Voltage mode control regulates the output by comparing the output voltage to a reference, offering simplicity and easy implementation in power converters. Current mode control directly monitors inductor current, enhancing response and stability under varying loads, improving overall performance--explore the article to determine which mode best suits Your application needs.
Table of Comparison
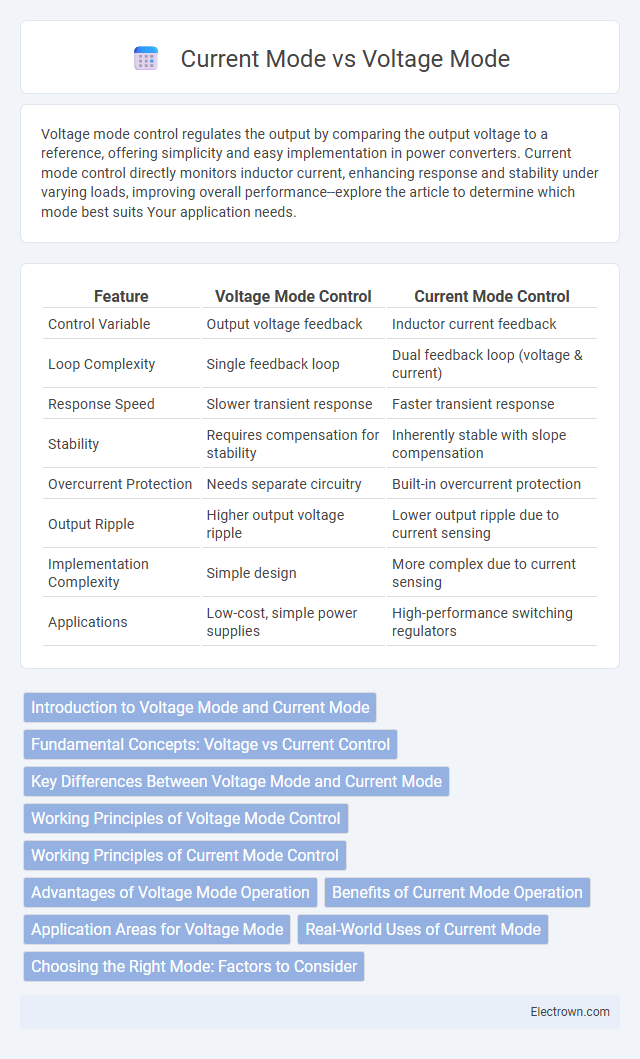
| Feature | Voltage Mode Control | Current Mode Control |
|---|---|---|
| Control Variable | Output voltage feedback | Inductor current feedback |
| Loop Complexity | Single feedback loop | Dual feedback loop (voltage & current) |
| Response Speed | Slower transient response | Faster transient response |
| Stability | Requires compensation for stability | Inherently stable with slope compensation |
| Overcurrent Protection | Needs separate circuitry | Built-in overcurrent protection |
| Output Ripple | Higher output voltage ripple | Lower output ripple due to current sensing |
| Implementation Complexity | Simple design | More complex due to current sensing |
| Applications | Low-cost, simple power supplies | High-performance switching regulators |
Introduction to Voltage Mode and Current Mode
Voltage mode control regulates the output by comparing the output voltage to a reference voltage, adjusting the duty cycle accordingly for stable voltage delivery in power converters. Current mode control directly monitors the inductor current, providing faster response and inherent overcurrent protection by modulating the switch based on current feedback. Your choice between these modes depends on factors like transient response requirements, system complexity, and noise sensitivity in electronic power supply design.
Fundamental Concepts: Voltage vs Current Control
Voltage mode control regulates the output voltage by adjusting the duty cycle based on a voltage feedback loop, ensuring a stable voltage level in power converters. Current mode control directly controls the inductor current through an inner current loop, providing faster response to load changes and inherent overcurrent protection. This fundamental difference affects system stability, transient response, and complexity, making voltage mode suitable for simple applications and current mode ideal for precise current regulation and dynamic load conditions.
Key Differences Between Voltage Mode and Current Mode
Voltage mode control regulates the output by adjusting the duty cycle based on feedback voltage, while current mode control directly manages the inductor current, providing faster response and inherent overcurrent protection. Voltage mode typically features a simpler design but slower transient response, whereas current mode offers improved stability and easier loop compensation, especially in high-frequency switching power supplies. Your choice depends on the desired speed, complexity, and protection requirements in your power supply application.
Working Principles of Voltage Mode Control
Voltage mode control regulates the output voltage by adjusting the duty cycle of the PWM signal based on the error between the reference voltage and the output voltage feedback. This control scheme uses a voltage error amplifier to compare the sensed output voltage with the setpoint, generating a control voltage that modulates the power switch. The continuous monitoring and modulation ensure stable output voltage, making voltage mode control suitable for applications requiring precise voltage regulation.
Working Principles of Current Mode Control
Current mode control regulates the power supply by directly controlling the inductor current, providing faster response and improved transient performance compared to voltage mode control. It uses a feedback loop that compares the sensed inductor current to a reference current, adjusting the duty cycle of the switching transistor to maintain stable operation. This control method inherently limits peak current, enhancing protection and simplifying loop compensation in DC-DC converters.
Advantages of Voltage Mode Operation
Voltage mode operation offers superior stability and simpler control loop design, making it ideal for applications requiring consistent voltage regulation. It provides faster transient response due to direct control of the output voltage, enhancing overall system performance in power converters. The approach also boasts lower output voltage ripple and improved noise immunity, which benefits sensitive electronic circuits and precision instruments.
Benefits of Current Mode Operation
Current mode operation enhances voltage regulator performance by providing improved transient response and simplified loop compensation. It offers inherent overcurrent protection by directly sensing the output current, increasing system reliability. Additionally, current mode control reduces output voltage ripple and improves line regulation, making it well-suited for high-performance power management applications.
Application Areas for Voltage Mode
Voltage mode control is widely applied in power supply designs, such as DC-DC converters, where stable output voltage regulation is crucial for sensitive electronics like microprocessors and communication devices. It is favored in applications requiring high output impedance and fast transient response, including LED drivers and battery chargers. Its simplicity and robustness also make it suitable for renewable energy systems such as solar inverters and wind power converters.
Real-World Uses of Current Mode
Current mode control is widely utilized in switch-mode power supplies (SMPS) due to its precise current regulation and enhanced response to load changes. In applications such as LED drivers, battery chargers, and motor controllers, current mode offers superior protection by preventing inrush currents and short circuits. Its ability to simplify compensator design and improve stability makes current mode advantageous in high-frequency, high-efficiency power electronics.
Choosing the Right Mode: Factors to Consider
Choosing between voltage mode and current mode control hinges on factors like stability requirements, transient response, and complexity of implementation. Voltage mode offers simpler compensation and is ideal for systems with stable input voltage, while current mode provides superior load regulation and faster transient response, making it suitable for applications with varying loads. Your specific system demands and performance goals will guide the selection of the optimal control mode.
Voltage mode vs current mode Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com