PFC (Power Factor Correction) improves the efficiency of electrical systems by reducing reactive power, while VFD (Variable Frequency Drive) controls motor speed and torque by varying the frequency and voltage supplied to the motor. Understand how these technologies differ and complement each other to optimize your power and motor control needs by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
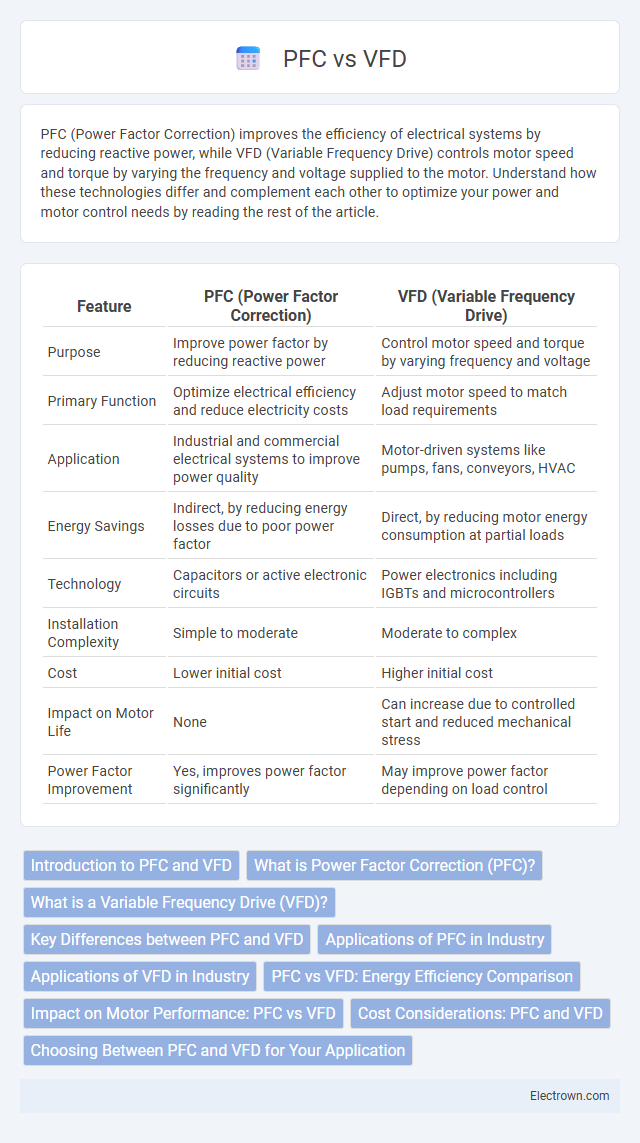
| Feature | PFC (Power Factor Correction) | VFD (Variable Frequency Drive) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Improve power factor by reducing reactive power | Control motor speed and torque by varying frequency and voltage |
| Primary Function | Optimize electrical efficiency and reduce electricity costs | Adjust motor speed to match load requirements |
| Application | Industrial and commercial electrical systems to improve power quality | Motor-driven systems like pumps, fans, conveyors, HVAC |
| Energy Savings | Indirect, by reducing energy losses due to poor power factor | Direct, by reducing motor energy consumption at partial loads |
| Technology | Capacitors or active electronic circuits | Power electronics including IGBTs and microcontrollers |
| Installation Complexity | Simple to moderate | Moderate to complex |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Impact on Motor Life | None | Can increase due to controlled start and reduced mechanical stress |
| Power Factor Improvement | Yes, improves power factor significantly | May improve power factor depending on load control |
Introduction to PFC and VFD
Power Factor Correction (PFC) and Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) are essential technologies used to improve electrical system efficiency. PFC optimizes the power factor by reducing reactive power, thereby minimizing energy losses and lowering utility charges. VFD controls motor speed by adjusting supply frequency, enhancing process control and reducing energy consumption in variable load applications.
