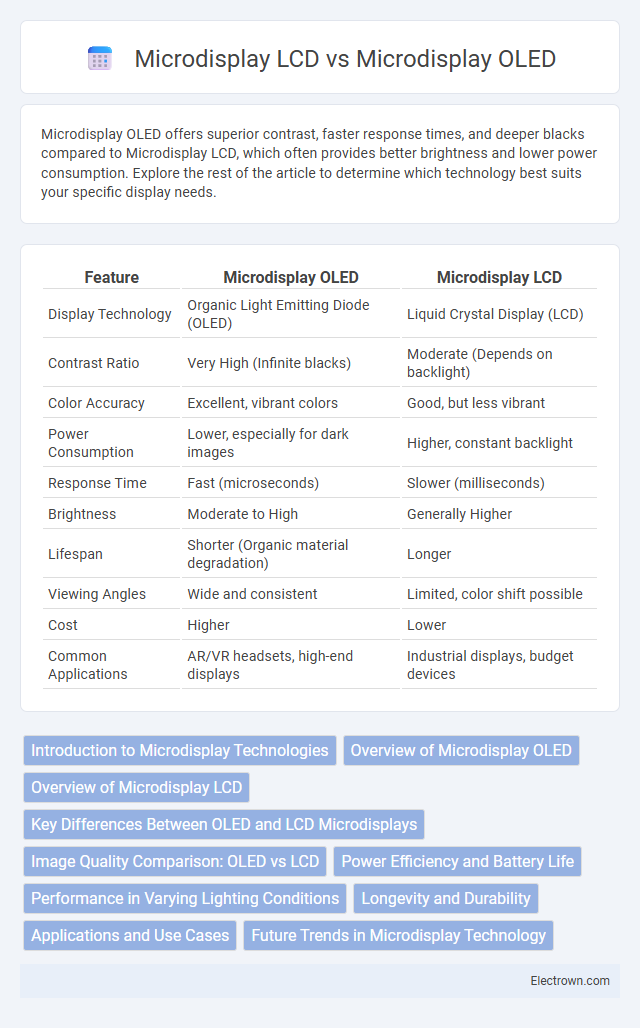
| Feature | Microdisplay OLED | Microdisplay LCD |
|---|---|---|
| Display Technology | Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED) | Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) |
| Contrast Ratio | Very High (Infinite blacks) | Moderate (Depends on backlight) |
| Color Accuracy | Excellent, vibrant colors | Good, but less vibrant |
| Power Consumption | Lower, especially for dark images | Higher, constant backlight |
| Response Time | Fast (microseconds) | Slower (milliseconds) |
| Brightness | Moderate to High | Generally Higher |
| Lifespan | Shorter (Organic material degradation) | Longer |
| Viewing Angles | Wide and consistent | Limited, color shift possible |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Common Applications | AR/VR headsets, high-end displays | Industrial displays, budget devices |
Introduction to Microdisplay Technologies
Microdisplay OLED technology provides self-emissive pixels, delivering higher contrast ratios and deeper black levels compared to Microdisplay LCD, which relies on backlighting and offers more consistent color accuracy and brightness. OLED microdisplays excel in power efficiency and response time, making them ideal for compact, wearable devices and augmented reality applications. Your choice between Microdisplay OLED and LCD depends on the specific needs for image quality, power consumption, and application environment.
Overview of Microdisplay OLED
Microdisplay OLED technology features organic light-emitting diodes that offer higher contrast ratios, faster response times, and deeper blacks compared to Microdisplay LCDs, making them ideal for applications requiring vivid image quality. These displays are self-emissive, eliminating the need for backlighting and enabling thinner, lighter devices with lower power consumption. Microdisplay OLEDs are widely used in augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and high-end viewfinder applications due to their superior color accuracy and wide viewing angles.
Overview of Microdisplay LCD
Microdisplay LCD technology utilizes liquid crystals to modulate light and create images with high resolution and brightness, making it ideal for applications requiring sharp visuals and color accuracy. These displays offer energy efficiency and longer lifespan compared to some OLED variants, especially in environments with prolonged static image usage. Your decision between Microdisplay OLED and LCD should consider factors like contrast ratios, power consumption, and specific use cases such as augmented reality or head-mounted displays.
Key Differences Between OLED and LCD Microdisplays
OLED microdisplays use organic light-emitting diodes that independently illuminate each pixel, offering superior contrast ratios, deeper blacks, and faster response times compared to LCD microdisplays, which rely on backlighting through liquid crystals. LCD microdisplays typically provide higher brightness levels and better color accuracy under strong ambient light, making them ideal for outdoor applications. Your choice between these technologies depends on priorities like power efficiency, image quality, and environmental conditions where the display will be used.
Image Quality Comparison: OLED vs LCD
Microdisplay OLED offers superior image quality with deeper blacks, higher contrast ratios, and more vibrant colors compared to Microdisplay LCD, which relies on backlighting that can reduce contrast and color accuracy. OLED pixels emit their own light, enabling true blacks and improved color saturation, while LCDs often suffer from light bleed and lower dynamic range. Your choice should consider OLED's enhanced visual experience optimal for applications requiring high-fidelity images and true-to-life color reproduction.
Power Efficiency and Battery Life
Microdisplay OLEDs offer superior power efficiency compared to Microdisplay LCDs due to their self-emissive pixels, which illuminate only active areas and reduce overall energy consumption. This technology significantly extends battery life in portable devices by minimizing power draw during darker or mixed-content display conditions. In contrast, Microdisplay LCDs rely on constant backlighting, resulting in higher energy usage and shorter battery runtime.
Performance in Varying Lighting Conditions
Microdisplay OLEDs offer superior contrast ratios and true black levels due to their self-emissive pixels, enhancing visibility in low-light and high-glare environments. In contrast, Microdisplay LCDs rely on backlighting, which can cause lower contrast and reduced clarity under direct sunlight or bright ambient conditions. OLED technology delivers faster response times and better color accuracy, making it more effective for applications requiring performance across diverse lighting scenarios.
Longevity and Durability
Microdisplay OLEDs typically offer superior color contrast and faster response times but can suffer from reduced longevity due to organic material degradation, especially under high brightness conditions. Microdisplay LCDs tend to have longer lifespan and enhanced durability, making them more resistant to burn-in and environmental stress such as humidity and temperature fluctuations. Choosing between these technologies depends on your application's need for vibrant visuals versus long-term reliability.
Applications and Use Cases
Microdisplay OLED technology excels in applications requiring high contrast ratios and vibrant color reproduction, such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) headsets and medical imaging devices. Microdisplay LCDs are preferred in environments needing higher brightness and durability, including industrial heads-up displays (HUDs), camera viewfinders, and automotive displays. Both technologies serve critical roles in compact devices, with OLEDs offering superior image quality for immersive experiences and LCDs providing reliability in bright or rugged conditions.
Future Trends in Microdisplay Technology
Microdisplay OLED technology is expected to lead future trends due to its superior contrast ratios, faster response times, and wider color gamut compared to Microdisplay LCD. Innovations in OLED materials and manufacturing will enhance durability and energy efficiency, making them ideal for augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) applications. Your choice will benefit from OLED's ability to deliver more immersive visuals in compact devices, while Microdisplay LCD technology focuses on improving brightness and resolution for specific industrial uses.
Microdisplay OLED vs Microdisplay LCD Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com