A level shifter translates voltage levels between different logic families without altering signal information, while a comparator compares two voltages and outputs a digital signal indicating which is higher. Understanding the distinct functions of these devices can optimize Your electronic circuit design; explore further to learn their specific applications and advantages.
Table of Comparison
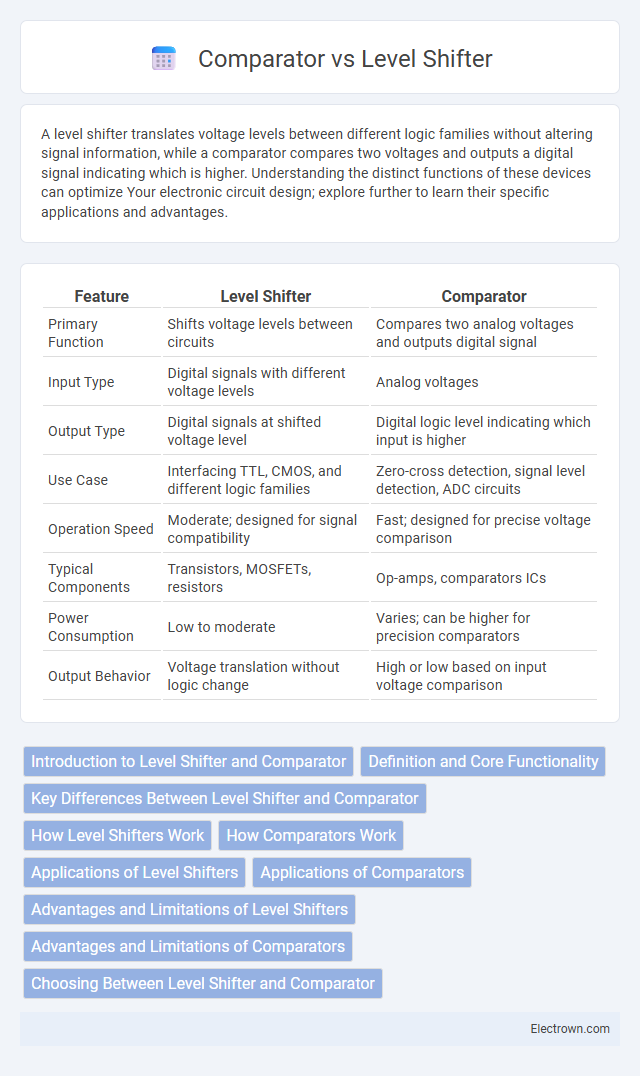
| Feature | Level Shifter | Comparator |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Shifts voltage levels between circuits | Compares two analog voltages and outputs digital signal |
| Input Type | Digital signals with different voltage levels | Analog voltages |
| Output Type | Digital signals at shifted voltage level | Digital logic level indicating which input is higher |
| Use Case | Interfacing TTL, CMOS, and different logic families | Zero-cross detection, signal level detection, ADC circuits |
| Operation Speed | Moderate; designed for signal compatibility | Fast; designed for precise voltage comparison |
| Typical Components | Transistors, MOSFETs, resistors | Op-amps, comparators ICs |
| Power Consumption | Low to moderate | Varies; can be higher for precision comparators |
| Output Behavior | Voltage translation without logic change | High or low based on input voltage comparison |
Introduction to Level Shifter and Comparator
A level shifter is an electronic circuit designed to translate voltage signals between different logic levels, enabling compatibility between components operating at different voltage domains. A comparator is an analog device that compares two input voltages and outputs a digital signal indicating which input is higher, commonly used in threshold detection and analog-to-digital conversion. Both devices serve distinct roles in electronic systems, with level shifters facilitating signal interfacing and comparators enabling voltage comparison and decision-making functions.
Definition and Core Functionality
A level shifter is an electronic circuit designed to translate signals between different voltage domains, ensuring proper communication between components operating at varying voltage levels. A comparator is an analog device that compares two input voltages and outputs a digital signal indicating which input is higher. While level shifters focus on voltage translation for interfacing, comparators serve as decision-making elements in signal processing and analog-to-digital conversion.
Key Differences Between Level Shifter and Comparator
Level shifters translate signal voltages between different logic levels, ensuring compatibility between circuits operating at different voltage domains. Comparators compare two input voltages and output a digital signal indicating which input is higher, functioning as an analog-to-digital converter. Key differences include their purpose--level shifters focus on voltage translation for interfacing, while comparators perform voltage comparison for decision-making in circuits.
How Level Shifters Work
Level shifters work by translating voltage signals between different logic levels, enabling communication between components operating at incompatible voltage domains. They typically use transistor pairs or dedicated ICs to shift input voltage to a desired output voltage without altering the signal's logic state. Your circuits benefit from level shifters in mixed-voltage environments, ensuring reliable data transfer and preventing damage to sensitive components.
How Comparators Work
Comparators work by comparing two input voltages and outputting a digital signal indicating which input is higher, typically producing a high or low logic level. They utilize differential amplifiers to detect voltage differences and switch states instantly when the input crosses a reference threshold. This operation enables precise voltage level detection, essential for analog-to-digital conversion and signal thresholding.
Applications of Level Shifters
Level shifters are essential in interfacing circuits operating at different voltage domains, commonly used in communication protocols like I2C, SPI, and UART to ensure signal integrity and prevent damage. They are widely applied in mixed-voltage systems, such as integrating 3.3V microcontrollers with 5V sensors or modules in embedded systems. Level shifters also facilitate power management in complex SoCs by enabling cross-voltage data transfer between low-power and high-performance components.
Applications of Comparators
Comparators are essential in analog-to-digital conversion for detecting voltage thresholds and triggering digital signals, widely used in sensor interfaces and signal conditioning circuits. They play a critical role in zero-crossing detectors, pulse-width modulation circuits, and over-voltage protection systems for precise monitoring and control. Unlike level shifters, comparators actively compare input signals against reference voltages to produce binary output rather than merely translating voltage levels.
Advantages and Limitations of Level Shifters
Level shifters enable seamless voltage translation between different logic levels, ensuring compatibility in mixed-voltage systems and preventing damage to components due to voltage mismatches. They offer low power consumption and simple design, making them ideal for interfacing modern low-voltage microcontrollers with higher voltage peripherals. However, level shifters may exhibit slower switching speeds compared to comparators and are not suitable for signal conditioning where precise threshold detection is required.
Advantages and Limitations of Comparators
Comparators offer high accuracy in signal comparison, enabling precise detection of voltage thresholds in analog-to-digital conversion and signal processing applications. Their limitation lies in susceptibility to noise and input offset voltage, which can affect the reliability of output signals in low-level or high-frequency operations. Unlike level shifters, comparators do not primarily serve to shift voltage levels but instead provide a binary output indicating the relative magnitude of input voltages.
Choosing Between Level Shifter and Comparator
Choosing between a level shifter and a comparator depends on the specific voltage translation and signal conditioning requirements of your circuit. A level shifter is ideal for converting signals between different voltage domains without altering the signal shape, while a comparator provides voltage comparison with a digital output, useful for detecting voltage thresholds. Consider your need for precise threshold detection or simple voltage adaptation when selecting the appropriate device for your application.
Level shifter vs comparator Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com