Zigzag transformers provide phase shift and grounding with minimal harmonic distortion, ideal for power system grounding, while autotransformers offer efficient voltage regulation with less copper usage but lack isolation between windings. Explore the detailed comparison to understand which transformer best suits your electrical system needs.
Table of Comparison
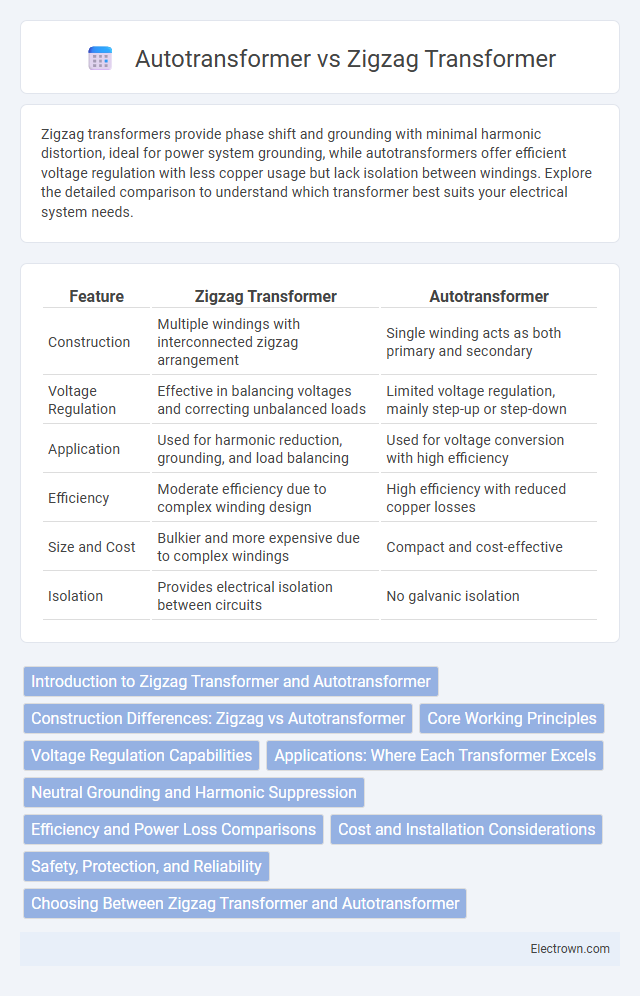
| Feature | Zigzag Transformer | Autotransformer |
|---|---|---|
| Construction | Multiple windings with interconnected zigzag arrangement | Single winding acts as both primary and secondary |
| Voltage Regulation | Effective in balancing voltages and correcting unbalanced loads | Limited voltage regulation, mainly step-up or step-down |
| Application | Used for harmonic reduction, grounding, and load balancing | Used for voltage conversion with high efficiency |
| Efficiency | Moderate efficiency due to complex winding design | High efficiency with reduced copper losses |
| Size and Cost | Bulkier and more expensive due to complex windings | Compact and cost-effective |
| Isolation | Provides electrical isolation between circuits | No galvanic isolation |
Introduction to Zigzag Transformer and Autotransformer
Zigzag transformers utilize a winding configuration that provides excellent harmonic suppression and grounding capabilities, making them ideal for power quality improvement and neutral grounding in distribution systems. Autotransformers, featuring a single winding with taps, offer efficient voltage transformation with reduced size and cost but lack electrical isolation between primary and secondary circuits. Both types serve distinct purposes in electrical networks, with zigzag transformers emphasizing harmonic mitigation and grounding, while autotransformers prioritize compact and economical voltage regulation.
