Multi-mode fiber transmits multiple light modes, making it ideal for short-distance communication with lower costs, while single-mode fiber supports a single light mode for long-distance transmission and higher bandwidth. Discover how understanding these differences can enhance Your network performance by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
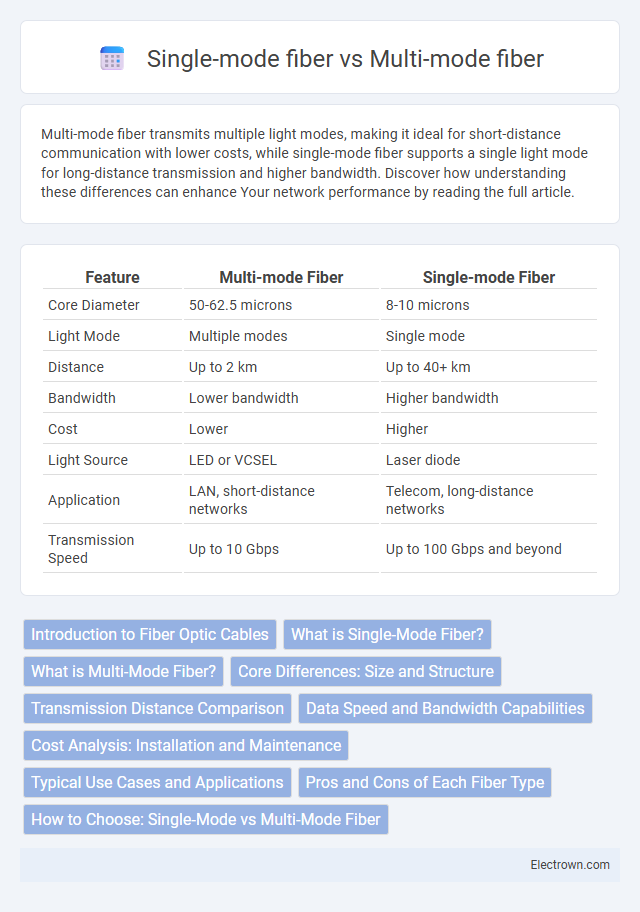
| Feature | Multi-mode Fiber | Single-mode Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Core Diameter | 50-62.5 microns | 8-10 microns |
| Light Mode | Multiple modes | Single mode |
| Distance | Up to 2 km | Up to 40+ km |
| Bandwidth | Lower bandwidth | Higher bandwidth |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Light Source | LED or VCSEL | Laser diode |
| Application | LAN, short-distance networks | Telecom, long-distance networks |
| Transmission Speed | Up to 10 Gbps | Up to 100 Gbps and beyond |
Introduction to Fiber Optic Cables
Multi-mode fiber and single-mode fiber are two primary types of fiber optic cables used for data transmission. Multi-mode fiber features a larger core diameter, allowing multiple light modes to propagate, making it ideal for short-distance communication such as within data centers and office buildings. Single-mode fiber has a smaller core designed for long-distance, high-bandwidth applications, offering reduced signal attenuation and minimal modal dispersion to support your network's most demanding needs.
What is Single-Mode Fiber?
Single-mode fiber is a type of optical fiber designed to transmit light directly down the fiber with a single light mode, minimizing signal attenuation and distortion over long distances. It features a small core diameter of approximately 8 to 10 microns, allowing only one mode of light to propagate, which results in higher bandwidth and improved performance for telecommunications and data networks. Single-mode fiber is ideal for long-haul communication and high-speed data transfer, supporting distances up to 40 kilometers or more without signal boosters.
What is Multi-Mode Fiber?
Multi-mode fiber is an optical fiber designed with a larger core diameter, typically 50 or 62.5 microns, allowing multiple light modes to propagate simultaneously for short-distance data transmission. It is commonly used in local area networks (LANs) and data centers due to its cost-effectiveness and compatibility with LED light sources, supporting distances up to 550 meters at 10 Gbps.
Core Differences: Size and Structure
Multi-mode fiber features a larger core diameter, typically 50 to 62.5 microns, allowing multiple light modes to propagate simultaneously, while single-mode fiber has a much smaller core around 8 to 10 microns that supports only one light mode. This core size difference results in multi-mode fiber being ideal for shorter distance data transmission and easier connectivity, whereas single-mode fiber suits long-distance communication with higher bandwidth and minimal signal attenuation. Your network design choice should consider these core differences to optimize performance and cost-efficiency.
Transmission Distance Comparison
Multi-mode fiber supports transmission distances typically up to 550 meters at 10 Gbps, making it ideal for short-range applications such as data centers and enterprise networks. Single-mode fiber enables much longer transmission distances, often exceeding 40 kilometers without signal degradation, suitable for telecommunications and long-haul network infrastructure. The core diameter difference, approximately 50 microns for multi-mode and 9 microns for single-mode, directly impacts modal dispersion and thus transmission reach.
Data Speed and Bandwidth Capabilities
Multi-mode fiber supports data speeds up to 100 Gbps over shorter distances, typically within 500 meters, making it ideal for local area networks and data centers. Single-mode fiber, however, offers significantly higher bandwidth capabilities and supports data transmission over much longer distances, often exceeding 40 kilometers, without signal degradation. Your choice depends on the required data speed and distance, with single-mode fibers preferable for high-speed, long-distance communication needs.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Maintenance
Multi-mode fiber typically offers lower initial installation costs due to its larger core size, which simplifies alignment and allows the use of less expensive LED transmitters. Single-mode fiber presents higher upfront expenses, driven by the precise splicing and connectors needed for its smaller core and the use of costly laser transmitters. Maintenance costs for single-mode fiber can be higher due to its sensitivity to physical damage and complex testing requirements, whereas multi-mode fiber often requires less frequent and less specialized upkeep.
Typical Use Cases and Applications
Multi-mode fiber is commonly used in short-distance applications such as data centers, local area networks (LANs), and enterprise campus networks due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of installation. Single-mode fiber is preferred for long-distance telecommunications, metro networks, and high-speed internet backbone connections because of its higher bandwidth and lower attenuation. Both fiber types support critical infrastructure but differ significantly in range and data transmission capacity tailored to their respective use cases.
Pros and Cons of Each Fiber Type
Multi-mode fiber offers easier installation and lower cost for short-distance data transmission, making it ideal for local area networks; however, it suffers from higher modal dispersion, limiting bandwidth and distance. Single-mode fiber excels in long-distance communication with minimal signal loss and high bandwidth capacity, though it requires more precise alignment and higher cost equipment. Your choice depends on the application's distance requirements, budget, and network speed, balancing multi-mode's affordability against single-mode's superior performance.
How to Choose: Single-Mode vs Multi-Mode Fiber
Choosing between single-mode and multi-mode fiber depends on distance, bandwidth requirements, and budget. Single-mode fiber offers higher bandwidth and longer transmission distances, making it ideal for telecommunications and long-haul networks. Multi-mode fiber is cost-effective for shorter distances, such as within data centers or enterprise networks, where higher attenuation and modal dispersion are less impactful.
Multi-mode fiber vs Single-mode fiber Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com