Single phase inverters are typically used for residential or small-scale applications, converting DC to AC power in a single alternating current phase, while three phase inverters are designed for industrial or large-scale operations, providing three alternating current phases for more efficient and stable power delivery. Explore the rest of the article to understand which inverter suits your energy needs best and how each type impacts system performance.
Table of Comparison
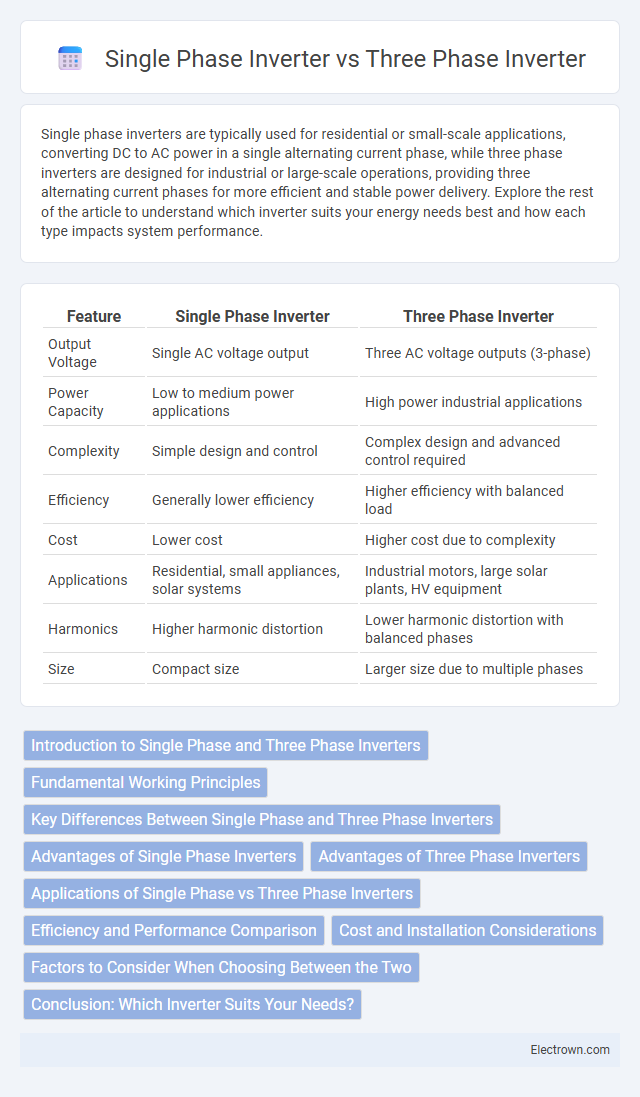
| Feature | Single Phase Inverter | Three Phase Inverter |
|---|---|---|
| Output Voltage | Single AC voltage output | Three AC voltage outputs (3-phase) |
| Power Capacity | Low to medium power applications | High power industrial applications |
| Complexity | Simple design and control | Complex design and advanced control required |
| Efficiency | Generally lower efficiency | Higher efficiency with balanced load |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to complexity |
| Applications | Residential, small appliances, solar systems | Industrial motors, large solar plants, HV equipment |
| Harmonics | Higher harmonic distortion | Lower harmonic distortion with balanced phases |
| Size | Compact size | Larger size due to multiple phases |
Introduction to Single Phase and Three Phase Inverters
Single phase inverters convert direct current (DC) into single phase alternating current (AC), commonly used in residential and light commercial applications due to their simpler design and lower cost. Three phase inverters transform DC into three phase AC, providing more efficient power delivery and smoother operation, ideal for industrial and large-scale commercial systems. The choice between single phase and three phase inverters depends on application power requirements, load type, and system complexity.
Fundamental Working Principles
Single phase inverters convert DC to AC by switching the input through two transistors or switches to create a single sinusoidal output, primarily used in low power applications. Three phase inverters utilize six switches arranged in a bridge configuration to generate three separate AC outputs, each phase shifted by 120 degrees, providing a more stable and efficient power supply ideal for industrial and high power scenarios. Your choice between single and three phase inverters depends on the required load capacity and application complexity.
Key Differences Between Single Phase and Three Phase Inverters
Single phase inverters convert DC power into a single AC waveform suitable for residential or small commercial applications, while three phase inverters generate three separate AC waveforms, providing more consistent power ideal for industrial and large-scale systems. You will find that single phase inverters are simpler, cost-effective, and easier to install, whereas three phase inverters offer higher efficiency, better load distribution, and reduced harmonic distortion. The key differences also include power capacity, waveform quality, and applications, with three phase inverters preferred for heavy machinery and grid-tied solar systems.
Advantages of Single Phase Inverters
Single phase inverters offer advantages such as simpler design, lower cost, and easier installation compared to three phase inverters. They are ideal for residential applications and small-scale systems where power demand is moderate and balanced loads are common. Your choice of a single phase inverter ensures efficient operation in settings with limited space and budget constraints.
Advantages of Three Phase Inverters
Three phase inverters offer higher efficiency and smoother power delivery compared to single phase inverters, making them ideal for industrial and large-scale applications. Their ability to provide balanced loads reduces the risk of equipment damage and improves the lifespan of electrical systems. If you need reliable and consistent power output for complex machinery, three phase inverters are the superior choice.
Applications of Single Phase vs Three Phase Inverters
Single-phase inverters are primarily used in residential solar power systems, small-scale uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and portable electronics due to their simplicity and cost-effectiveness for low power applications. Three-phase inverters dominate industrial environments, commercial power systems, and large-scale renewable energy installations, providing efficient power conversion and smoother output for heavy machinery and three-phase motors. The choice between single-phase and three-phase inverters depends on the application's power requirements, load balancing, and grid integration needs.
Efficiency and Performance Comparison
Single-phase inverters typically offer lower efficiency, around 85-95%, due to higher harmonic distortion and less optimal power conversion for large loads. Three-phase inverters achieve efficiencies above 95%, providing smoother power delivery with reduced harmonic losses, making them ideal for industrial and high-power applications. Performance-wise, three-phase inverters ensure balanced power output and better thermal management, enhancing reliability and operational lifespan compared to single-phase inverters.
Cost and Installation Considerations
Single phase inverters generally have lower upfront costs and simpler installation requirements, making them suitable for small-scale residential applications. Three phase inverters, while more expensive and complex to install due to additional wiring and components, offer higher efficiency and better performance for commercial or industrial systems. Your choice depends on balancing budget constraints with the scale and power needs of the installation site.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between the Two
When choosing between a single phase inverter and a three phase inverter, consider your power requirements, load type, and efficiency needs. Single phase inverters are suitable for residential applications with lower power demands, while three phase inverters offer better performance for industrial or commercial use with higher loads and balanced power distribution. Your decision should also account for installation complexity, cost, and the specific electrical infrastructure available.
Conclusion: Which Inverter Suits Your Needs?
Single phase inverters are ideal for residential and small-scale applications due to their simpler design and lower cost, providing efficient power conversion for household appliances. Three phase inverters suit industrial and commercial environments requiring higher power capacity, better efficiency, and smoother motor operation. Choosing between them depends on load requirements, system complexity, and budget considerations.
Single phase inverter vs Three phase inverter Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com