What is Power Factor Correction (PFC)?
Power Factor Correction (PFC) is an electrical technique designed to improve the power factor of an AC power system by reducing the phase difference between voltage and current. It enhances energy efficiency by minimizing reactive power, which leads to lower electricity costs and decreased strain on electrical infrastructure. PFC is often implemented using passive components like capacitors or active electronic circuits to achieve optimal power delivery in industrial and commercial applications.
What is a Variable Frequency Drive (VFD)?
A Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) is an electronic device that controls motor speed and torque by varying the frequency and voltage supplied to an electric motor. VFDs enhance energy efficiency and extend equipment lifespan by enabling precise motor operation tailored to specific load requirements. Common applications include HVAC systems, conveyor belts, and pumps where adjustable motor speed improves performance and reduces energy consumption.
Key Differences between PFC and VFD
Power Factor Correction (PFC) improves electrical efficiency by reducing reactive power and enhancing power factor, whereas Variable Frequency Drives (VFD) control motor speed and torque by adjusting voltage and frequency. PFC devices primarily optimize energy consumption on the electrical supply side, while VFDs provide precise motor control and energy savings through variable speed operation. Your choice between PFC and VFD depends on whether the goal is improving power quality or controlling motor performance.
Applications of PFC in Industry
Power Factor Correction (PFC) is widely applied in industries to enhance energy efficiency and reduce electricity costs by minimizing reactive power consumption in electrical systems. Common industrial applications include large motors, lighting systems, and transformer loads where PFC devices improve overall power quality and reduce penalties from utility providers. Your facility benefits from PFC by achieving optimized energy usage, extended equipment lifespan, and compliance with power regulations.
Applications of VFD in Industry
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) are extensively used in industries to control motor speed and torque, enhancing energy efficiency in HVAC systems, conveyors, and pumps. They enable precise process control in manufacturing lines, reducing wear and extending equipment lifespan. VFD applications also include optimizing compressor performance in refrigeration and improving performance in mining and water treatment plants.
PFC vs VFD: Energy Efficiency Comparison
PFC (Power Factor Correction) improves energy efficiency by reducing reactive power and optimizing the electrical system's power factor, leading to lower electricity costs and less strain on the grid. VFD (Variable Frequency Drive) enhances efficiency by adjusting motor speed to match load requirements, significantly reducing energy consumption in variable-load applications. Your choice between PFC and VFD depends on whether your goal is to improve power quality or optimize motor control for energy savings.
Impact on Motor Performance: PFC vs VFD
Power Factor Correction (PFC) improves motor efficiency by optimizing the power factor, reducing reactive power and minimizing energy losses without altering motor speed or torque characteristics. Variable Frequency Drives (VFD) enhance motor performance by controlling motor speed and torque through adjustable frequency and voltage, leading to precise motor control, energy savings, and reduced mechanical stress during starts and stops. Unlike PFC, which primarily targets power quality improvement, VFDs directly influence motor operational dynamics for performance optimization.
Cost Considerations: PFC and VFD
Power Factor Correction (PFC) devices generally incur lower initial costs compared to Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs), making them more cost-effective for applications primarily targeting power factor improvement. VFDs, while more expensive upfront, offer energy savings and enhanced process control by adjusting motor speed, leading to reduced operational costs over time. Maintenance and installation expenses for VFDs tend to be higher due to their complexity, whereas PFC units have simpler designs with lower ongoing costs.
Choosing Between PFC and VFD for Your Application
Choosing between Power Factor Correction (PFC) and Variable Frequency Drives (VFD) depends on your application's specific needs for energy efficiency and motor control. PFC improves power quality by reducing reactive power and enhancing system power factor, which lowers electricity costs and prevents penalties from utilities. VFDs offer precise motor speed regulation and energy savings by adjusting frequency and voltage, making them ideal for applications requiring variable speed and torque control.
pfc vs vfd Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com