OSA (Optical Spectrum Analyzer) measures the power distribution of light across various wavelengths, providing detailed insight into signal quality and spectral characteristics, while OTDR (Optical Time-Domain Reflectometer) identifies faults and measures loss in fiber optic cables by sending pulses and analyzing reflections over distance. Understanding the differences between OSA and OTDR can enhance Your ability to troubleshoot and maintain fiber optic networks effectively--explore the rest of the article to learn more.
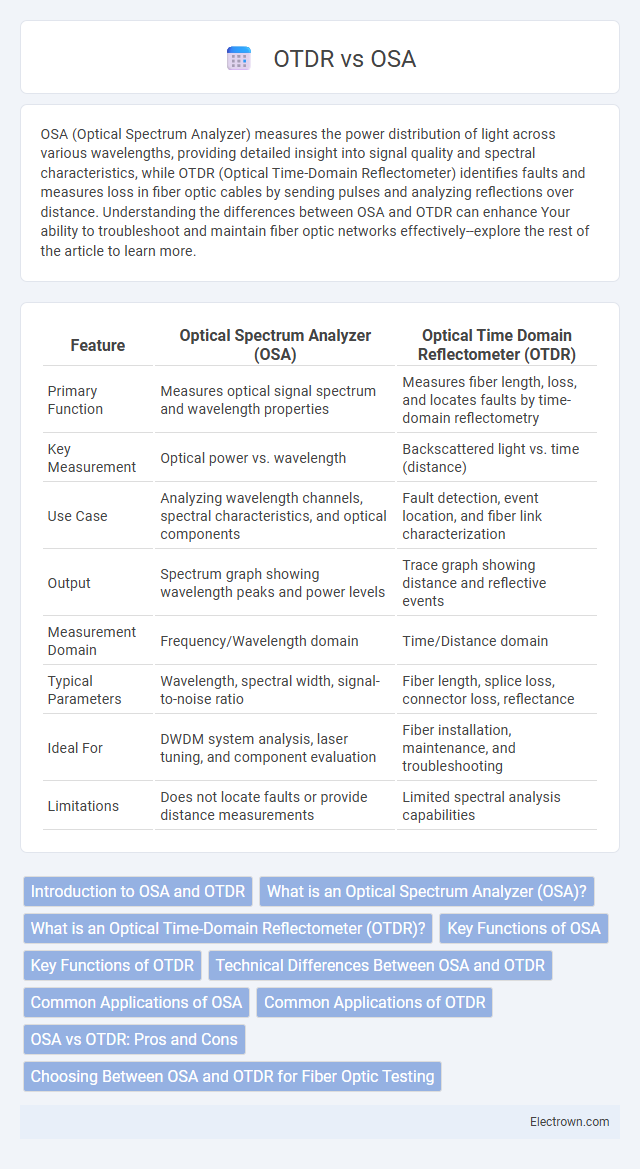
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Optical Spectrum Analyzer (OSA) | Optical Time Domain Reflectometer (OTDR) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Measures optical signal spectrum and wavelength properties | Measures fiber length, loss, and locates faults by time-domain reflectometry |
| Key Measurement | Optical power vs. wavelength | Backscattered light vs. time (distance) |
| Use Case | Analyzing wavelength channels, spectral characteristics, and optical components | Fault detection, event location, and fiber link characterization |
| Output | Spectrum graph showing wavelength peaks and power levels | Trace graph showing distance and reflective events |
| Measurement Domain | Frequency/Wavelength domain | Time/Distance domain |
| Typical Parameters | Wavelength, spectral width, signal-to-noise ratio | Fiber length, splice loss, connector loss, reflectance |
| Ideal For | DWDM system analysis, laser tuning, and component evaluation | Fiber installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting |
| Limitations | Does not locate faults or provide distance measurements | Limited spectral analysis capabilities |
Introduction to OSA and OTDR
Optical Spectrum Analyzers (OSA) measure the power distribution of optical signals across different wavelengths, essential for analyzing signal quality and identifying spectral characteristics in fiber optic communications. Optical Time Domain Reflectometers (OTDR) detect fiber faults and measure fiber length by analyzing backscattered light as a function of time, providing detailed information about fiber integrity and splice losses. Your choice between OSA and OTDR depends on whether the focus is on spectral analysis or physical fiber diagnostics.
What is an Optical Spectrum Analyzer (OSA)?
