A synchronous generator produces electricity by rotating a magnetic field within stationary armature windings, offering consistent frequency and voltage ideal for large-scale power applications, while an inverter generator converts AC to DC and then back to clean, stable AC, providing more efficient, portable, and quieter power suitable for sensitive electronics. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right generator for your specific needs; continue reading to explore their detailed comparisons and advantages.
Table of Comparison
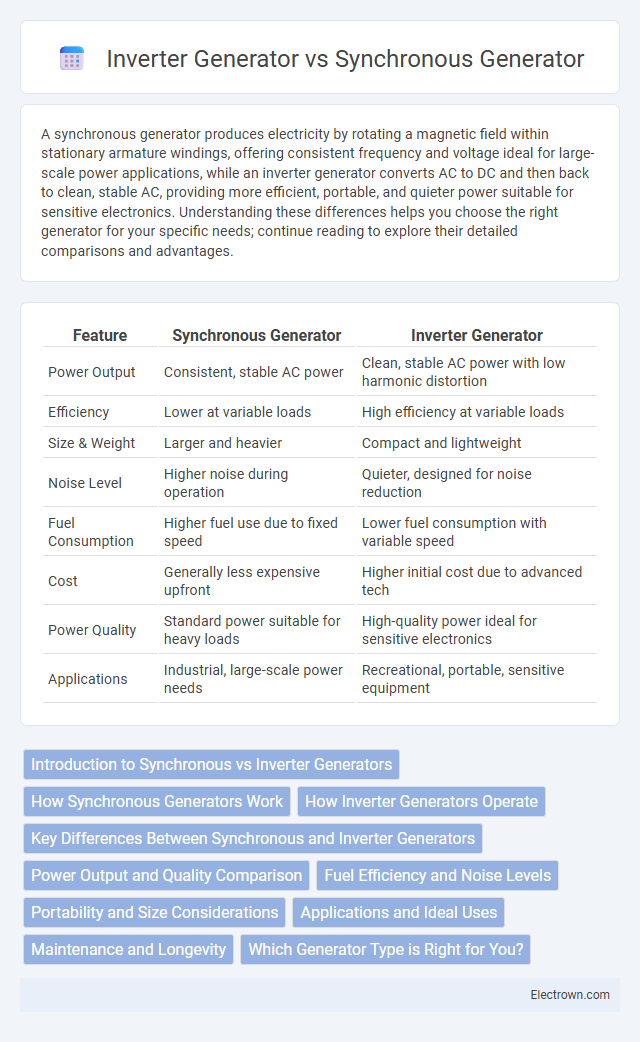
| Feature | Synchronous Generator | Inverter Generator |
|---|---|---|
| Power Output | Consistent, stable AC power | Clean, stable AC power with low harmonic distortion |
| Efficiency | Lower at variable loads | High efficiency at variable loads |
| Size & Weight | Larger and heavier | Compact and lightweight |
| Noise Level | Higher noise during operation | Quieter, designed for noise reduction |
| Fuel Consumption | Higher fuel use due to fixed speed | Lower fuel consumption with variable speed |
| Cost | Generally less expensive upfront | Higher initial cost due to advanced tech |
| Power Quality | Standard power suitable for heavy loads | High-quality power ideal for sensitive electronics |
| Applications | Industrial, large-scale power needs | Recreational, portable, sensitive equipment |
Introduction to Synchronous vs Inverter Generators
Synchronous generators produce electricity through the mechanical rotation of a magnetic field inside stationary coils, offering stable voltage output and high efficiency suitable for large-scale power applications. Inverter generators convert AC power to DC and then back to stable AC output using electronic circuitry, providing cleaner, more consistent electricity ideal for sensitive electronics and portable use. The key difference lies in the energy conversion and regulation process, affecting noise level, fuel efficiency, and power quality.
How Synchronous Generators Work
Synchronous generators operate by rotating a magnetic field within a stationary armature, producing alternating current (AC) at a constant frequency synchronized with the rotor speed. The rotor, energized by a DC field winding, creates a rotating magnetic flux that induces voltage in the stator windings through electromagnetic induction. This synchronous operation ensures stable voltage and frequency output, making synchronous generators ideal for grid power generation and large-scale industrial applications.
How Inverter Generators Operate
Inverter generators convert raw AC power into DC using a rectifier, then invert it back to stable, clean AC electricity through electronic circuits, ensuring consistent voltage and frequency. Unlike synchronous generators that rely on mechanical speed control for output stability, inverter generators use advanced microprocessors to adjust engine speed efficiently based on load demand. This process results in quieter operation, improved fuel efficiency, and cleaner power suitable for sensitive electronics.
Key Differences Between Synchronous and Inverter Generators
Synchronous generators produce electricity by rotating a magnetic field within stationary coils, providing consistent voltage output ideal for stable power applications. Inverter generators convert AC power to DC and then invert it back to stable AC, enabling variable engine speeds that improve fuel efficiency and reduce noise. Synchronous generators are generally larger and louder, while inverter generators offer portable, quieter operation with cleaner power suitable for sensitive electronics.
Power Output and Quality Comparison
Synchronous generators deliver stable power output with consistent frequency and voltage, ideal for industrial and heavy-duty applications requiring high reliability and efficiency. Inverter generators provide cleaner, more stable electrical signals with low total harmonic distortion (THD), making them suitable for sensitive electronics and variable loads. Power output in synchronous generators scales with engine speed, while inverter generators adjust output electronically, enabling better fuel efficiency and quieter operation.
Fuel Efficiency and Noise Levels
Synchronous generators typically offer better fuel efficiency under consistent loads due to their direct mechanical energy conversion, making them ideal for steady power demands. Inverter generators use advanced electronics to regulate engine speed, resulting in significantly lower noise levels and improved efficiency during variable loads. Your choice depends on whether fuel economy or quieter operation is your primary concern.
Portability and Size Considerations
Inverter generators are typically more compact and lightweight than synchronous generators, making them highly portable and ideal for outdoor activities or emergency use. Synchronous generators tend to be larger and heavier due to their robust construction and traditional design, limiting their suitability for mobile applications. Your choice depends on whether ease of transport and space-saving are priorities for your power needs.
Applications and Ideal Uses
Synchronous generators are commonly used in large-scale power plants and industrial applications due to their ability to provide stable, consistent voltage and handle heavy loads efficiently. Inverter generators excel in portable and outdoor applications such as camping, tailgating, and emergency backup power, thanks to their lightweight design, fuel efficiency, and clean, stable power output ideal for sensitive electronics. Your choice depends on whether you need robust, high-capacity energy production or quiet, portable, and reliable power for smaller-scale uses.
Maintenance and Longevity
Synchronous generators require regular maintenance such as brush replacement, bearing lubrication, and periodic inspection of rotor windings to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Inverter generators, featuring solid-state electronics and fewer moving parts, demand less frequent maintenance and typically offer a longer operational lifespan with minimal upkeep. Your choice between them should consider the balance between maintenance efforts and desired generator longevity for your specific application.
Which Generator Type is Right for You?
A synchronous generator is ideal for applications requiring stable voltage and frequency, such as industrial power systems, due to its efficiency and reliability in continuous operation. Inverter generators excel in portability, fuel efficiency, and producing clean, stable power suitable for sensitive electronics and outdoor activities. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize heavy-duty performance or quiet, versatile power for electronic devices.
synchronous generator vs inverter generator Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com