A coupling capacitor and a DC blocking capacitor both serve to prevent DC current from passing between circuit stages while allowing AC signals to flow, but coupling capacitors primarily connect two active circuit elements for signal transfer, whereas DC blocking capacitors are often used to isolate sensitive components from unwanted DC. Understanding the subtle differences in their applications can enhance your circuit design; continue reading to explore their functions and uses in detail.
Table of Comparison
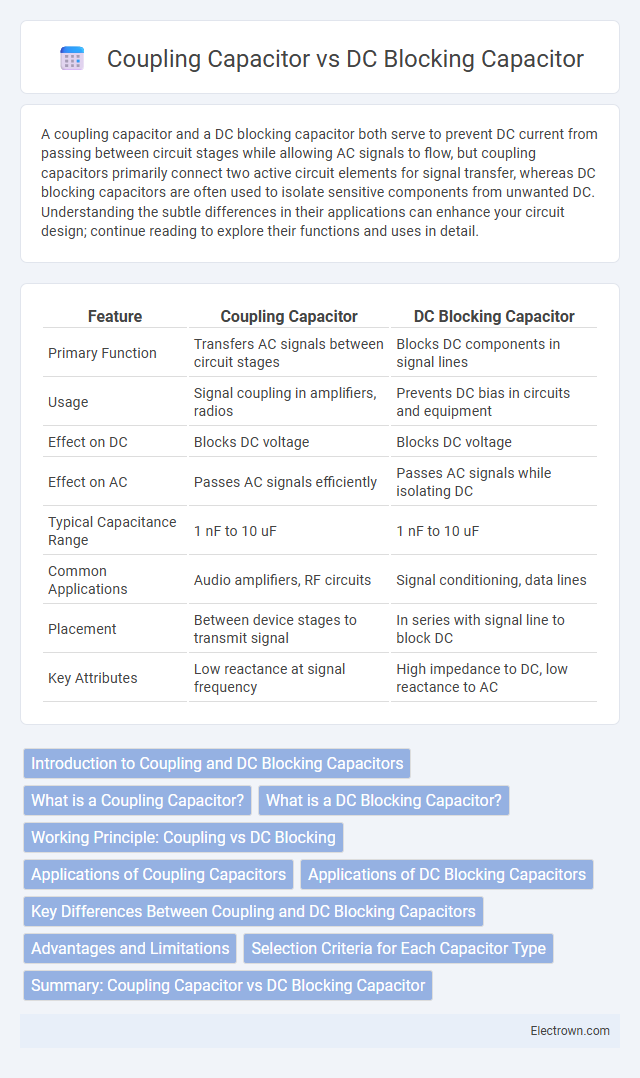
| Feature | Coupling Capacitor | DC Blocking Capacitor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Transfers AC signals between circuit stages | Blocks DC components in signal lines |
| Usage | Signal coupling in amplifiers, radios | Prevents DC bias in circuits and equipment |
| Effect on DC | Blocks DC voltage | Blocks DC voltage |
| Effect on AC | Passes AC signals efficiently | Passes AC signals while isolating DC |
| Typical Capacitance Range | 1 nF to 10 uF | 1 nF to 10 uF |
| Common Applications | Audio amplifiers, RF circuits | Signal conditioning, data lines |
| Placement | Between device stages to transmit signal | In series with signal line to block DC |
| Key Attributes | Low reactance at signal frequency | High impedance to DC, low reactance to AC |
Introduction to Coupling and DC Blocking Capacitors
Coupling capacitors and DC blocking capacitors are essential components in electronic circuits that control signal transmission while isolating DC voltage levels. Coupling capacitors transfer AC signals between circuit stages without allowing DC current to pass, ensuring proper biasing and signal integrity. DC blocking capacitors specifically prevent DC components from reaching sensitive parts of the circuit, protecting components and maintaining desired operating points.
What is a Coupling Capacitor?
