Lidar and Time-of-Flight (ToF) cameras both measure distances by calculating the time it takes for light to reflect off objects, but Lidar uses laser pulses for higher precision over longer ranges while ToF cameras use LED or laser illumination suitable for shorter distances and faster real-time depth mapping. Understanding these differences can enhance Your choice for applications such as autonomous vehicles, robotics, or 3D scanning; read on to explore their unique advantages and use cases.
Table of Comparison
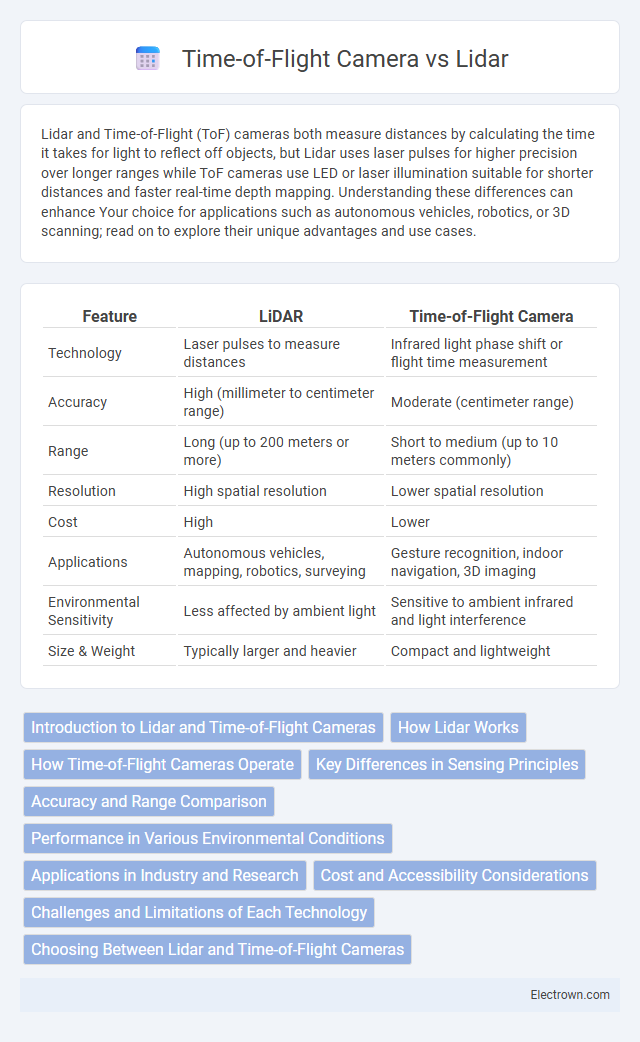
| Feature | LiDAR | Time-of-Flight Camera |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Laser pulses to measure distances | Infrared light phase shift or flight time measurement |
| Accuracy | High (millimeter to centimeter range) | Moderate (centimeter range) |
| Range | Long (up to 200 meters or more) | Short to medium (up to 10 meters commonly) |
| Resolution | High spatial resolution | Lower spatial resolution |
| Cost | High | Lower |
| Applications | Autonomous vehicles, mapping, robotics, surveying | Gesture recognition, indoor navigation, 3D imaging |
| Environmental Sensitivity | Less affected by ambient light | Sensitive to ambient infrared and light interference |
| Size & Weight | Typically larger and heavier | Compact and lightweight |
Introduction to Lidar and Time-of-Flight Cameras
Lidar uses laser pulses to measure distances by calculating the time it takes for light to reflect back from objects, enabling high-precision 3D mapping and environmental scanning. Time-of-Flight (ToF) cameras emit infrared light and capture the reflected light to create depth maps in real-time, commonly used in gesture recognition and augmented reality. Both technologies provide depth sensing but differ in range, accuracy, and typical application areas, with Lidar excelling at long-range measurements and ToF cameras optimized for short-range, high-speed imaging.