An Optical Spectrum Analyzer (OSA) measures the power distribution of optical signals across a specific wavelength range, providing detailed spectral information crucial for analyzing laser sources, filters, and wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) systems. Unlike an Optical Time Domain Reflectometer (OTDR), which identifies faults and measures fiber length by analyzing reflected light over time, the OSA delivers precise wavelength and intensity data for characterizing signal quality. Your choice between OSA and OTDR depends on whether spectral analysis or fiber fault location is the primary diagnostic need.
What is an Optical Time-Domain Reflectometer (OTDR)?
An Optical Time-Domain Reflectometer (OTDR) is a precision instrument used for characterizing optical fibers by sending a series of light pulses into the fiber and measuring the reflected signals caused by Rayleigh scattering and Fresnel reflections. OTDRs provide detailed information about fiber length, attenuation, splices, connectors, and faults, enabling effective fiber optic network troubleshooting and maintenance. This device is essential for identifying breaks, bends, and other physical defects within fiber optic cables with high spatial resolution.
Key Functions of OSA
Optical Spectrum Analyzers (OSA) are essential for measuring the spectral power distribution of optical signals, enabling precise wavelength characterization and signal quality assessment. Unlike OTDRs, which primarily analyze fiber integrity by detecting faults and measuring loss over distance, OSAs provide detailed spectral analysis crucial for wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) systems and laser tuning. You rely on an OSA to optimize performance in complex photonic networks by monitoring spectral purity, channel power, and signal-to-noise ratio.
Key Functions of OTDR
OTDR (Optical Time Domain Reflectometer) key functions include measuring fiber optic cable length, locating faults, and identifying signal loss or splices within the fiber. It provides detailed backscatter and reflection data, enabling precise troubleshooting and network maintenance. Your fiber network diagnostics benefit from OTDR's capability to deliver accurate, time-based trace analysis for effective performance optimization.
Technical Differences Between OSA and OTDR
Optical Spectrum Analyzers (OSA) measure the spectral composition and power levels of optical signals, providing detailed wavelength and amplitude information critical for characterizing light sources and fiber transmissions. In contrast, Optical Time Domain Reflectometers (OTDR) analyze fiber optic cables by sending pulses of light and measuring backscattered signals to detect faults, splices, and overall fiber length through time-domain reflections. While OSA emphasizes spectral analysis and signal quality, OTDR focuses on spatial diagnostics and fiber integrity assessment.
Common Applications of OSA
Optical Spectrum Analyzers (OSA) are commonly used for detailed wavelength and spectral power distribution analysis in optical networks, enabling precise characterization of laser sources, wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) systems, and optical amplifiers. They play a critical role in identifying channel spacing, signal crosstalk, and spectral bandwidth in fiber optic communication systems. OSAs support testing and troubleshooting advanced photonic devices by providing high-resolution spectral data essential for optimizing network performance and ensuring signal integrity.
Common Applications of OTDR
Optical Time-Domain Reflectometers (OTDR) are commonly used for fiber optic network testing, enabling precise measurement of fiber length, loss, and fault location. OTDR devices are essential in the installation, troubleshooting, and maintenance of long-haul, metro, and access fiber optic networks, including Passive Optical Networks (PON) and data center cabling. Their ability to detect breaks, bends, splices, and connectors ensures optimal network performance and rapid fault isolation.
OSA vs OTDR: Pros and Cons
Optical Spectrum Analyzers (OSA) provide high-resolution spectral analysis essential for characterizing wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) systems but are generally expensive and less effective for locating faults in long fiber links. Optical Time Domain Reflectometers (OTDR) excel in pinpointing fiber breaks and measuring loss over distance, offering cost-effective field diagnostics but with limited spectral information compared to OSAs. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize detailed spectral data (OSA) or efficient fault location and fiber integrity assessment (OTDR).
Choosing Between OSA and OTDR for Fiber Optic Testing
Choosing between Optical Spectrum Analyzer (OSA) and Optical Time-Domain Reflectometer (OTDR) for fiber optic testing depends on the specific diagnostic needs of the network. OSA excels in analyzing spectral characteristics, signal quality, and wavelength validation, making it ideal for DWDM systems and signal integrity troubleshooting. OTDR provides detailed distance-based fault location, splice, and connector loss measurements, essential for identifying breaks, bends, and overall fiber integrity in long-haul or installed fiber networks.
OSA vs OTDR Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com