A coupling capacitor is an electronic component used to transmit AC signals between circuit stages while blocking DC voltage, preventing unwanted DC bias from affecting subsequent stages. Unlike general DC blocking capacitors that solely prevent DC flow, coupling capacitors specifically facilitate signal transfer without distortion or loss. Understanding the role of a coupling capacitor helps you maintain signal integrity in amplifiers, audio equipment, and communication devices.
What is a DC Blocking Capacitor?
A DC blocking capacitor is designed to prevent direct current (DC) from passing through a circuit while allowing alternating current (AC) signals to flow. It is commonly used in signal processing and communication systems to isolate different stages without affecting the AC signal integrity. Unlike general coupling capacitors, which can serve various purposes, DC blocking capacitors specifically protect sensitive components from DC bias or voltage shifts.
Working Principle: Coupling vs DC Blocking
Coupling capacitors transfer AC signals between circuit stages while blocking DC, allowing only alternating current to pass through by charging and discharging in sync with the AC waveform. DC blocking capacitors specifically prevent the flow of direct current, isolating different circuit sections from DC biasing and protecting sensitive components. Your choice depends on whether you need to maintain signal integrity by passing AC components or completely block DC to prevent interference.
Applications of Coupling Capacitors
Coupling capacitors are primarily used in audio and radio frequency circuits to transfer AC signals between stages while blocking DC components, preserving biasing conditions. They enable signal integrity in amplifiers, mixers, and filters by isolating different circuit sections without affecting the AC signal path. These capacitors are critical in communication systems, sensor circuits, and audio equipment where maintaining proper signal transmission and minimizing distortion is essential.
Applications of DC Blocking Capacitors
DC blocking capacitors are primarily used in RF and audio circuits to prevent direct current from passing between stages while allowing AC signals to transmit, protecting sensitive components from DC bias. These capacitors are essential in coupling circuits of amplifiers, mixers, and antenna systems to maintain signal integrity without altering the DC operating points. Their application extends to power supply decoupling and signal line isolation, ensuring stable performance and preventing unwanted DC interference.
Key Differences Between Coupling and DC Blocking Capacitors
Coupling capacitors primarily transfer AC signals between circuit stages while blocking DC components, enabling signal isolation and preventing DC bias from affecting subsequent stages. DC blocking capacitors specifically prevent DC current from passing through a circuit without significantly affecting the AC signal frequencies, ensuring the integrity of AC signal transmission. The key difference lies in their application focus: coupling capacitors are used for signal interfacing and amplification purposes, whereas DC blocking capacitors mainly serve to protect circuit elements from unwanted DC voltages.
Advantages and Limitations
Coupling capacitors enable AC signal transmission between stages while blocking DC, preserving biasing conditions and minimizing signal distortion, but they may introduce low-frequency roll-off and size constraints. DC blocking capacitors specifically prevent DC current flow in circuits to protect components and maintain signal integrity, yet they can cause signal attenuation at low frequencies and require careful capacitance selection to balance performance. Both capacitors play vital roles in electronic circuit design, with trade-offs in frequency response and physical size influencing their application.
Selection Criteria for Each Capacitor Type
Selection criteria for coupling capacitors emphasize low impedance at the signal frequency to ensure efficient AC signal transfer while blocking DC components, typically favoring film or ceramic types due to their stability and low loss characteristics. DC blocking capacitors require high voltage ratings and minimal leakage current to effectively isolate DC voltage levels between circuit stages without signal distortion, often leading to the selection of polypropylene or tantalum capacitors. Consideration of frequency response, voltage handling, and dielectric absorption is critical when distinguishing coupling capacitors from DC blocking capacitors in design applications.
Summary: Coupling Capacitor vs DC Blocking Capacitor
Coupling capacitors and DC blocking capacitors both prevent DC current from passing between circuit stages while allowing AC signals to flow. Coupling capacitors are primarily used in amplifier and signal processing circuits to connect different stages without altering their DC bias points. DC blocking capacitors serve a similar function but are often employed in communication and RF circuits to isolate DC components and protect sensitive components from DC voltage.
Coupling capacitor vs DC blocking capacitor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com