Construction Differences: Zigzag vs Autotransformer
Zigzag transformers feature multiple winding segments arranged in a zigzag pattern on the core limbs, which helps in balancing load and reducing harmonic distortion, while autotransformers have a single continuous winding with taps that serve as both primary and secondary windings, making them more compact and efficient. The zigzag winding configuration is designed specifically for grounding and neutral grounding applications, providing a stable neutral point, whereas autotransformers primarily provide voltage transformation with a simple winding arrangement. Your choice between these transformers depends on whether you prioritize harmonic mitigation and grounding (zigzag) or cost-effective voltage regulation with reduced material (autotransformer).
Core Working Principles
Zigzag transformers operate by connecting windings in a zigzag pattern, which effectively cancels triplen harmonics and improves neutral grounding by providing a stable neutral point. Autotransformers use a single winding with taps, allowing part of the winding to act as both primary and secondary, resulting in reduced size, weight, and copper usage compared to traditional transformers. The core working principle of zigzag transformers centers on harmonic mitigation and grounding, whereas autotransformers focus on efficient voltage transformation through shared winding sections.
Voltage Regulation Capabilities
Zigzag transformers offer superior voltage regulation capabilities by effectively balancing unbalanced loads and minimizing voltage fluctuations in three-phase systems. Autotransformers provide limited voltage regulation as they share part of the winding between primary and secondary, resulting in reduced impedance and less voltage drop under load conditions. Your choice depends on the need for stable voltage output and system protection requirements.
Applications: Where Each Transformer Excels
Zigzag transformers excel in grounding and harmonic mitigation applications, commonly used in distribution systems to provide stable neutral grounding and reduce triplen harmonics, enhancing power quality. Autotransformers are preferred in voltage regulation and interconnection scenarios, offering efficient voltage step-up or step-down with reduced material use, making them ideal for power transmission and industrial motor starting. While zigzag transformers enhance system stability in distribution networks, autotransformers optimize energy efficiency in voltage transformation tasks.
Neutral Grounding and Harmonic Suppression
Zigzag transformers provide effective neutral grounding by creating a stable neutral point, which helps in limiting earth fault currents and improving system safety. They excel in harmonic suppression by canceling triplen harmonics due to their unique winding configuration, reducing distortion in the power system. Your choice between zigzag and autotransformers should consider these benefits, especially for applications requiring enhanced neutral grounding and harmonic control.
Efficiency and Power Loss Comparisons
Zigzag transformers exhibit lower core losses and improved harmonic reduction compared to autotransformers, enhancing efficiency in specific applications. Autotransformers typically deliver higher overall efficiency due to reduced copper losses from their shared winding design, especially under partial load conditions. Power loss in zigzag transformers is primarily associated with complex magnetic flux distribution, while autotransformers benefit from minimized copper usage but may introduce voltage regulation challenges.
Cost and Installation Considerations
Zigzag transformers typically have lower manufacturing costs due to simpler core designs but may require more complex installation because of their specific grounding requirements and phase-shift configurations. Autotransformers offer cost savings in material use and weight for similar voltage ratings, leading to easier and faster installation with less space needed. When choosing between the two, evaluating site constraints and budget for installation labor versus transformer unit cost is crucial.
Safety, Protection, and Reliability
Zigzag transformers provide enhanced safety through effective grounding and harmonic mitigation, reducing fault currents and electrical noise for reliable system operation. Autotransformers offer improved efficiency and reliability with lower losses but pose higher risks of electrical shock due to the shared primary and secondary winding design. Protective measures such as circuit breakers and fuses are critical for both types to ensure system stability and prevent damage from overloads or short circuits.
Choosing Between Zigzag Transformer and Autotransformer
Choosing between a zigzag transformer and an autotransformer depends on application-specific requirements such as grounding, voltage regulation, and cost efficiency. Zigzag transformers excel in neutral grounding and harmonic mitigation, making them ideal for stabilizing unbalanced loads, while autotransformers provide a more cost-effective and compact solution for voltage stepping with higher efficiency where isolation is not critical. Evaluating system needs like isolation, load balancing, and budget constraints is crucial for selecting the appropriate transformer type.
zigzag transformer vs autotransformer Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com