How Lidar Works
Lidar operates by emitting laser pulses toward a target and measuring the time it takes for the light to reflect back to the sensor, creating highly accurate 3D maps. Unlike Time-of-Flight cameras that use infrared light and lower resolution sensors, Lidar provides superior spatial precision and range capabilities. Your applications in autonomous vehicles or topographical surveys benefit from Lidar's ability to capture detailed environmental data with millimeter accuracy.
How Time-of-Flight Cameras Operate
Time-of-Flight (ToF) cameras operate by emitting infrared light pulses and measuring the time it takes for the light to reflect back from objects, enabling precise depth mapping. This technology captures 3D spatial information by calculating distance based on the phase shift or time delay of the returned signal. Compared to traditional LiDAR systems, ToF cameras provide real-time depth data with reduced complexity and cost, making them ideal for applications like gesture recognition and robotics.
Key Differences in Sensing Principles
Lidar uses laser pulses to measure distances by calculating the time it takes for light to travel to an object and back, enabling precise 3D mapping of environments. Time-of-Flight cameras emit infrared light and capture the phase shift or time delay of returned light to create depth images at high frame rates but with lower spatial resolution. Your choice between these technologies depends on the required accuracy, range, and application context in 3D sensing.
Accuracy and Range Comparison
Lidar systems offer superior accuracy and longer range capabilities compared to Time-of-Flight (ToF) cameras, with typical Lidar sensors achieving range measurements up to several hundred meters and accuracy within a few centimeters. ToF cameras generally provide shorter detection distances, often limited to 10-30 meters, with lower spatial resolution and accuracy due to sensor noise and environmental interference. Enhanced Lidar performance in complex environments makes it preferable for precision mapping and autonomous navigation, while ToF cameras suit applications requiring compact size and cost efficiency over shorter distances.
Performance in Various Environmental Conditions
LiDAR systems provide high-precision distance measurements by emitting laser pulses, maintaining accuracy in low-light and varied weather conditions such as fog, rain, and dust. Time-of-Flight (ToF) cameras use infrared light to capture depth information but often experience reduced performance in strong ambient light or highly reflective surfaces. For outdoor applications requiring reliable range sensing under diverse environmental challenges, LiDAR technology generally delivers superior robustness and consistency.
Applications in Industry and Research
Lidar systems excel in creating precise 3D maps for autonomous vehicles and industrial automation, offering high-resolution data essential for safety and navigation. Time-of-Flight (ToF) cameras provide real-time depth sensing ideal for robotics, gesture recognition, and augmented reality, enabling faster data processing in research environments. Your choice between Lidar and ToF depends on the required range, resolution, and application complexity in industrial or scientific projects.
Cost and Accessibility Considerations
Lidar systems typically come with higher costs due to complex sensor components and precision requirements, making them less accessible for budget-conscious projects. Time-of-Flight cameras offer a more affordable alternative with simpler design and widespread commercial availability, often integrated into consumer devices like smartphones. Choosing between the two depends on your budget constraints and the level of spatial accuracy required for your application.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Technology
LiDAR faces challenges such as high cost, sensitivity to weather conditions like fog and rain, and limited resolution in capturing fine details. Time-of-Flight (ToF) cameras are constrained by shorter effective ranges, susceptibility to ambient light interference, and lower depth accuracy compared to LiDAR. Both technologies encounter difficulties in real-time processing and integration for complex environments, impacting their widespread adoption in autonomous systems.
Choosing Between Lidar and Time-of-Flight Cameras
Choosing between LiDAR and Time-of-Flight (ToF) cameras depends on the specific application requirements such as range, accuracy, and environmental conditions. LiDAR offers high-resolution 3D mapping with long-range capabilities, making it ideal for autonomous vehicles and large-scale surveying. ToF cameras provide faster depth sensing at a lower cost, suitable for short-range indoor applications like gesture recognition and augmented reality.
Lidar vs Time-of-Flight camera Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com