A unidirectional diode allows current to flow in only one direction, making it ideal for rectification and circuit protection where current control is essential, while a bidirectional diode permits current flow in both directions, commonly used in AC signal applications and surge protection. Discover how understanding the differences between these diodes can enhance Your electronic designs by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
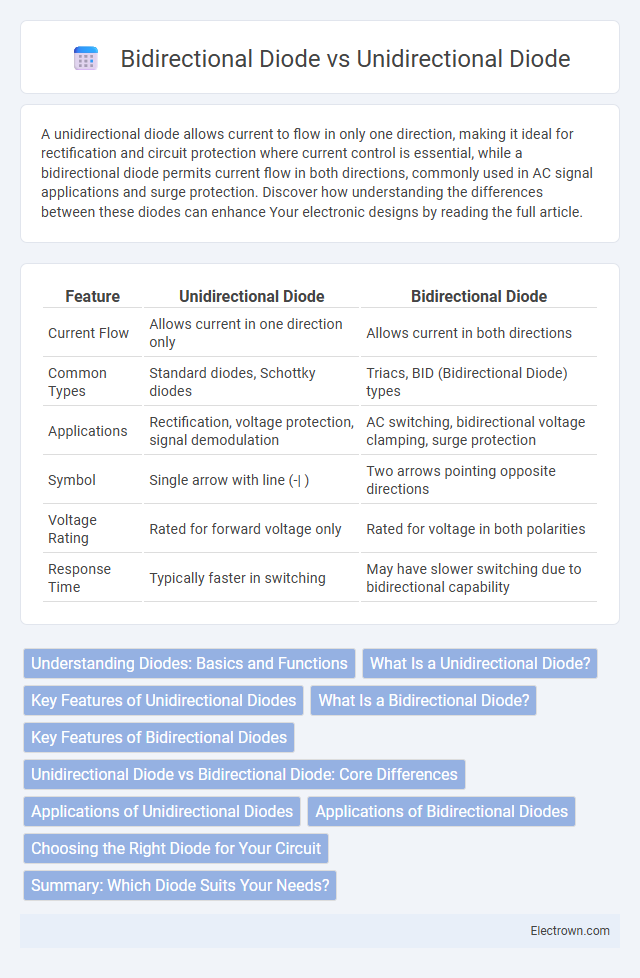
| Feature | Unidirectional Diode | Bidirectional Diode |
|---|---|---|
| Current Flow | Allows current in one direction only | Allows current in both directions |
| Common Types | Standard diodes, Schottky diodes | Triacs, BID (Bidirectional Diode) types |
| Applications | Rectification, voltage protection, signal demodulation | AC switching, bidirectional voltage clamping, surge protection |
| Symbol | Single arrow with line (-| ) | Two arrows pointing opposite directions |
| Voltage Rating | Rated for forward voltage only | Rated for voltage in both polarities |
| Response Time | Typically faster in switching | May have slower switching due to bidirectional capability |
Understanding Diodes: Basics and Functions
Unidirectional diodes, such as standard rectifier diodes, allow current to flow in a single direction, making them essential for converting AC to DC in power supplies and protecting circuits from reverse voltage. Bidirectional diodes, like transient voltage suppression (TVS) diodes or DIACs, can conduct current in both directions, offering enhanced protection against voltage spikes and enabling triggering functions in AC circuits. Understanding these operational differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate diode in applications involving current flow control, voltage regulation, and circuit protection.
What Is a Unidirectional Diode?
A unidirectional diode allows current to flow in only one direction, making it essential for tasks like rectification in power supplies. Unlike bidirectional diodes, which can conduct current both ways and are often used in AC voltage protection, unidirectional diodes prevent reverse current that could damage circuits. Your electronic designs benefit from choosing a unidirectional diode to ensure precise control of current flow and protect sensitive components.
Key Features of Unidirectional Diodes
Unidirectional diodes allow current flow in a single direction, providing efficient rectification and protection against reverse voltage. Their key features include low forward voltage drop, fast switching speed, and high reverse voltage ratings, making them ideal for applications like power supplies and signal demodulation. You can rely on their precise control of electrical current to safeguard circuits and ensure consistent performance.
What Is a Bidirectional Diode?
A bidirectional diode, also known as a triac or bidirectional thyristor, allows current to flow in both directions when triggered, making it suitable for AC switching applications. Unlike a unidirectional diode, which conducts current in only one direction and blocks it in the reverse direction, a bidirectional diode can control alternating current by switching on during both positive and negative cycles. Bidirectional diodes are commonly used in dimmer switches, AC power control, and motor speed regulators due to their ability to handle bidirectional current flow efficiently.
Key Features of Bidirectional Diodes
Bidirectional diodes, also known as Transient Voltage Suppression (TVS) diodes, protect circuits by clamping voltage spikes in both directions, making them ideal for AC signals or environments with unpredictable voltage polarity. Unlike unidirectional diodes that allow current flow in only one direction, bidirectional diodes conduct equally in forward and reverse bias when triggered by voltage surges. Your circuit gains enhanced protection against transient voltage events, minimizing damage from electrostatic discharge (ESD) or lightning-induced surges.
Unidirectional Diode vs Bidirectional Diode: Core Differences
Unidirectional diodes allow current to flow in only one direction, making them ideal for rectification in DC circuits. Bidirectional diodes, such as TRIACs, conduct current in both directions and are commonly used in AC power control applications. Understanding these core differences helps you select the appropriate diode type for your circuit's voltage and current requirements.
Applications of Unidirectional Diodes
Unidirectional diodes are crucial in rectification processes, converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) in power supplies and battery charging circuits. They are widely used in signal demodulation, voltage clamping, and protecting circuits from voltage spikes in automotive and industrial applications. Their ability to allow current flow in only one direction makes them ideal for ensuring the correct polarity in electronic devices and preventing reverse current damage.
Applications of Bidirectional Diodes
Bidirectional diodes, commonly used in circuit protection, serve as voltage clamps to safeguard sensitive components from voltage spikes in AC power systems and signal lines. Their ability to conduct current in both directions makes them ideal for suppressing transient voltage surges in devices such as surge protectors, telecommunications equipment, and power supplies. Unlike unidirectional diodes, bidirectional diodes efficiently handle alternating currents, ensuring reliable overvoltage protection in symmetric waveforms.
Choosing the Right Diode for Your Circuit
Choosing the right diode for your circuit depends on the direction of current flow and voltage requirements. A unidirectional diode allows current to flow in only one direction, making it ideal for rectification and protection against reverse polarity, while a bidirectional diode, such as a TRIAC or a bidirectional TVS diode, handles current flow in both directions and is used for AC applications or transient voltage suppression. Your circuit's specific needs for current direction control and voltage protection determine whether a unidirectional diode or a bidirectional diode is the optimal choice.
Summary: Which Diode Suits Your Needs?
Unidirectional diodes allow current flow in a single direction, ideal for rectification and protection circuits where polarity matters, while bidirectional diodes conduct in both directions, making them suitable for AC signal clipping and transient voltage suppression. Your choice depends on whether your application involves DC circuits requiring polarity control or AC environments needing symmetrical protection. Understanding the role of each diode type ensures you select the component that best suits your electrical and electronic design requirements.
unidirectional diode vs bidirectional diode Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com