Analog phase shifters provide continuous phase adjustment with low latency and minimal signal distortion, ideal for applications requiring smooth phase transitions, while digital phase shifters offer precise, discrete phase control with easier integration into digital systems and better repeatability. Discover which type of phase shifter best suits your specific needs by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
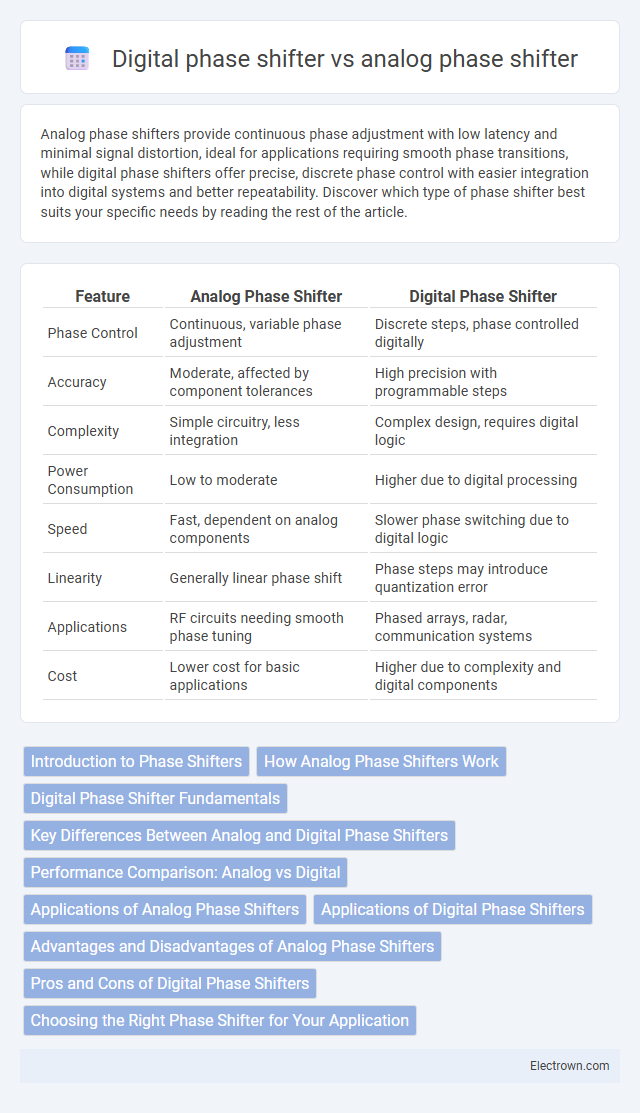
| Feature | Analog Phase Shifter | Digital Phase Shifter |
|---|---|---|
| Phase Control | Continuous, variable phase adjustment | Discrete steps, phase controlled digitally |
| Accuracy | Moderate, affected by component tolerances | High precision with programmable steps |
| Complexity | Simple circuitry, less integration | Complex design, requires digital logic |
| Power Consumption | Low to moderate | Higher due to digital processing |
| Speed | Fast, dependent on analog components | Slower phase switching due to digital logic |
| Linearity | Generally linear phase shift | Phase steps may introduce quantization error |
| Applications | RF circuits needing smooth phase tuning | Phased arrays, radar, communication systems |
| Cost | Lower cost for basic applications | Higher due to complexity and digital components |
Introduction to Phase Shifters
Phase shifters alter the phase of an RF signal to control wave propagation in communication systems. Analog phase shifters provide continuous phase variation using varactors or ferrite elements, offering low insertion loss and fine-tuned adjustments. Digital phase shifters employ discrete steps controlled by digital signals, enabling precise, repeatable phase shifts with greater integration in modern phased array antennas.
How Analog Phase Shifters Work
Analog phase shifters operate by continuously varying the phase of an input signal using components such as varactor diodes, ferrite materials, or transmission line elements, enabling smooth phase adjustment across a range of frequencies. Unlike digital phase shifters that use discrete steps controlled by switches or digital circuits, analog phase shifters offer finer resolution and minimal signal distortion due to their continuous tuning nature. These devices are crucial in RF and microwave applications where precise phase control impacts beam steering, signal synchronization, and impedance matching.
Digital Phase Shifter Fundamentals
Digital phase shifters manipulate signal phase by using discrete time delays or digitally controlled phase steps, offering precise and repeatable phase adjustments compared to analog phase shifters, which rely on continuous analog components. These devices utilize digital control signals to switch between predefined phase states, making them highly suitable for applications requiring rapid and accurate phase modulation. Your system benefits from digital phase shifters' immunity to component aging and temperature variations, resulting in stable performance over time.
Key Differences Between Analog and Digital Phase Shifters
Analog phase shifters provide continuous phase adjustment through voltage-controlled elements like varactors or ferrite components, enabling smooth phase variation ideal for narrowband applications. Digital phase shifters use discrete phase steps controlled by digital signals, offering precise, repeatable phase shifts with better integration in complex systems such as phased array antennas. The main differences lie in resolution, linearity, power consumption, and complexity, where analog shifters excel in fine-tuning and low power, while digital shifters provide scalability and improved reliability through digital control.
Performance Comparison: Analog vs Digital
Analog phase shifters offer continuous phase adjustment with low insertion loss and minimal signal distortion, making them ideal for high-frequency applications requiring smooth phase variation. Digital phase shifters provide precise and repeatable phase control through discrete steps, enabling easier integration with digital systems and improved stability over temperature variations. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize analog signal fidelity or digital control accuracy in your specific application.
Applications of Analog Phase Shifters
Analog phase shifters are widely applied in radar systems, communication antennas, and phased array beamforming where continuous phase adjustment is crucial. Their ability to provide low insertion loss and high linearity makes them ideal for applications requiring precise amplitude and phase control. These devices are commonly used in satellite communication, electronic warfare, and instrumentation for signal processing and direction finding.
Applications of Digital Phase Shifters
Digital phase shifters are widely used in radar systems, satellite communications, and phased array antennas due to their precise phase control and programmability. Their ability to provide fast switching speeds and repeatability makes them ideal for beam steering and adaptive signal processing in modern wireless networks. Digital phase shifters also enhance signal integrity in microwave and millimeter-wave applications, improving overall system performance.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Analog Phase Shifters
Analog phase shifters offer continuous phase adjustment and low insertion loss, making them ideal for applications requiring smooth and precise phase control, such as phased array antennas. However, they suffer from issues like limited linearity, temperature sensitivity, and calibration complexity, which can affect performance stability over time. Despite these drawbacks, their simplicity and low power consumption remain advantageous in cost-sensitive and analog signal processing scenarios.
Pros and Cons of Digital Phase Shifters
Digital phase shifters offer precise and repeatable phase control with high resolution, making them ideal for applications requiring accurate beam steering and signal alignment. They provide programmability and ease of integration with digital control systems, enabling rapid adjustments and automation. However, digital phase shifters may introduce increased insertion loss and power consumption compared to analog counterparts, and their discrete phase steps can cause quantization errors in certain high-precision applications.
Choosing the Right Phase Shifter for Your Application
Analog phase shifters offer continuous phase adjustment with low insertion loss, making them ideal for applications requiring smooth phase control and minimal signal distortion. Digital phase shifters provide discrete phase steps with high precision and repeatability, suitable for systems needing programmable and stable phase settings. Selecting the right phase shifter depends on factors such as desired phase resolution, insertion loss tolerance, control complexity, and the specific application's frequency range.
Analog phase shifter vs digital phase shifter Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com