RC snubbers and MOVs are both used to protect electronic circuits from voltage spikes, but RC snubbers combine resistors and capacitors to dampen transient oscillations and control voltage rise time, while MOVs (Metal Oxide Varistors) absorb high-energy surges by clamping voltage to a safe level. Understanding the differences in their operation and applications will help You choose the right protection for Your circuit; continue reading to explore their detailed comparison and practical uses.
Table of Comparison
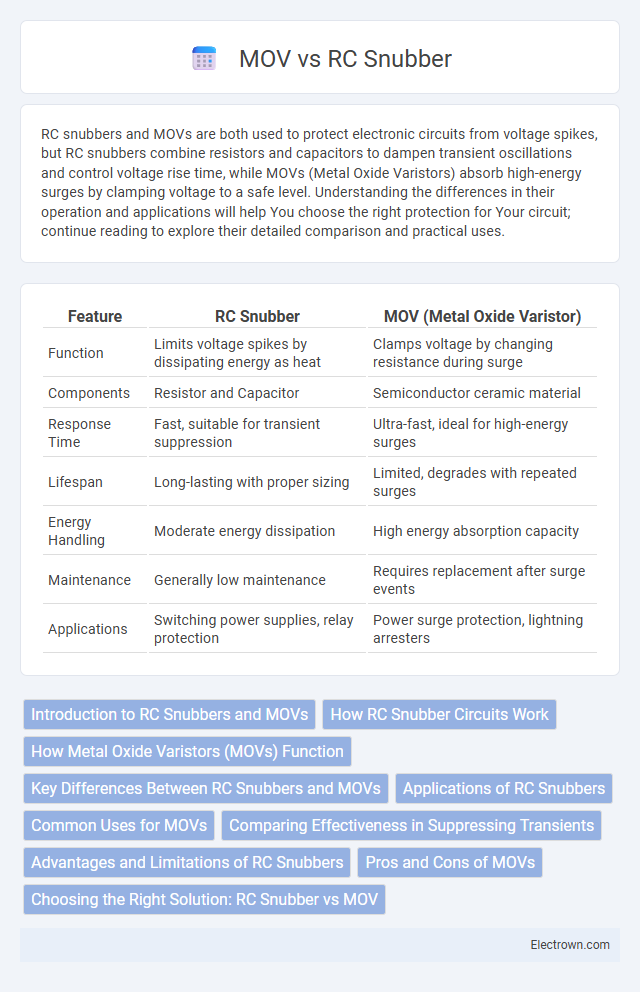
| Feature | RC Snubber | MOV (Metal Oxide Varistor) |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Limits voltage spikes by dissipating energy as heat | Clamps voltage by changing resistance during surge |
| Components | Resistor and Capacitor | Semiconductor ceramic material |
| Response Time | Fast, suitable for transient suppression | Ultra-fast, ideal for high-energy surges |
| Lifespan | Long-lasting with proper sizing | Limited, degrades with repeated surges |
| Energy Handling | Moderate energy dissipation | High energy absorption capacity |
| Maintenance | Generally low maintenance | Requires replacement after surge events |
| Applications | Switching power supplies, relay protection | Power surge protection, lightning arresters |
Introduction to RC Snubbers and MOVs
RC snubbers consist of a resistor-capacitor network designed to suppress voltage spikes and oscillations in electrical circuits, enhancing the lifespan and performance of switching devices. Metal Oxide Varistors (MOVs) are voltage-dependent resistors used to protect circuits from transient overvoltages by clamping high voltage surges. Both RC snubbers and MOVs are essential for transient voltage suppression but differ in functionality, with RC snubbers providing controlled damping and MOVs offering spike absorption.
How RC Snubber Circuits Work
RC snubber circuits absorb voltage spikes by combining a resistor and capacitor in series to control transient energy and limit voltage overshoot in power electronics. The capacitor stores and dissipates the sudden energy surge while the resistor regulates the discharge rate, protecting components from damage. Your electronic devices benefit from reduced electromagnetic interference and increased reliability through effective voltage spike attenuation provided by RC snubbers.
How Metal Oxide Varistors (MOVs) Function
Metal Oxide Varistors (MOVs) protect circuits by clamping high voltage spikes, utilizing a nonlinear resistance that decreases sharply when voltage exceeds a threshold, thereby diverting surge current away from sensitive components. MOVs consist of zinc oxide grains that form numerous grain boundary junctions, enabling rapid response and energy absorption during transient voltage events. Their effectiveness depends on voltage rating, energy absorption capacity, and response time, making them suitable for transient voltage suppression in power and signal lines.
Key Differences Between RC Snubbers and MOVs
RC snubbers combine a resistor and capacitor to suppress voltage spikes and control transient oscillations, offering precise damping and energy dissipation for sensitive electronic circuits. MOVs (Metal Oxide Varistors) provide nonlinear voltage clamping by changing resistance rapidly during voltage surges, protecting devices from high-energy transient spikes by diverting excessive current. RC snubbers excel in reducing high-frequency noise and oscillations, while MOVs are more suited for bulk surge absorption and overvoltage protection in power systems.
Applications of RC Snubbers
RC snubbers effectively protect switching devices in power electronics by suppressing voltage spikes and reducing electromagnetic interference in inductive load applications. They are commonly used in DC circuits, motor drives, and transformer switching to enhance circuit reliability and extend component lifespan. Your equipment benefits from reduced transient voltages and improved noise control when employing RC snubbers in sensitive switching environments.
Common Uses for MOVs
MOVs are commonly used as surge protection devices in power strips, circuit breakers, and consumer electronics to safeguard against voltage spikes. They protect sensitive components by clamping high voltage transients and diverting excess energy away from your devices. The simple design and cost-effectiveness of MOVs make them ideal for applications where transient voltage suppression is critical.
Comparing Effectiveness in Suppressing Transients
RC snubbers and MOVs both protect circuits from voltage transients but operate differently in effectiveness. RC snubbers excel at damping high-frequency transients and reducing voltage overshoot due to their resistive and capacitive components providing controlled energy dissipation. MOVs clamp voltage spikes by diverting excess energy but degrade over time and may be less precise in transient suppression, making RC snubbers often more reliable for protecting sensitive electronic components in your applications.
Advantages and Limitations of RC Snubbers
RC snubbers effectively suppress voltage spikes and reduce electromagnetic interference in switching circuits by dissipating energy through the resistor and capacitor, enhancing circuit longevity. They provide precise control over damping characteristics and can handle repetitive transient voltages with minimal power loss. However, RC snubbers require careful component selection for optimal performance and may introduce heat dissipation challenges, making them less suitable for high-energy surge protection compared to Metal Oxide Varistors (MOVs).
Pros and Cons of MOVs
Metal Oxide Varistors (MOVs) excel at providing effective transient voltage suppression with fast response times, making them ideal for protecting sensitive electronic circuits from voltage spikes. MOVs are cost-effective and simple to install but degrade over time as repeated surges cause permanent changes to their resistance, leading to eventual failure. Your choice should consider that MOVs may require periodic replacement, whereas RC snubbers offer more consistent performance and longer service life in high-frequency switching environments.
Choosing the Right Solution: RC Snubber vs MOV
Choosing between an RC snubber and an MOV depends on your circuit's voltage spike characteristics and response time requirements. RC snubbers provide precise damping and energy dissipation for fast transient suppression in sensitive electronic components, while MOVs excel at absorbing higher energy surges and are more cost-effective for general surge protection. Understanding your device's voltage thresholds and transient frequency helps optimize protection, ensuring longevity and reliability.
RC snubber vs MOV Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com